Filipinos
Filipinos (Filipino: Mga Pilipino) are the people who are native to, or identified with the country of the Philippines. Filipinos come from various ethnolinguistic groups. Currently, there are more than 175 ethnolinguistic groups, each with its own language, identity, culture and history. The modern Filipino identity, with its Austronesian roots, was developed in conjunction with Spanish, Chinese and American influences.
The Philippines was a Spanish colony for 333 years, setting a foundation for contemporary Filipino culture. Under Spanish rule, most of the Filipino populace embraced Roman Catholicism, yet revolted many times against its hierarchy. Almost all Filipinos adopted Spanish surnames from the Catálogo alfabético de apellidos published in 1849 by the Spanish colonial government.[31] As neither past governments nor the modern Philippine Statistics Authority account for the racial background of an individual, the exact percentage of Filipino people of Spanish ancestry is unknown.
Names
The name Filipino was derived from the term "las Islas Filipinas" ("the Philippine Islands"),[32] the name given to the archipelago in 1543 by the Spanish explorer and Dominican priest Ruy López de Villalobos, in honour of Philip II of Spain (Spanish: Felipe II). The lack of the letter "F" in the pre-1987 Philippine alphabet, Abakada, had caused the letter "F" to be substituted with "P". Upon official adoption of the modern, 28-letter Filipino alphabet in 1987, the term Filipino was preferred over Pilipino. However the ABAKADA is only the alphabet of the Tagalogs as other ethnic nations also have their own alphabets and/or writing scripts and these other ethnic nations did have the letter "F" in their alphabets.
Use of the term "Filipino" in the Philippines started during the Spanish colonial period. The original meaning was "a person of Spanish descent born in the Philippines" (a person of Austronesian ancestry and not of Spanish descent was called an "Indio").[31] This original usage is now archaic and obsolete. Historian Ambeth Ocampo has suggested that the first documented use of the word to refer to Indios was the Spanish language poem A la juventud filipina, published in 1879 by José Rizal.[33]
A number of Filipinos refer to themselves colloquially as "Pinoy" (feminine: "Pinay"), which is a slang word formed by taking the last four letters of "Filipino" and adding the diminutive suffix "-y". The term, although in popular usage, is still considered by some Filipinos as a racial slur and derogatory.[34]
Other collective endonyms for the Filipino people include: "Patria Adorada" (Spanish for "Beloved Fatherland") as popularized by Jose Rizal through his poem "Mi último adiós", "Bayang Pilipino" (Tagalog: "Filipino nation") or the more poetic "Sambayanáng Pilipino" (a formal term in Tagalog meaning "one/entire Filipino nation").
History
Prehistory
In 2010, a metatarsal from "Callao Man", discovered in 2007, was dated through uranium-series dating as being 67,000 years old.[35]
Prior to that, the earliest human remains found in the Philippines were thought to be the fossilized fragments of a skull and jawbone, discovered in the 1960s by Dr. Robert B. Fox, an anthropologist from the National Museum.[36] Anthropologists who examined these remains agreed that they belonged to modern human beings. These include the Homo sapiens, as distinguished from the mid-Pleistocene Homo erectus species.
The "Tabon Man" fossils are considered to have come from a third group of inhabitants, who worked the cave between 22,000 and 20,000 BCE. An earlier cave level lies so far below the level containing cooking fire assemblages that it must represent Upper Pleistocene dates like 45 or 50 thousand years ago.[37] Researchers say this indicates that the human remains were pre-Mongoloid, from about 40,000 years ago. Mongoloid is the term which anthropologists applied to the ethnic group which migrated to Southeast Asia during the Holocene period and evolved into the Austronesian people (associated with the Haplogroup O1 (Y-DNA) genetic marker), a group of Malayo-Polynesian-speaking people including those from Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia, Malagasy, the non-Chinese Taiwan Aboriginals.[38]
Fluctuations in ancient shorelines between 150,000 BC and 17,000 BC connected the Malay Archipelago region with Maritime Southeast Asia and the Philippines. This may have enabled ancient migrations into the Philippines from Maritime Southeast Asia approximately 50,000 BC to 13,000 BC.[39]
A January 2009 study of language phylogenies by R. D. Gray at the University of California, Los Angeles published in the journal Science, suggests that the population expansion of Austronesian peoples was triggered by rising sea levels of the Sunda shelf at the end of the last ice age. This was a two-pronged expansion, which moved north through the Philippines and into Taiwan, while a second expansion prong spread east along the New Guinea coast and into Oceania and Polynesia.[40]
The Negritos are likely descendants of the indigenous populations of the Sunda landmass and New Guinea, pre-dating the Mongoloid peoples who later entered Southeast Asia.[41] Multiple studies also show that Negritos from Southeast Asia to New Guinea share a closer cranial affinity with Australo-Melanesians.[41][42] They were the ancestors of such tribes of the Philippines as the Aeta, Agta, Ayta, Ati, Dumagat and other similar groups. Today they comprise just 0.03% of the total Philippine population.[43]
The majority of present-day Filipinos are a product of the long process of evolution and movement of people.[44] After the mass migrations through land bridges, migrations continued by boat during the maritime era of South East Asia. The ancient races became homogenized into the Malayo-Polynesians which colonized the majority of the Philippine, Malaysian and Indonesian archipelagos.[45][46]
Archaic epoch (to 1565 CE)


Since at least the 3rd century, various ethnic groups established several communities. These were formed by the assimilation of various native Philippine kingdoms.[43] South Asian and East Asian people together with the people of the Indonesian archipelago and the Malay Peninsula, traded with Filipinos and introduced Hinduism and Buddhism to the native tribes of the Philippines. Most of these people stayed in the Philippines where they were slowly absorbed into local societies.
Many of the barangay (tribal municipalities) were, to a varying extent, under the de jure jurisprudence of one of several neighboring empires, among them the Malay Srivijaya, Javanese Majapahit, Brunei, Malacca, Indian Chola, Champa and Khmer empires, although de facto had established their own independent system of rule. Trading links with Sumatra, Borneo, Java, Malay Peninsula, Indochina, China, Japan, India and Arabia. A thalassocracy had thus emerged based on international trade.
Even scattered barangays, through the development of inter-island and international trade, became more culturally homogeneous by the 4th century. Hindu-Buddhist culture and religion flourished among the noblemen in this era.
