Second Battle of Champagne
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Second Battle of Champagne (Herbstschlacht or Autumn Battle) in World War I was a French offensive against the German army.
Battle
On 25 September 1915, twenty divisions of the Second Army and Fourth Army of Groupe d'armées du Centre (GAC, Central Army Group), attacked at 9:15 a.m., with each division on a 1,500–2,000 yards (1,400–1,800 m) front. A second line of seven divisions followed, with one infantry division and six cavalry divisions in reserve. Six German divisions held the line opposite, in a front position and a reserve position the R-Stellung (Rückstellung, Reserve Position) further back. French artillery observers benefitted from good weather but on the night of 24/25 September, heavy rain began and fell until midday.[1]
The German front position was broken in four places and two of the penetrations reached as far as the R-Stellung, where uncut barbed wire prevented the French from advancing further. The French took 14,000 prisoners and several guns but French casualties were also high; the Germans had anticipated the French attack, having been able to watch the French preparations from their high ground and outposts. The main defensive effort was made at the R-Stellung, behind which the bulk of the German field artillery had been withdrawn. A supporting attack by the French 3rd Army on the Aisne took no ground.[2]
Joffre allotted two reserve divisions to the GAC and ordered the Groupe d'armées de l'Est (GAE, Eastern Army Group) to send all 75 mm field gun ammunition, except for 500 rounds per gun, to the Second and Fourth armies. On 26 September, the French attacked again, closed up to the R-Stellung on a 7.5-mile (12.1 km) front and gained a foothold in one place. Another 2,000 German troops were captured but attacks against the R-Stellung from 27–29 September, broke through on 28 September. A German counter-attack next day recaptured the ground, most of which was on a reverse slope, which had deprived the French artillery of ground observation; Joffre suspended the offensive until more ammunition could be supplied and ordered that the captured ground be consolidated and cavalry units be withdrawn. Smaller French attacks against German salients continued from 30 September – 5 October.[3][4]
Aftermath
Analysis
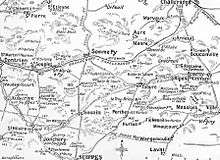
On 3 October, Joffre abandoned the attempt at a breakthrough in Champagne, ordered the local commanders to fight a battle of attrition and then terminated the offensive on 6 November. The offensive in Champagne had advanced the French line for about 4 kilometres (2.5 mi), at a cost of c. 100,000 more French and British casualties than German losses. The French had attacked in Champagne with 35 divisions against the equivalent of 16 German divisions. On the Champagne front, the Fourth, Second and Third armies had fired 2,842,400 field artillery and 577,700 heavy shells, which with the consumption in Artois during the Third Battle of Artois, exhausted the French ammunition supply. French methods and equipment were insufficient for the demands of trench warfare and a lull followed, as the French rested the survivors of the offensive, replaced losses and accumulated more equipment and ammunition.[5] On 22 October, Joffre claimed that the autumn offensive had resulted in important tactical gains, inflicted many casualties and achieved a moral superiority over the Germans and that only a lack of artillery had led to a failure to achieve the strategic objectives of the offensive. To keep as many German troops as possible away from the Eastern Front, offensive operations must continue but troops in the front line were to be kept to the minimum over the winter and a new strategy was to be formulated.[6]
The theoretical bases of the French offensives of 1915 had been collected in But et conditions d'une action offensive d'ensemble (Purpose and Conditions of all Offensive Action, 16 April 1915) and its derivative Note 5779, which had been compiled from analyses of reports received from the front since 1914. The document contained instructions on infiltration tactics, rolling barrages and poison gas, which were to be used systematically in continuous battles to create rupture.[7][lower-alpha 1] Continuous battle was to be replaced by step-by-step advances, through successive German defence lines. Methodical attacks were to be made each time and would inexorably consume German infantry reserves. The German defences would eventually collapse and make a breakthrough attack feasible. The slower, more deliberate methods, would conserve French infantry, as they battered through the deeper defences built by the Germans since 1914.[8]
In the autumn battles, the Allies had outnumbered the Westheer (German army in the west) by 600 infantry battalions but had not achieved a breakthrough and after the first day, German reinforcements made one impossible.[5] Several divisions had returned from the Eastern Front but were tired and of little value. The German commander in chief, General Erich von Falkenhayn had underestimated the possibility of an offensive and kept the Oberste Heeresleitung (OHL, German high command) reserve spread all along the Western Front, rather than concentrating it in threatened areas. French reviews of the offensive found that reserves had moved close to the front, ready to exploit a breakthrough and had advanced on time. The troops had then become bunched up with the leading divisions, blocked the lines of communication and suffered many casualties, while held up. Communications failed and commanders had been in ignorance of the situation, artillery co-ordination with the infantry had been poor and rain grounded French artillery-observation aircraft. Many of the French commanders concluded that a breakthrough could not be forced in one attack and that it would take several set-piece battles, to make the defenders collapse and be unable to prevent a return to mobile operations.[9]
