First ScotRail
 | |
 | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Franchise(s) |
ScotRail 17 October 2004 – 31 March 2015 |
| Main Region(s) | Scotland |
| Other Region(s) |
North West England North East England |
| Fleet size | 311 |
| Stations operated | 344 |
| Route km operated | 3032.0 |
| National Rail abbreviation | SR |
| Parent company | FirstGroup |
| Website | [http://www.scotrail.co.uk www.scotrail.co.uk] |
First ScotRail[1] was a train operating company in Scotland owned by FirstGroup which operated the ScotRail franchise from October 2004 until March 2015. Prior to October 2004 trains were run by ScotRail (National Express). It was succeeded by Abellio ScotRail in March 2015.
It operated most commuter and long-distance services within the country as well as some cross-border services to England, including the Caledonian Sleeper. Of FirstGroup's four train operating companies, ScotRail was the second largest (in terms of number of passenger journeys 2013–14) after First Great Western at the time of closure.[2]
History

National Express operated the ScotRail franchise from March 1997 until October 2004 as ScotRail.
In July 2003, the Scottish Executive and the Strategic Rail Authority announced Arriva, FirstGroup and National Express had been shortlisted to bid for the new franchise.[3] In June 2004, the franchise was awarded to FirstGroup, with the services operated by ScotRail transferring to First ScotRail on 17 October 2004.[4]
On 1 January 2006, Transport Scotland was created to carry out the Scottish Executive's transport responsibilities including its then newly devolved powers over rail franchising.[5]
In April 2008, Transport Scotland granted First ScotRail a three-year franchise extension until November 2014.[6][7]
In September 2008, Transport Scotland announced that all First ScotRail trains, including those previously operated on behalf of the Strathclyde Partnership for Transport, would be repainted in a new blue livery with white saltire markings on the carriage ends.[8] The rebranding put less emphasis on the First and is marketed as "ScotRail: Scotland's Railway".[9] The first unit to receive the new livery was 170434, unveiled at Glasgow Queen Street on 22 September 2008.
On 8 October 2014, First ScotRail confirmed its bid to retain the franchise had been unsuccessful and that the franchise transferred to Abellio ScotRail on 1 April 2015.[10][11][12]
On the evening of 31 March 2015, the Caledonian Sleeper services were split into a new franchise, operated by Serco.
Network
Main lines
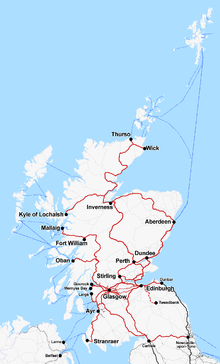
Express trains operated between Edinburgh, Glasgow, Inverness, Dundee and Aberdeen. The Highland Main Line links Inverness to the south. Some stretches of main line, such as the Highland Main Line, are single track, and express trains must call at intermediate stations to permit trains coming in the opposite direction to pass.
The main lines of Scotland are:
- Ayrshire Coast Line
- Edinburgh to Aberdeen Line
- Fife Circle Line
- Glasgow-Edinburgh via Carstairs Line
- Glasgow-Edinburgh via Falkirk Line
- Glasgow to Aberdeen Line
- Glasgow South Western Line
- Highland Main Line
Glasgow
The densest part of the network was the suburban network around Glasgow, with 183 stations, the second-largest suburban rail network in the UK, after London. Much of it is 25 kV AC electrified. Glasgow’s main terminal stations are Central and Queen Street stations. ScotRail operated trains in this area under the Strathclyde Partnership for Transport (SPT) brand. However, the Strathclyde Partnership for Transport no longer has any input into specifying rail services in the Glasgow area. DMUs and EMUs that are liveried in the carmine and cream livery are being stripped of the Strathclyde logos.[13] Lines in and around Glasgow were:
- Motherwell to Cumbernauld Line
- North Clyde Line (now extended to Cumbernauld & Edinburgh[14])
- Paisley Canal Line
- Shotts Line
- Glasgow South Western Line
- Whifflet Line (now incorporated into the Argyle Line)
The North Clyde Line is now linked to the Edinburgh-Bathgate Line (see Edinburgh, below) with the completion of the Airdrie-Bathgate Rail Link, creating a new direct link between Glasgow and Edinburgh. There is also a proposal to create a new rail link across the city with the Crossrail Glasgow project.