In the period between the 7th to the beginning of the 15th centuries, numerous prosperous centers of trade had emerged, including the Kingdom of Namayan which flourished alongside Manila Bay,[47][47][48] Cebu, Iloilo,[49] Butuan, the Kingdom of Sanfotsi situated in Pangasinan, the Kingdom of Luzon now known as Pampanga which specialized in trade with most of what is now known as Southeast Asia, and with China, Japan and the Kingdom of Ryukyu in Okinawa.
From the 9th century onwards, a large number of Arab traders from the Middle East settled in the Malay Archipelago and intermarried with the local Malay, Bruneian, Malaysian, Indonesian, and Luzon and Visayas indigenous populations.[50]
In the years leading up to 1000 CE, there were already several maritime societies existing in the islands but there was no unifying political state encompassing the entire Philippine archipelago. Instead, the region was dotted by numerous semi-autonomous barangays (settlements ranging is size from villages to city-states) under the sovereignty of competing thalassocracies ruled by datus, rajahs or sultans[51] or by upland agricultural societies ruled by "petty plutocrats". States such as the Wangdoms of Ma-i and Pangasinan, Kingdom of Maynila, Namayan, the Kingdom of Tondo, the Kedatuan of Madja-as, the Rajahnates of Butuan and Cebu and the sultanates of Maguindanao, Lanao and Sulu existed alongside the highland societies of the Ifugao and Mangyan.[52][53][54][55] Some of these regions were part of the Malayan empires of Srivijaya, Majapahit and Brunei.[56][57][58]
Historic caste systems
Maginoo – The Tagalog maginoo, the Kapampangan ginu, and the Visayan tumao were the nobility social class among various cultures of the pre-colonial Philippines. Among the Visayans, the tumao were further distinguished from the immediate royal families, the kadatuan or a ruling class.
Maharlika – Members of the Tagalog warrior class known as maharlika had the same rights and responsibilities as the timawa, but in times of war they were bound to serve their datu in battle. They had to arm themselves at their own expense, but they did get to keep the loot they won – or stole, depending on which side of the transaction you want to look at. Although they were partly related to the nobility, the maharlikas were technically less free than the timawas because they could not leave a datu’s service without first hosting a large public feast and paying the datu between 6 and 18 pesos in gold – a large sum in those days.
Timawa – The timawa class were free commoners of Luzon and the Visayas who could own their own land and who did not have to pay a regular tribute to a maginoo, though they would, from time to time, be obliged to work on a datu’s land and help in community projects and events. They were free to change their allegiance to another datu if they married into another community or if they decided to move.
Alipin – Today, the word alipin (or oripun in the Visayas) means slave and that’s how the Spaniards translated it, too, but the alipins were not really slaves in the Western sense of the word. They were not bought and sold in markets with chains around their necks. A better description would be to call them debtors. They could be born alipins, inheriting their parents' debt, and their obligations could be transferred from one master to another. However, it was also possible for them to buy their own freedom. A person in extreme poverty might even want to become an alipin voluntarily – preferably to relatives who saw this as a form of assistance rather than punishment.
By the 15th century, Arab and Indian missionaries and traders from Malaysia and Indonesia brought Islam to the Philippines, where it both replaced and was practiced together with indigenous religions. Before that, indigenous tribes of the Philippines practiced a mixture of Animism, Hinduism and Buddhism. Native villages, called barangays were populated by locals called Timawa (Middle Class/ freemen) and Alipin (servants & slaves). They were ruled by Rajahs, Datus and Sultans, a class called Maginoo (royals) and defended by the Maharlika (Lesser nobles, royal warriors and aristocrats).[43] These Royals and Nobles are descended from native Filipinos with varying degrees of Indo-Aryan and Dravidian, which is evident in today's DNA analysis among South East Asian Royals. This tradition continued among the Spanish and Portuguese traders who also intermarried with the local populations.[59]
Hispanic settlement and rule (1521–1898)

The arrival of Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan in 1521 began a period of European colonization. During the period of Spanish colonialism the Philippines was part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain, which was governed and controlled from Mexico City. Early Spanish settlers were mostly explorers, soldiers, government officials and religious missionaries born in Spain and Mexico. Most Spaniards who settled were of Andalusian ancestry but there were also Catalan, Moorish and Basque settlers. The Peninsulares (governors born in Spain), mostly of Castilian ancestry, settled in the islands to govern their territory. Most settlers married the daughters of rajahs, datus and sultans to reinforce the colonization of the islands. The Ginoo and Maharlika castes (royals and nobles) in the Philippines prior to the arrival of the Spanish formed the privileged Principalía (nobility) during the Spanish period. In the 16th and 17th centuries, thousands of Japanese traders also migrated to the Philippines and assimilated into the local population.[60]
As a part of the Seven Years' War, British forces occupied Manila between 1762 and 1764. However, the only part of the Philippines which the British held was the Spanish colonial capital of Manila and the principal naval port of Cavite, both of which are located on Manila Bay. The war was ended by the Treaty of Paris (1763). At the end of the war the treaty signatories were not aware that Manila had been taken by the British and was being administered as a British colony. Consequently, no specific provision was made for the Philippines. Instead they fell under the general provision that all other lands not otherwise provided for be returned to the Spanish Empire.[61] Many Indian Sepoy troops and their British captains mutinied and were left in Manila and some parts of the Ilocos and Cagayan. The ones in Manila settled at Cainta, Rizal and the ones in the north settled in Isabela. Most were assimilated into the local population.
The arrival of the Spaniards to the Philippines attracted new waves of immigrants from China, and maritime trade flourished during the Spanish period. The Spanish recruited thousands of Chinese migrant workers called sangleys to build the colonial infrastructure in the islands. Many Chinese immigrants converted to Christianity, intermarried with the locals, and adopted Hispanized names and customs and became assimilated, although the children of unions between Filipinos and Chinese that became assimilated continued to be designated in official records as mestizos de sangley. The Chinese mestizos were largely confined to the Binondo area until the 19th century. However, they eventually spread all over the islands, and became traders, landowners, and moneylenders.
A total of 110 Manila-Acapulco galleons set sail between 1565 and 1815, during the Philippines trade with Mexico. Until 1593, three or more ships would set sail annually from each port bringing with them the riches of the archipelago to Spain. European criollos, mestizos and Portuguese, French and Mexican descent from the Americas, mostly from Latin America came in contact with the Filipinos. Japanese, Indian and Cambodian Christians who fled from religious persecutions and killing fields also settled in the Philippines during the 17th until the 19th centuries.