The German report, Experiences of the 3rd Army in the Autumn Battles in the Champagne, 1915, noted that unyielding defence of the most forward positions had failed several times, because the attackers had severely damaged German field fortifications and cut the barbed wire obstacles in front of them, by long artillery bombardments. The second position had not been broken into and the 3rd Army reported that the decision to construct the second position had been vindicated, since the French had to suspend their attacks until artillery had been moved forward, which took until 4 October. The momentum of the initial breakthrough had not been maintained, because the French troops crowding forward had become disorganised, which made co-ordinated attacks impossible to arrange. French prisoners were reported to have said that there had been no methodical staging of the reserves to exploit a breakthrough and concluded with the view that a breakthrough might still be possible.[10]
Lack of troops made it impossible for the Germans to respond with big counter-attacks but smaller hasty counter-attacks by local troops, had succeeded against French units weakened by losses, which had not had time to consolidate captured ground. It was recommended that such reserves should be made available by reducing the number of German troops in the front line, as one man every 2–3 metres (2.2–3.3 yd) in the front line was enough. Co-operation between all arms, assistance from neighbouring sectors and the exploitation of flanking moves had defeated the French offensive. More intermediate strong points, built for all-round defence were recommended, between the first and second positions. Defence of the first position was still the intention but deeper defences would dissipate the effect of a breakthrough and force the attackers to make numerous individual attacks, in areas where local knowledge and preparation of the ground would be advantageous to the defenders. Observation posts should be made secure from attack, reconnaissance reports acted on promptly and communication links were to be made as robust as possible. A wide field of fire was unnecessary and to be dispensed with, to make each part of the position defensible by placing defences on reverse slopes, concealed from ground observation [11]
In his memoirs (1919), Falkenhayn wrote that the autumn battle showed that on the Western Front, quantity was not enough to defeat armies sheltering in field defences
.... the lessons to be deduced from the failure of our enemies' mass attacks are decisive against any imitation of their battle methods. Attempts at a mass breakthrough, even with the extreme accumulation of men and material, cannot be regarded as holding out the prospects of success.— Falkenhayn[12]
and that the plans made earlier in 1915, for an offensive in France were obsolete. Falkenhayn needed to resolve the paradoxical lessons of the war since 1914, to find a way to end the war favourably for Germany, which culminated at Verdun in 1916, when Falkenhayn tried to induce the French to repeat the costly failure of the Second Battle of Champagne.[13]
Casualties
The offensive had been disappointing for the French. Despite their new 'attack in echelon' they had only made quick progress during the time it took for the Germans to strip reserves from elsewhere and rush them up. They had lost 145,000 men, while the Germans had 72,500 casualties, (Foley gave 97,000 casualties based on Der Weltkrieg the German Official History.)[14] The French had taken 25,000 prisoners and captured 150 guns. In Der Weltkrieg, French casualties in the Fourth, Second and Third armies from 25 September – 7 October were recorded as 143,567 men, with 48,230 more casualties in the Tenth Army from 25 September – 15 October and 56,812 casualties in the British First Army from 25 September – 16 October, a total of c. 250,000 casualties against c. 150,000 losses in the German armies, of which 81,000 casualties were suffered in the Champagne battle from 22 September – 14 October.[15] The French Official History recorded 191,795 casualties in the fighting in Champagne and Artois.[16]
Notes
Footnotes
- ↑ Edmonds 1928, pp. 270–271.
- ↑ Edmonds 1928, p. 271.
- ↑ Edmonds 1928, pp. 271, 348.
- ↑ Humphries & Maker 2010, p. 320.
- 1 2 Humphries & Maker 2010, pp. 329–330.
- ↑ Doughty 2005, p. 202.
- 1 2 Krause 2013, pp. 4–5, 20.
- ↑ Doughty 2005, p. 253.
- ↑ Humphries & Maker 2010, pp. 330–333.
- ↑ Humphries & Maker 2010, pp. 334–335.
- ↑ Humphries & Maker 2010, pp. 335–336.
- ↑ Foley 2005, p. 179.
- ↑ Foley 2005, pp. 179–180.
- ↑ Foley 2005, p. 97.
- ↑ Humphries & Maker 2010, pp. 328–329.
- ↑ Doughty 2005, p. 201.
References
- Doughty, R. A. (2005). Pyrrhic Victory: French Strategy and Operations in the Great War. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press. ISBN 0-67401-880-X.
- Edmonds, J. E. (1928). Military Operations France and Belgium, 1915: Battles of Aubers Ridge, Festubert, and Loos. History of the Great War Based on Official Documents by Direction of the Historical Section of the Committee of Imperial Defence. II. London: Macmillan. OCLC 58962526.
- Foley, R. T. (2007) [2005]. German Strategy and the Path to Verdun: Erich von Falkenhayn and the Development of Attrition, 1870–1916. Cambridge: CUP. ISBN 978-0-521-04436-3.
- Humphries, M. O.; Maker, J. (2010). Germany's Western Front, 1915: Translations from the German Official History of the Great War. II (1st ed.). Waterloo Ont.: Wilfrid Laurier University Press. ISBN 978-1-55458-259-4.
- Krause, J. (2013). Early Trench Tactics in the French Army: the Second Battle of Artois, May–June 1915 (1st ed.). Farnham, Surrey: Ashgate Publishing. ISBN 1-40945-500-9.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Second Battle of Champagne. |