Edinburgh

Edinburgh’s suburban network is less dense than Glasgow’s. Edinburgh’s main station is Waverley. The main railway line through the city centre runs in a cutting immediately below Edinburgh Castle. A secondary station is at Haymarket in the west of the city. Railway lines running north from Edinburgh to Fife and the Highlands cross the Firth of Forth via the Forth Bridge. Lines in and around Edinburgh were:
- Edinburgh-Bathgate Line (now incorporated into the North Clyde Line[14])
- Edinburgh Crossrail
- Edinburgh-Dunblane line
- North Berwick Line
- Shotts Line
- Edinburgh to Aberdeen Line
The Edinburgh rail network is being expanded with the construction of the Waverley Line to the Borders, and the Edinburgh-Bathgate Line has been extended by the Airdrie-Bathgate Rail Link. A project to open a rail link to Edinburgh Airport was cancelled in September 2007 by the Scottish Government in favour of construction of a station at nearby Gogar which will connect with the Edinburgh tram network to take passengers to the terminal.[15] A proposal to re-open the Edinburgh suburban railway line has been made by campaigning groups.[16]
Rural lines

Rural lines include the scenic West Highland Line, Kyle Line and Far North Line. These lines carried more passengers, mostly tourists, during the summer months, but provided a valuable link and social service during the winter months.
Many rural lines are single track. Trains terminating at the coastal towns of Oban and Mallaig connected with the Caledonian MacBrayne ferry services to Skye, Colonsay, Lismore, Islay and the Outer Hebrides and Inner Hebrides.
The rural lines were:
InterCity & Sleeper services
First ScotRail operated some services that ventured south of the border: principally the Caledonian Sleeper to London Euston along the West Coast Main Line, and a three times daily cross-country service between Newcastle upon Tyne and Glasgow Central via Carlisle and Kilmarnock.
Performance
Performance figures for National Express’s last quarter as franchise holder, July to September 2004, were:
| Period | % trains arriving within 5 mins of scheduled time | Change |
|---|---|---|
| Jul - Sep 2004 | 82.8% | Down 4.2% on the same quarter the previous year |
| Jul - Sep 2004 | 84.2% | Down 1.0% on the previous year as a whole |
Performance figures for FirstGroup’s first quarter as franchise holder, October to December 2004, were:
| Period | % trains arriving within 5 mins of scheduled time | Change |
|---|---|---|
| Oct - Dec 2004 | 79.8% | Down 1.9% on the same quarter the previous year |
| Oct - Dec 2004 | 83.7% | Down 0.5% on the previous year as a whole |
FirstGroup started operating the franchise on 17 October 2004.
The performance figures released by the Office for Rail Regulation (ORR) are as follows:
| Period | % trains arriving within 5 mins of scheduled time (over three months) | Change over same quarter the previous year | % trains arriving within 5 mins of scheduled time Moving Annual Average (MAA) | Change over previous year as a whole |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apr - Jun 2007[17] | 91.4% | Up 0.8% | 89.0% | Up 0.2% |
| Jul - Sep 2007[18] | 93.0% | Up 2.2% | 89.6% | Up 0.7% |
| Oct - Dec 2007[19] | 87.3% | Up 2.8% | 90.1% | Up 0.6% |
| Jan - Mar 2008[20] | 90.5% | Up 2.0% | 90.6% | Up 0.6% |
| Apr - Jun 2008[21] | 93.6% | Up 2.4% | 91.1% | Up 0.6% |
| Jul - Sep 2008[22] | 92.8% | Down 0.2% | 91.0% | Up 0.4% |
| Oct - Dec 2008[23] | 86.5% | Down 0.9% | 90.9% | Up 0.3% |
| Jan - Mar 2009[24] | 89.6% | Down 1.0%> | 90.6% | Down 0.3% |
| Apr - Jun 2009[25] | 93.0% | Down 0.6% | 90.5% | Down 0.1% |
| Jul - Sep 2009[26] | 93.5% | Up 0.9% | 90.7% | Up 0.2% |
| Oct - Dec 2009[27] | 86.7% | Up 0.2% | 90.7% | Unchanged |
| Jan - Mar 2010[28] | 89.5% | Down 0.1% | 90.7% | Unchanged |
| Jul - Sep 2010[29] | 94.5% | Up 1.1% | 91.4% | Up 0.8% |
| Oct - Dec 2010[29] | 78.4% | Down 9.6% | 92.9% | Up 2.4% |
| Jan - Mar 2011[30] | 89.1% | Down 0.0% | 90.1% | Down 0.0% |
Note:
- The percentage change figures are not the actual increases in % but the percentage increase in the % value.