With the inauguration of the Suez Canal in 1867, Spain opened the Philippines for international trade. European investors such as British, Dutch, German, Portuguese, Russian, Italian and French were among those who settled in the islands as business increased. More Spaniards arrived during the next century. Many of these European migrants intermarried with local mestizos and some assimilated with the indigenous population.
Late modern
After the defeat of Spain during the Spanish–American War in 1898, Filipino general, Emilio Aguinaldo declared independence on 12 June while General Wesley Merritt became the first American governor of the Philippines. On 10 December 1898, the Treaty of Paris formally ended the war, with Spain ceding the Philippines and other colonies to the United States in exchange for $20 million.[62][63] After the Philippine–American War, the United States civil governance was established in 1901, with William Howard Taft as the first American Governor-General.[64] A number of Americans settled in the islands and thousands of interracial marriages between Americans and Filipinos have taken place since then. Due to the strategic location of the Philippines, as many as 21 bases and 100,000 military personnel were stationed there since the United States first colonized the islands in 1898. These bases were decommissioned in 1992 after the end of the Cold War, but left behind thousands of Amerasian children.[65] The country gained independence from the United States in 1946. The Pearl S. Buck International Foundation estimates there are 52,000 Amerasians scattered throughout the Philippines. In addition, numerous Filipino men enlisted in the US Navy and made careers in it, often settling with their families in the United States. Some of their second or third generation-families returned to the country.
Following its independence, the Philippines has seen both small and large-scale immigration into the country, mostly involving American, European, Chinese and Japanese peoples. After World War II, South Asians continued to migrate into the islands, most of which assimilated and avoided the local social stigma instilled by the early Spaniards against them by keeping a low profile and/or by trying to pass as Spanish mestizos. This was also true for the Arab and Chinese immigrants, many of whom are also post WWII arrivals. More recent migrations into the country by Koreans, Persians, Brazilians, and other Southeast Asians have contributed to the enrichment of the country's ethnic landscape, language and culture. Centuries of migration, diaspora, assimilation, and cultural diversity made most Filipinos accepting of interracial marriage and multiculturalism.
Philippine nationality law is currently based upon the principle of jus sanguinis and, therefore, descent from a parent who is a citizen of the Republic of the Philippines is the primary method of acquiring national citizenship. Birth in the Philippines to foreign parents does not in itself confer Philippine citizenship, although RA9139, the Administrative Naturalization Law of 2000, does provide a path for administrative naturalization of certain aliens born in the Philippines. Filipinos of mixed ethnic origins are still referred to today as mestizos. However, in common parlance, mestizos are only used to refer to Filipinos mixed with Spanish or any other European ancestry. Filipinos mixed with any other foreign ethnicities are named depending on the non-Filipino part.
Hispanized caste system
The history of racial mixture in the Philippines occurred on a smaller scale than other Spanish territories during the Spanish colonial period from the 16th to the 19th century. A caste system, like that used in the Americas (Spanish America), existed in the Philippines, with some major differences. The indigenous peoples of the Philippines were referred to as Indios and Negritos.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Negrito | indigenous person of pure Negrito ancestry |
| Indio | indigenous person of pure Austronesian ancestry |
| Moros | indigenous person of Islam in faith living in the Archipelago of the Philippines |
| Sangley/Chino | person of pure Chinese ancestry |
| Mestizo de Sangley/Chino | person of mixed Chinese and Austronesian ancestry |
| Mestizo de Español | person of mixed Spanish and Austronesian ancestry |
| Tornatrás | person of mixed Spanish, Austronesian and Chinese ancestry |
| Insulares/Filipino | person of pure Spanish descent born in the Philippines |
| Americanos | person of Criollo (either pure Spanish blood, or mostly), Castizo (1/4 Native American, 3/4 Spanish) or Mestizo (1/2 Spanish, 1/2 Native American) descent born in Spanish America ("from the Americas") |
| Peninsulares | person of pure Spanish descent born in Spain ("from the Iberian peninsula") |

People classified as 'blancos' (whites) were the insulares or "Filipinos" (a person born in the Philippines of pure Spanish descent), peninsulares (a person born in Spain of pure Spanish descent), Español mestizos (a person born in the Philippines of mixed Austronesian and Spanish ancestry), and tornatrás (a person born in the Philippines of mixed Austronesian, Chinese and Spanish ancestry). Manila was racially segregated, with blancos living in the walled city of Intramuros, un-Christianized sangleys in Parían, Christianized sangleys and mestizos de sangley in Binondo, and the rest of the 7,000 islands for the indios, with the exception of Cebu and several other Spanish posts. Only mestizos de sangley were allowed to enter Intramuros to work for whites (including mestizos de español) as servants and various occupations needed for the colony. Indio were native Austronesians, but as a legal classification, Indio were those who embraced Roman Catholicism and Austronesians who lived in proximity to the Spanish colonies.

People who lived outside of Manila, Cebu and the major Spanish posts were classified as such: 'Naturales' were Catholic Austronesians of the lowland and coastal towns. The un-Catholic Negritos and Austronesians who lived in the towns were classified as 'salvajes' (savages) or 'infieles' (the unfaithful). 'Remontados' (Spanish for 'situated in the mountains') and 'tulisanes' (bandits) were indigenous Austronesians and Negritos who refused to live in towns and took to the hills, all of whom were considered to live outside the social order as Catholicism was a driving force in Spanish colonials everyday life, as well as determining social class in the colony. People of pure Spanish descent living in the Philippines who were born in Spanish America were classified as 'americanos'. Mestizos and africanos born in Spanish America living in the Philippines kept their legal classification as such, and usually came as indentured servants to the 'americanos'. The Philippine-born children of 'americanos' were classified as 'Ins'. The Philippine-born children of mestizos and Africanos from Spanish America were classified based on patrilineal descent.
The term negrito was coined by the Spaniards based on their appearance. The word 'negrito' would be misinterpreted and used by future European scholars as an ethnoracial term in and of itself. Both Christianized negritos who lived in the colony and un-Christianized negritos who lived in tribes outside of the colony were classified as 'negritos'. Christianized negritos who lived in Manila were not allowed to enter Intramuros and lived in areas designated for indios. A person of mixed Negrito and Austronesian ancestry were classified based on patrilineal descent; the father's ancestry determined a child's legal classification. If the father was 'negrito' and the mother was 'India' (Austronesian), the child was classified as 'negrito'. If the father was 'indio' and the mother was 'negrita', the child was classified as 'indio'. Persons of Negrito descent were viewed as being outside of the social order as they usually lived in tribes outside of the colony and resisted conversion to Christianity.
This legal system of racial classification based on patrilineal descent had no parallel anywhere in the Spanish-ruled colonies in the Americas. In general, a son born of a sangley male and an indio or mestizo de sangley female was classified as mestizo de sangley; all subsequent male descendants were mestizos de sangley regardless of whether they married an India or a mestiza de sangley. A daughter born in such a manner, however, acquired the legal classification of her husband, i.e., she became an India if she married an indio but remained a mestiza de sangley if she married a mestizo de sangley or a sangley. In this way, a chino mestizo male descendant of a paternal sangley ancestor never lost his legal status as a mestizo de sangley no matter how little percentage of Chinese blood he had in his veins or how many generations had passed since his first Chinese ancestor; he was thus a mestizo de sangley in perpetuity.
However, a 'mestiza de sangley' who married a blanco ('Filipino', 'mestizo de español', 'peninsular', or 'americano') kept her status as 'mestiza de sangley'. But her children were classified as tornatrás. An 'India' who married a blanco also kept her status as India, but her children were classified as mestizo de español.
A mestiza de español who married another blanco would keep her status as mestiza, but became an India if she married an indio (which would force her to pay the indio tax rate). But her status will never change from mestiza de español if she married a mestizo de español, Filipino, or peninsular.
On the contrast, a mestizo (de sangley or español) man's status stayed the same regardless of whom he married. If a mestizo (de sangley or español) married a filipina (woman of pure Spanish descent), she would lose her status as a 'filipina' and would acquire the legal status of her husband and become a mestiza de español or sangley. If a 'filipina' married an 'indio', her legal status would change to 'India', despite being of pure Spanish descent.
The social stratification system based on class that continues to this day in the Philippines has its beginnings in the Spanish colonial area with this caste system.
The system was used for tax purposes. Indios paid a base tax, mestizos de sangley paid twice the base tax, sangleys paid four times the base tax, and the blancos or whites (Filipinos, peninsulares, mestizos de español, and tornatrás) paid no tax. Negritos who lived within the colony paid the same tax rate as the indios.
The Spanish colonizers reserved the term Filipino to refer to Spainards born in the Philippines. The use of the term was later extended to include Spanish and Chinese mestizos, or those born of mixed Chinese-indio or Spanish-indio descent. Late in the 19th century, Jose Rizal popularized the use of the term Filipino to refer to all those born in the Philippines, including the Indios.[66] When ordered to sign the notification of his death sentence, which described him as a Chinese mestizo, Rizal refused. He went to his death saying that he was indio puro.[67][68]
The Spanish caste system based on race was abolished after the Philippines' independence from Spain in 1898, and the word 'Filipino' expanded to include the entire population of the Philippines regardless of racial ancestry.
Origins and genetic studies

The majority of Filipinos are Austronesians, a linguistic and genetic group that includes other ethnicities from maritime Southeast Asia, Madagascar, and the Pacific islands.[69] The current predominant theory on Austronesian expansion holds that Austronesians settled the Philippine islands through successive southward and eastward seaborne migrations from the Neolithic Austronesian populations of Taiwan.[70]
Other hypotheses have also been put forward based on linguistic, archeological, and genetic studies. These include an origin from mainland South China (linking them to the Liangzhu culture and the Tapengkeng culture, later displaced or assimilated by the expansion of Sino-Tibetan peoples);[72][73] an in situ origin from the Sundaland continental shelf prior to the sea level rise at the end of the last glacial period (c. 10,000 BC);[74][75] or a combination of the two (the Nusantao Maritime Trading and Communication Network hypothesis) which advocates cultural diffusion rather than a series of linear migrations.[76]
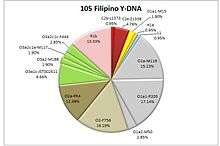
The most frequently occurring Y-DNA haplogroup among modern Filipinos is Haplogroup O3-M122, which is found with high frequency in populations from East Asia, Southeast Asia, and Polynesia. In particular, the type of O3-M122 that is found frequently in Filipinos, O-P201(xM7, M134), is also found frequently in other Austronesian populations, especially the Batak Toba from Sumatra and the Polynesians.[77] Haplogroup O1a-M119 (labeled as "Haplogroup H" in this study) is also commonly found among Filipinos and is shared with other Austronesian-speaking populations, especially those in Taiwan, western Indonesia, and Madagascar.[78][79] After the 16th century, the colonial period saw the influx of limited genetic influence from Europeans and other populations from the Americas, Oceania, and Asia. This is evidenced by the presence of the Western European Y-DNA Haplogroup R1b which is present among 13.33% of the Philippine population. According to a genetic study done by the University of California (San Francisco), Filipinos possess moderate amounts of European DNA coming from the Spanish settlers.[80]
Dental morphology provides clues to prehistoric migration patterns of the Philippines, with Sinodont dental patterns occurring in East Asia, Central Asia, North Asia, and the Americas. Sundadont patterns occur in mainland and maritime Southeast Asia as well as Oceania.[81] Filipinos exhibit Sundadonty,[81][82] and are regarded as having a more generalised dental morphology and having a longer ancestry than its offspring, Sinodonty.
Languages

Austronesian languages have been spoken in the Philippines for thousands of years. According to a 2014 study by Mark Donohue of the Australian National University and Tim Denham of Monash University, there is no linguistic evidence for an orderly north-to-south dispersal of the Austronesian languages from Taiwan through the Philippines and into Island Southeast Asia (ISEA).[74] Many adopted words from Sanskrit were incorporated during the strong wave of Indian (Hindu-Buddhist) cultural influence starting from the 5th century BC, in common with its Southeast Asian neighbours. Starting in the second half of the 16th century, Spanish was the official language of the country for the more than three centuries that the islands were governed through Mexico City on behalf of the Spanish Empire. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, Spanish was the preferred language among Ilustrados and educated Filipinos in general. Significant agreements exist, however, on the extent Spanish use beyond that. It has been argued that the Philippines were less hispanized than Canaries and America, with Spanish only being adopted by the ruling class involved in civil and judicial administration and culture. Spanish was the language of only approximately ten percent of the Philippine population when Spanish rule ended in 1898.[83] As a lingua franca or creole language of Filipinos, major languages of the country like Chavacano, Cebuano, Tagalog, Kapampangan, Pangasinan, Bicolano, Hiligaynon, and Ilocano assimilated many different words and expressions from Castilian Spanish.