- These values are very similar to the sector performance level.
Controversy
In June 2009 a report by Strathclyde Partnership for Transport revealed passenger figures from ScotRail contain 7.2 million more passenger journeys than were actually made.[31] Transport Scotland said this gross overestimate did not affect the decision to extend the franchise (the franchise having been extended under controversial conditions in 2008).[32]
Rolling stock

First ScotRail inherited a fleet of Class 150, Class 156, Class 158, Class 170, Class 314, Class 318, Class 320 and Class 334s from National Express, as well as Mark 2 carriages and Mark 3 sleepers for use on the Caledonian Sleeper.
First ScotRail contracted EWS to haul the Caledonian Sleeper services. Class 90s were used south of Edinburgh and Glasgow Central with Class 67s used on the portions to Fort William, Aberdeen and Inverness. A dedicated pool has been created due to the need to fit cast steel brakes. Three Class 90s were repainted in First ScotRail livery with EWS logos.
First ScotRail took the delivery of the last few Class 170 Turbostars when it took over the franchise.[33] These released the Class 150s for transfer to Arriva Trains Wales in late 2004 / early 2005.[34]
During 2005 the Edinburgh - North Berwick Line services were operated by English Welsh & Scottish Class 90s with former Virgin Trains Mark 3 carriages and a Driving Van Trailer. In late 2005, five Class 322s were transferred from One to replace these.
In 2007, First ScotRail received eight Class 158s from First Great Western, Northern Rail and South West Trains.[35]
From December 2008, ScotRail operated a set of DB Schenker Mark 2 carriages on a peak-hour Fife Circle Line service hauled by a Class 67. A second set was operated for a while.
In July 2008, Transport Scotland funded the acquisition of 22 three-carriage and 16 four-carriage Class 380 Desiros with the first entering service in December 2010. These trains operated Ayrshire and Inverclyde services, adding extra capacity and allowed the cascade of existing stock to the new Glasgow to Edinburgh services via the reopened Airdrie to Bathgate line.[36][37]
Fleet at time of closure
Stations
The majority of Scotland’s 340 passenger stations were operated by First ScotRail under Network Rail ownership. Glasgow Prestwick Airport station is owned and operated by the airport, Dunbar is operated by East Coast, and Edinburgh Waverley and Glasgow Central by Network Rail itself. ScotRail operated Lockerbie railway station but none of its services called there.
Depots
First ScotRail's fleet was maintained at Edinburgh Haymarket, Glasgow Shields Road, Corkerhill and Inverness depots. In early 2005 the rebuilt Glasgow Eastfield reopened.[38]
End of the franchise
In June 2012, the Scottish Government announced that when the franchise is retendered in 2014, the Caledonian Sleeper services would be transferred to a standalone own franchise,[39][40] which has been operated by Serco since April 2015.[41]
In October 2014, it was announced First had been unsuccessful in its bid to retain the franchise, which was taken over by Abellio ScotRail on 1 April 2015.[42]
Abellio ScotRail took over the franchise, as planned, at midnight on 1 April. Several hours prior to that, during the evening of 31 March, the Caledonian Sleeper services had already been handed over to Serco.
See also
- Transport in Scotland
- Transport in Edinburgh
- Transport in Glasgow
- Category:Transport in Scotland by council area
- Caledonian Sleeper
- Strathclyde Partnership for Transport
- Transport Initiatives Edinburgh
- Glasgow Subway
- Transport Scotland (government agency)
- List of railway lines in Great Britain
- Abellio ScotRail
References
- ↑ Companies House extract company no SC185018 Archived 12 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine. First ScotRail Limited
- ↑ FirstGroup plc UK Rail Overview
- ↑ "Shortlist of ScotRail bidders puts three in the ring". The Herald. 18 October 2016. Retrieved 19 November 2016. Herald Scotland 28 October 2003
- ↑ FirstGroup clinches Scottish rail franchise Archived 13 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine. The Daily Telegraph 12 June 2004
- ↑ Transport Scotland Framework Document (PDF), Scottish Executive, December 2005, retrieved 19 November 2016
- ↑ Scot Rail franchise extension agreed Archived 4 January 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Transport Scotland News 3 April 2008
- ↑ FirstGroup Plc statement: Extension of First ScotRail Franchise Archived 6 October 2014 at the Wayback Machine. First ScotRail 3 April 2008
- ↑ ScotRail 25th Anniversary Publicity Materials Archived 6 July 2010 at the Wayback Machine. Transport Scotland
- ↑ Dalton, Alastair (23 September 2008). "ScotRail marks birthday with Saltire look". The Scotsman. Edinburgh. Retrieved 19 November 2016.