It should be noted that Chavacano is the only Spanish-based creole language in Asia. Its vocabulary is 90 percent Spanish, and the remaining 10 percent is a mixture of predominantly Portuguese, Nahuatl (Mexican Indian), Hiligaynon, and some English. Chavacano is considered by the Instituto Cervantes to be a Spanish-based language .[84]
In sharp contrast, another view is that the ratio of the population which spoke Spanish as their mother tongue in the last decade of Spanish rule was 10% or 14%.[85] An additional 60% is said to have spoken Spanish as a second language until World War II, but this is also disputed as to whether this percentage spoke "kitchen Spanish," which was used as marketplace lingua compared to those who were actual fluent Spanish speakers.[85]
In 1863 a Spanish decree introduced universal education, creating free public schooling in Spanish, yet it was never implemented, even before the advent of American annexation.[86] It was also the language of the Philippine Revolution, and the 1899 Malolos Constitution proclaimed it as the "official language" of the First Philippine Republic, albeit a temporary official language. Spanish continued to be the predominant lingua franca used in the islands by the elite class before and during the American colonial regime. Following the American occupation of the Philippines and the imposition of English, the overall use of Spanish declined gradually, especially after the 1940s.
According to Ethnologue, there are about 180 languages spoken in the Philippines.[87] The 1987 Constitution of the Philippines impose Filipino[88][89] as the national language and designates, along with English, as one of the official languages. Regional languages are designated as auxiliary official languages. The constitution also provides that Spanish and Arabic shall be promoted on a voluntary and optional basis.[90]
Other Philippine languages in the country with at least 1,000,000 native and indigenous speakers include Cebuano, Ilocano, Hiligaynon, Waray, Central Bikol, Kapampangan, Pangasinan, Chavacano (Spanish-based creole), Albay Bikol, Maranao, Maguindanao, Kinaray-a, Tausug, Surigaonon, Masbateño, Aklanon and Ibanag. The 28-letter modern Filipino alphabet, adopted in 1987, is the official writing system. Also, language of each ethnicity has also their own writing scripts, which are no longer used and set of alphabets.[91]
Religion
Most Filipinos today (over 80%) are Christians, with around eighty-seven percent of the population professing Roman Catholicism. The latter was introduced by the Spanish beginning in 1521, and during their 377-year colonization of the islands, they managed to convert a vast majority of Filipinos, resulting in the Philippines becoming the largest Catholic country in Asia. There are also large groups of Protestant denominations, which either grew or were founded following the disestablishment of the Catholic Church during the American Colonial period. The Iglesia ni Cristo is currently the single largest indigenous church, followed by United Church of Christ in the Philippines. The Iglesia Filipina Independiente (also known as the Aglipayan Church) was an earlier development, and is a national church directly resulting from the 1898 Philippine Revolution. Other Christian groups such as the Victory Church,[92] Jesus Miracle Crusade, Mormonism, Orthodoxy, and the Jehovah's Witnesses have a visible presence in the country. Other native inhabitants follow Islam, forming a large minority. Islam in the Philippines is mostly concentrated in southwestern Mindanao and the Sulu Archipelago which, though part of the Philippines, are very close to the neighboring Islamic countries of Malaysia and Indonesia. The Muslims call themselves Moros, a Spanish word that refers to the Moors (albeit the two groups have little cultural connection other than Islam).
Historically, ancient Filipinos held animistic beliefs that were influenced by Hinduism and Buddhism, which were brought by traders from neighbouring Asian states. Indigenous groups like the Aeta are Animists, while Igorot and Lumad tribes still observe traditional religious practises, often alongside Christianity or Islam.
As of 2013, religious groups together constituting less than five percent of the population included Hinduism, Buddhism, Seventh-day Adventists, United Church of Christ, United Methodists, the Episcopal Church in the Philippines, Assemblies of God, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormons), and Philippine (Southern) Baptists; and the following domestically established churches: Iglesia ni Cristo (Church of Christ), Philippine Independent Church (Aglipayan), Members Church of God International, and The Kingdom of Jesus Christ, the Name Above Every Name. In addition, there are Lumad, who are indigenous peoples of various animistic and syncretic religions.[93]
Diaspora

There are currently more than 10 million Filipinos who live overseas. Filipinos form a minority ethnic group in the Americas, Europe, Oceania,[94][95] the Middle East, and other regions in the world.
There are an estimated 3.4 million Americans of Filipino ancestry in the United States, and more than 300,000 American citizens in the Philippines.[96] According to the U.S. Census Bureau, immigrants from the Philippines made up the second largest group after Mexico that sought family reunification.[97]
Filipinos make up about half of the entire population of the Northern Marianas Islands, an American territory in the North Pacific Ocean, and a large proportion of the populations of Guam, Palau, the British Indian Ocean Territory, and Sabah.[95]
See also
References
- ↑ "ASIAN ALONE OR IN ANY COMBINATION BY SELECTED GROUPS: 2015". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved April 25, 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 Stock Estimates of Filipinos Overseas 2007 Report Archived 6 March 2009 at the Wayback Machine.. Philippine Overseas Employment Administration. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ↑ http://www.positivelyfilipino.com/magazine/2013/7/know-your-diaspora-united-arab-emirates
- ↑ Statistics Canada. "2011 National Household Survey: Data tables". Retrieved 18 February 2014.
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20090209101514/http://globalnation.inquirer.net/news/breakingnews/view/20090206-187868/No-foreign-workers-layoffs-in-Malaysia
- ↑ "Department of Foreign Affairs to Filipinos in Japan 'Heed advisories'". Japan. 12 March 2011.
- ↑ Australia Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 21 June 2012.
- ↑ Filipinos in Hong Kong Hong Kong Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 30 June 2009.
- ↑ "I cittadini non comunitari regolarmente soggiornanti". 30 November 2013. Archived from the original on 13 November 2014.
- ↑ "PGMA meets members of Filipino community in Spain". Gov.Ph. Retrieved 1 July 2006.
- ↑ 外僑居留-按國籍別 (Excel) (in Chinese). National Immigration Agency, Ministry of the Interior. 2011-02-28. Retrieved 2013-05-21.
- ↑ Filipinos in South Korea. Korean Culture and Information Service (KOIS). Retrieved 21 July 2009.
- ↑ "Ethnic group profiles".
- ↑ "Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics". Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics.
- ↑ Amojelar, Darwin G. (2013-04-26) Papua New Guinea thumbs down Philippine request for additional flights. InterAksyon.com. Retrieved 28 July 2013.
- ↑ "Anzahl der Ausländer in Deutschland nach Herkunftsland (Stand: 31. Dezember 2014)".
- ↑ "A brief history of Philippine – Netherlands relations". The Philippine Embassy in The Hague. Archived from the original on 2012-07-16.
- ↑ "ต่างด้าวอาเซียนทำงานในไทยกว่า 1.3 ล้านคน "ฟิลิปปินส์" ครองแชมป์ทำงานระดับฝีมือสูงสุด". April 2017. Retrieved 16 April 2017.
- ↑ "Macau Population Census". Census Bureau of Macau. May 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2016.
- ↑ "pinoys-sweden-protest-impending-embassy-closure". ABS-CBN.com.
- ↑ "CSO Emigration" (PDF). Census Office Ireland. Retrieved 29 January 2013.
- ↑ "Statistic Austria".
- ↑ "8 Folkemengde, etter norsk / utenlandsk statsborgerskap og landbakgrunn 1. januar 2009". Statistisk sentralbyra (Statistics Norway). Archived from the original on 2009-05-15. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- ↑ "President Aquino to meet Filipino community in Beijing". Ang Kalatas-Australia. 30 August 2011.
- ↑ "Backgrounder: Overseas Filipinos in Switzerland". Office of the Press Secretary. 2007. Retrieved 23 October 2009.
- ↑ Welcome to Embassy of Kazakhstan in Malaysia Website. Kazembassy.org.my. Retrieved 28 July 2013.
- ↑ Tan, Lesley (2006-06-06). "A tale of two states". Cebu Daily News. Retrieved 11 April 2008.
- ↑ "Statistical Yearbook of Greece 2009 & 2010" (PDF). Hellenic Statistical Authority. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 December 2013. Retrieved 2014-09-09.
- ↑ "No Filipino casualty in Turkey quake - DFA". GMA News. 3 August 2010.
- ↑ "Table 1.10; Household Population by Religious Affiliation and by Sex; 2010" (PDF). 2015 Philippine Statistical Yearbook. East Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority: 1–30. October 2015. ISSN 0118-1564. Retrieved August 15, 2016.
- 1 2 "Spanish Influence on Language, Culture, and Philippine History".
- ↑ "Filipino". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- ↑ Ocampo, Ambeth R. (1995). Bonifacio's bolo. Anvil Pub. p. 21. ISBN 978-971-27-0418-5.
- ↑ Roberto Reyes Mercado, "Pinoy and Flip are Racial Slurs", Published 2002 by MBC.
- ↑ Henderson, Barney (3 August 2010). "Archaeologists unearth 67000-year-old human bone in Philippines". The Daily Telegraph. UK.
- ↑ "Archaeology in the Philippines, the National Museum and an Emergent Filipino Nation". Wilhelm G. Solheim II Foundation for Philippine Archaeology, Inc.
- ↑ Scott 1984, pp. 14–15
- ↑ History.com Archived 20 April 2009 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Harold K. Voris. "Maps of Pleistocene sea levels in Southeast Asia". Journal of Biogeography. Field Museum of Natural History. 27: 1153–1167. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2699.2000.00489.x. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- ↑ R. D. Gray (January 2009). "Language Phylogenies Reveal Expansion Pulses and Pauses in Pacific Settlement". Science. 323: 479–483. PMID 19164742. doi:10.1126/science.1166858. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- 1 2 Howells, William White (1 January 1997). "Getting Here: The Story of Human Evolution". Howells House – via Google Books.
- ↑ David Bulbeck; Pathmanathan Raghavan; Daniel Rayner (2006). "Races of Homo sapiens: if not in the southwest Pacific, then nowhere" (PDF). World Archaeology. Taylor & Francis. 38 (1): 109–132. ISSN 0043-8243. JSTOR 40023598. doi:10.1080/00438240600564987.
- 1 2 3 "Background note: Philippines". U.S. Department of State Diplomacy in Action. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- ↑ "The People of the Philippines". Asian Info.
- ↑ Jocano 2001, pp. 34–56
- ↑ Mong Palatino (27 February 2013). "Are Filipinos Malays?". The Diplomat. Retrieved 18 June 2015.
- 1 2 "About Pasay – History: Kingdom of Namayan". Pasay City Government website. City Government of Pasay. Archived from the original on 20 November 2007. Retrieved 5 February 2008.
- ↑ Huerta, Felix, de (1865). Estado Geografico, Topografico, Estadistico, Historico-Religioso de la Santa y Apostolica Provincia de San Gregorio Magno. Binondo: Imprenta de M. Sanchez y Compañia.
- ↑ Remains of ancient barangays in many parts of Iloilo testify to the antiquity and richness of these pre-colonial settlements. Pre-Hispanic burial grounds are found in many towns of Iloilo. These burial grounds contained antique porcelain burial jars and coffins made of hard wood, where the dead were put to rest with abundance of gold, crystal beads, Chinese potteries, and golden masks. These Philippine national treasures are sheltered in Museo de Iloilo and in the collections of many Ilongo old families. Early Spanish colonizers took note of the ancient civilizations in Iloilo and their organized social structure ruled by nobilities. In the late 16th century, Fray Gaspar de San Agustin in his chronicles about the ancient settlements in Panay says: "También fundó convento el Padre Fray Martin de Rada en Araut- que ahora se llama el convento de Dumangas- con la advocación de nuestro Padre San Agustín ... Está fundado este pueblo casi a los fines del río de Halaur, que naciendo en unos altos montes en el centro de esta isla (Panay) ... Es el pueblo muy hermoso, ameno y muy lleno de palmares de cocos. Antiguamente era el emporio y corte de la más lucida nobleza de toda aquella isla." Gaspar de San Agustin, O.S.A., Conquistas de las Islas Filipinas (1565–1615), Manuel Merino, O.S.A., ed., Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas: Madrid 1975, pp. 374–375.