- ↑ Dutch firms wins ScotRail franchise from FirstGroup Archived 21 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine. BBC News 8 October 2014
- ↑ Abellio awarded ScotRail franchise Archived 5 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Railway Gazette 8 October 2014
- ↑ Abellio awarded contract to operate Scotland's National Railway, ScotRail Archived 15 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Abellio
- ↑ Today's Railways Issue 81
- 1 2 Airdrie-Bathgate rail link Archived 28 September 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "It's £30m down the drain". The Scotsman. Edinburgh: Johnston Publishing. 27 September 2007. Retrieved 7 September 2013.
- ↑ Capital Rail Action Group website Archived 16 May 2014 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ ORR Statistics for Q1 2007/08
- ↑ ORR Statistics for Q2 2007/08
- ↑ ORR Statistics for Q3 2007/08
- ↑ ORR Statistics for Q4 2007/08
- ↑ Office of Rail Regulation - National Rail Trends, (2008), p. 22
- ↑ Office of Rail Regulation - National Rail Trends, (2009), p. 5
- ↑ Office of Rail Regulation - National Rail Trends, (2009), p. 5
- ↑ Office of Rail Regulation - National Rail Trends, (2009), p. 24
- ↑ Office of Rail Regulation - National Rail Trends, (2009), p. 5
- ↑ Office of Rail Regulation - National Rail Trends, (2010), p. 5
- ↑ "Office of Rail Regulation - National Rail Trends" (PDF). ORR.
- ↑ "National Rail Trends Chapter 2" (PDF). ORR.
- 1 2 "National Rail Trends Chapter 2" (PDF). ORR. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-02-03.
- ↑ "National Rail Trends 2010-11. Chapter 2" (PDF). ORR.
- ↑ "Probe call over passenger figures". BBC News. 2009-06-24. Retrieved 2010-04-02.
- ↑ "Rail contract handling defended". BBC News. 2009-01-14. Retrieved 2010-04-02.
- ↑ Class 170 scot-rail.co.uk
- ↑ Class 150 scot-rail.co.uk
- ↑ Class 158 scot-rail.co.uk
- ↑ New Electric Trains for Scotland's Growing Railways Transport Scotland News 11 July 2008
- ↑ "Scotland orders Desiro fleet". Railway Gazette International. 11 July 2008.
- ↑ Eastfield Depot 1904 -1992
- ↑ £5 billion investment in rail improvement plan Scottish National Party Media Centre 21 June 2012
- ↑ Barrow, Keith (22 June 2012). "Scottish government sets out rail strategy". International Railway Journal. Retrieved 15 November 2015.
- ↑ "Serco wins franchise for Caledonian sleeper train service". BBC News. 28 May 2014.
- ↑ "Dutch firm Abellio wins ScotRail franchise from FirstGroup". BBC News. 8 October 2014.
- Scottish Government. Scottish Transport Statistics No. 24: 2005 Edition. Accessed on 2 October 2005.
- Scottish Parliament Information Centre. Changes to the regulation of Scotland's railways. Accessed on 2 October 2005.
- RailBritain.com. First ScotRail fleet size as of December 2004. Accessed on 2 October 2005.
External links
![]() Media related to First ScotRail at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to First ScotRail at Wikimedia Commons
- Company website
- ScotRail network map
- Map of Glasgow & Edinburgh rail network (National Rail)
- ScotRail reports - the Scotsman
- Friends of the Far North Line Website - Friends of the Far North Line
- rail enthusiast site
| Preceded by ScotRail ScotRail franchise |
Operator of ScotRail franchise 2004 - 2015 |
Succeeded by Abellio ScotRail ScotRail franchise |
| Succeeded by Caledonian Sleeper Caledonian Sleeper franchise |

.jpg)