- ↑ "Arab and native intermarriage in Austronesian Asia". ColorQ World. Retrieved 24 December 2008.
- ↑ Philippine History by Maria Christine N. Halili. "Chapter 3: Precolonial Philippines" (Published by Rex Bookstore; Manila, Sampaloc St. Year 2004)
- ↑ The Kingdom of Namayan and Maytime Fiesta in Sta. Ana of new Manila, Traveler On Foot self-published l journal.
- ↑ Volume 5 of A study of the Eastern and Western Oceans (Japanese: 東西洋考) mentions that Luzon first sent tribute to Yongle Emperor in 1406.
- ↑ "Akeanon Online – Aton Guid Ra! – Aklan History Part 3 – Confederation of Madyaas". Akeanon.com. 2008-03-27. Retrieved 2 January 2010.
- ↑ "Account Suspended". Archived from the original on 1 December 2008.
- ↑ Munoz 2006, p. 171
- ↑ Background Note: Brunei Darussalam, U.S. State Department.
- ↑ Mangyan Heritage Center (archived from the original on 2008-02-13)
- ↑ Tarling, Nicholas (1999). The Cambridge History of Southeast Asia. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 149. ISBN 0-521-66370-9.
- ↑ Leupp, Gary P. (2003). Interracial Intimacy in Japan. Continuum International Publishing Group. pp. 52–3. ISBN 0-8264-6074-7.
- ↑ Tracy, Nicholas (1995). Manila Ransomed: The British Assault on Manila in the Seven Years War. University of Exeter Press. p. 109. ISBN 978-0-85989-426-5. ISBN 0-85989-426-6, ISBN 978-0-85989-426-5.
- ↑ Article 3 of the treaty specifically associated the $20 million payment with the transfer of the Philippines.
- ↑ "American Conquest of the Philippines – War and Consequences: Benevolent Assimilation and the 1899 PhilAm War". oovrag.com. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- ↑ "The Philippines – A History of Resistance and Assimilation". voices.cla.umn.edu. Archived from the original on 2006-02-08. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- ↑ "Women and children, militarism, and human rights: International Women's Working Conference – Off Our Backs – Find Articles at BNET.com".
- ↑ Owen, Norman G. (2014). Routledge Handbook of Southeast Asian History. Routledge. p. 275. ISBN 978-1-135-01878-8.
- ↑ Delmendo, Sharon (2005). The Star-entangled Banner: One Hundred Years of America in the Philippines. UP Press. p. 28. ISBN 978-971-542-484-4.
- ↑ Owen, Norman G. (2014). Routledge Handbook of Southeast Asian History. Routledge. p. 275. ISBN 978-1-135-01878-8.
- ↑ Luigi Luca Cavalli-Sforza; Alberto Piazza; Paolo Menozzi; Joanna Mountain (1988). "Reconstruction of human evolution: Bringing together genetic, archaeological, and linguistic data" (PDF). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85 (16): 6002–6006. PMC 281893
 . PMID 3166138. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.16.6002.
. PMID 3166138. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.16.6002. - ↑ Stephen J. Marshall, Adele L. H. Whyte, J. Frances Hamilton, and Geoffrey K. Chambers1 (2005). "Austronesian prehistory and Polynesian genetics: A molecular view of human migration across the Pacific" (PDF). New Zealand Science Review. New Zealand Association of Scientists. 62 (3): 75–80. ISSN 0028-8667.
- ↑ With a sample population of 105 Filipinos, the company of Applied Biosystems, analyses the Y-DNA of the average Filipino.
- ↑ Albert Min-Shan Ko; Chung-Yu Chen; Qiaomei Fu; Frederick Delfin; Mingkun Li; Hung-Lin Chiu; Mark Stoneking; Ying-Chin Ko (2014). "Early Austronesians: Into and Out Of Taiwan". American Journal of Human Genetics. 94 (3): 426–436. PMC 3951936
 . PMID 24607387. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.02.003.
. PMID 24607387. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.02.003. - ↑ Chuan-Kun Ho (2002). "Rethinking the Origins of Taiwan Austronesians" (PDF). Proceedings of The International Symposium of Anthropological Studies at Fudan University: 17–19.
- 1 2 Mark Donohue; Tim Denham. "Farming and Language in Island Southeast Asia". Chicago Journals. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- ↑ "New DNA evidence overturns population migration theory in Island Southeast Asia". Phys.org. 23 May 2008. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- ↑ Wilhelm G. Solheim II (2002). "The Pre-Sa Huynh-Kalanay Pottery of Taiwan and Southeast Asia". Hukay. 13: 39–66.
- ↑ Karafet, Tatiana M.; Hallmark, Brian; Cox, Murray P.; et al. (2010). "Major East–West Division Underlies Y Chromosome Stratification across Indonesia". Mol. Biol. Evol. 27 (8): 1833–1844. PMID 20207712. doi:10.1093/molbev/msq063.
- ↑ Capelli, Cristian; James F. Wilson, Martin Richards, Michael P. H. Stumpf, Fiona Gratrix, Stephen Oppenheimer, Peter Underhill, Vincenzo L. Pascali, Tsang-Ming Ko, David B. Goldstein1 (2001). "A Predominantly Indigenous Paternal Heritage for the Austronesian-speaking Peoples of Insular Southeast Asia and Oceania" (PDF). American Journal of Human Genetics. 68 (2): 432–443. PMC 1235276
 . PMID 11170891. doi:10.1086/318205. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 February 2010. Retrieved 24 June 2007.
. PMID 11170891. doi:10.1086/318205. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 February 2010. Retrieved 24 June 2007. - ↑ Chang JG, Ko YC, Lee JC, Chang SJ, Liu TC, Shih MC, Peng CT (2002). "Molecular analysis of mutations and polymorphisms of the Lewis secretor type alpha(1,2)-fucosyltransferase gene reveals that Taiwanese aborigines are of Austronesian derivation". J. Hum. Genet. 47: 60–5. PMID 11916003. doi:10.1007/s100380200001.
- ↑ *Institute for Human Genetics, University of California San Francisco (2015). "Self-identified East Asian nationalities correlated with genetic clustering, consistent with extensive endogamy. Individuals of mixed East Asian-European genetic ancestry were easily identified; we also observed a modest amount of European genetic ancestry in individuals self-identified as Filipinos" (PDF). Genetics Online: 1.
- 1 2 Henke, Winfried; Tattersall, Ian; Hardt, Thorolf (2007). Handbook of Paleoanthropology: Vol I:Principles, Methods and Approaches Vol II:Primate Evolution and Human Origins Vol III:Phylogeny of Hominids. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 1903. ISBN 978-3-540-32474-4.
- ↑ George Richard Scott, Christy G. Turner (2000). The Anthropology of Modern Human Teeth: Dental Morphology and Its Variation in Recent Human Populations. Cambridge University Press. pp. 177, 179, . ISBN 978-0-521-78453-5.
- ↑ Penny & Penny 2002, pp. 29–30
- ↑ "El Torno Chabacano". Instituto Cervantes. Instituto Cervantes.
- 1 2 Gómez Rivera, Guillermo (2005). "Estadisticas: El idioma español en Filipinas". Retrieved 2 May 2010. "Los censos norteamericanos de 1903 y 1905, dicen de soslayo que los Hispano-hablantes de este archipiélago nunca han rebasado, en su número, a más del diez por ciento (10%) de la población durante la última década de los mil ochocientos (1800s). Esto quiere decir que 900,000 Filipinos, el diez porciento de los dados nueve millones citados por el Fray Manuel Arellano Remondo, tenían al idioma español como su primera y única lengua." (Emphasis added.) The same author writes: "Por otro lado, unos recientes estudios por el Dr. Rafael Rodríguez Ponga señalan, sin embargo, que los Filipinos de habla española, al liquidarse la presencia peninsular en este archipiélago, llegaban al catorce (14%) por ciento de la población de la década 1891–1900. Es decir, el 14% de una población de nueve millones (9,000,000), que serían un millón (1,260,000) y dos cientos sesenta mil de Filipinos que eran primordialmente de habla hispana. (Vea Cuadernos Hispanoamericanos, enero de 2003)." (La persecución del uso oficial del idioma español en Filipinas. Retrieved 8 July 2010.)
- ↑ "Philippines - EDUCATION".
- ↑ "Languages of the Philippines". Ethnologue.
- ↑ Thompson, Roger M. (2003). "3. Nationalism and the rise of the hegemonic Imposition of Tagalog 1936–1973". Filipino English and Taglish. John Benjamins Publishing Company. pp. 27–29. ISBN 978-90-272-4891-6., ISBN 90-272-4891-5, ISBN 978-90-272-4891-6.
- ↑ Andrew Gonzalez (1998). "The Language Planning Situation in the Philippines" (PDF). Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development. 19 (5, 6): 487–488. doi:10.1080/01434639808666365. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 June 2007. Retrieved 24 March 2007.
- ↑ Article XIV, Section 6, The 1987 Constitution of the Republic of the Philippines.
- ↑ Linda Trinh Võ; Rick Bonus (2002). Contemporary Asian American communities: intersections and divergences. Temple University Press. pp. 96, 100. ISBN 978-1-56639-938-8.
- ↑ Victory, Outreach. "Victory Outreach". Victory Outreach. Victory Outreach. Retrieved 10 April 2016.
- ↑ "Philippines". 2013 Report on International Religious Freedom. U.S. Department of State. 28 July 2014.
- ↑ "National Summary Tables". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 6 June 2001.
- 1 2 "Population Composition: Asian-born Australians". Australian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 6 June 2001.
- ↑ "Background Note: Philippines". Bureau of East Asian and Pacific Affairs. United States Department of State. 3 June 2011. Retrieved 8 June 2011.
- ↑ Castles, Stephen and Mark J. Miller. (July 2009). "Migration in the Asia-Pacific Region". Migration Information Source. Migration Policy Institute. Retrieved 17 December 2009.
- Penny, Ralph; Penny, Ralph John (2002). A history of the Spanish language (22nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-01184-6.
Publications
- Peter Bellwood (July 1991). "The Austronesian Dispersal and the Origin of Languages". Scientific American. 265 (1): 88–93. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0791-88.
- Bellwood, Peter; Fox, James; & Tryon, Darrell (1995). The Austronesians: Historical and comparative perspectives. Department of Anthropology, Australian National University. ISBN 0-7315-2132-3.
- Peter Bellwood (1998). "Taiwan and the Prehistory of the Austronesians-speaking Peoples". Review of Archaeology. 18: 39–48.
- Peter Bellwood; Alicia Sánchez-Mazas (June 2005). "Human Migrations in Continental East Asia and Taiwan: Genetic, Linguistic, and Archaeological Evidence". Current Anthropology. 46 (3): 480–485. doi:10.1086/430018.
- David Blundell. "Austronesian Disperal". Newsletter of Chinese Ethnology. 35: 1–26.
- Robert Blust (1985). "The Austronesian Homeland: A Linguistic Perspective". Asian Perspectives. 20: 46–67.
- Peter Fuller (2002). "Asia Pacific Research". Reading the Full Picture. Canberra, Australia: Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies. Retrieved 28 July 2005.
- "Homepage of linguist Dr. Lawrence Reid". Retrieved 28 July 2005.
- Malcolm Ross & Andrew Pawley (1993). "Austronesian historical linguistics and culture history". Annual Review of Anthropology. 22: 425–459. doi:10.1146/annurev.an.22.100193.002233.
- Frederic H. Sawyer (1900). The Inhabitants of the Philippines. Library of Alexandria. ISBN 978-1-4655-1185-0.
- Scott, William Henry (1984). Prehispanic Source Materials for the study of Philippine History. New Day Publishers. ISBN 978-971-10-0227-5. Retrieved 5 August 2008. ISBN 978-971-10-0226-8.
- John Edward Terrell (December 2004). "Introduction: 'Austronesia' and the great Austronesian migration". World Archaeology. 36 (4): 586–591. doi:10.1080/0043824042000303764.
- Zaide, Sonia M. (1999) [1994]. The Philippines: A Unique Nation. All-Nations Publishing. ISBN 971-642-071-4.
External links
-
 Media related to People of the Philippines at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to People of the Philippines at Wikimedia Commons