Antiparticle
| Antimatter |
|---|
 |
|
Bodies |
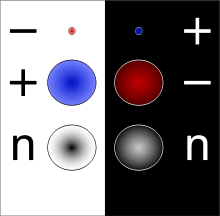
Corresponding to most kinds of particles, there is an associated antiparticle with the same mass and opposite charge (including electric charge). For example, the antiparticle of the electron is the positron (antielectron), which has positive charge and is produced naturally in certain types of radioactive decay. The opposite is also true: the antiparticle of the positron is the electron.
Some particles, such as the photon, are their own antiparticle. Otherwise, for each pair of antiparticle partners, one is designated as normal matter (the kind we are made of), and the other (usually given the prefix "anti-") as in antimatter.
Particle–antiparticle pairs can annihilate each other, producing photons; since the charges of the particle and antiparticle are opposite, total charge is conserved. For example, the positrons produced in natural radioactive decay quickly annihilate themselves with electrons, producing pairs of gamma rays, a process exploited in positron emission tomography.
The laws of nature are very nearly symmetrical with respect to particles and antiparticles. For example, an antiproton and a positron can form an antihydrogen atom, which is believed to have the same properties as a hydrogen atom. This leads to the question of why the formation of matter after the Big Bang resulted in a universe consisting almost entirely of matter, rather than being a half-and-half mixture of matter and antimatter. The discovery of Charge Parity violation helped to shed light on this problem by showing that this symmetry, originally thought to be perfect, was only approximate.
Antiparticles are produced naturally in beta decay, and in the interaction of cosmic rays in the Earth's atmosphere.
Because charge is conserved, it is not possible to create an antiparticle without either destroying a particle of the same charge (as in
β+
decay, when a proton (positive charge) is destroyed, a neutron created and a positron (positive charge, antiparticle) is also created and emitted) or by creating a particle of the opposite charge. The latter is seen in many processes in which both a particle and its antiparticle are created simultaneously, as in particle accelerators. This is the inverse of the particle–antiparticle annihilation process.
Although particles and their antiparticles have opposite charges, electrically neutral particles need not be identical to their antiparticles. The neutron, for example, is made out of quarks, the antineutron from antiquarks, and they are distinguishable from one another because neutrons and antineutrons annihilate each other upon contact. However, other neutral particles are their own antiparticles, such as photons, Z0 bosons,
π0
mesons, and hypothetical gravitons and some hypothetical WIMPs.
History
Experiment
In 1932, soon after the prediction of positrons by Paul Dirac, Carl D. Anderson found that cosmic-ray collisions produced these particles in a cloud chamber— a particle detector in which moving electrons (or positrons) leave behind trails as they move through the gas. The electric charge-to-mass ratio of a particle can be measured by observing the radius of curling of its cloud-chamber track in a magnetic field. Positrons, because of the direction that their paths curled, were at first mistaken for electrons travelling in the opposite direction. Positron paths in a cloud-chamber trace the same helical path as an electron but rotate in the opposite direction with respect to the magnetic field direction due to their having the same magnitude of charge-to-mass ratio but with opposite charge and, therefore, opposite signed charge-to-mass ratios.
The antiproton and antineutron were found by Emilio Segrè and Owen Chamberlain in 1955 at the University of California, Berkeley. Since then, the antiparticles of many other subatomic particles have been created in particle accelerator experiments. In recent years, complete atoms of antimatter have been assembled out of antiprotons and positrons, collected in electromagnetic traps.[1]
Dirac hole theory
Solutions of the Dirac equation contained negative energy quantum states. As a result, an electron could always radiate energy and fall into a negative energy state. Even worse, it could keep radiating infinite amounts of energy because there were infinitely many negative energy states available. To prevent this unphysical situation from happening, Dirac proposed that a "sea" of negative-energy electrons fills the universe, already occupying all of the lower-energy states so that, due to the Pauli exclusion principle, no other electron could fall into them. Sometimes, however, one of these negative-energy particles could be lifted out of this Dirac sea to become a positive-energy particle. But, when lifted out, it would leave behind a hole in the sea that would act exactly like a positive-energy electron with a reversed charge. These he interpreted as "negative-energy electrons" and attempted to identify them with protons in his 1930 paper A Theory of Electrons and Protons[3] However, these "negative-energy electrons" turned out to be positrons, and not protons.
This picture implied an infinite negative charge for the universe—a problem of which Dirac was aware. Dirac tried to argue that we would perceive this as the normal state of zero charge. Another difficulty was the difference in masses of the electron and the proton. Dirac tried to argue that this was due to the electromagnetic interactions with the sea, until Hermann Weyl proved that hole theory was completely symmetric between negative and positive charges. Dirac also predicted a reaction
e−
+
p+
→
γ
+
γ
, where an electron and a proton annihilate to give two photons. Robert Oppenheimer and Igor Tamm proved that this would cause ordinary matter to disappear too fast. A year later, in 1931, Dirac modified his theory and postulated the positron, a new particle of the same mass as the electron. The discovery of this particle the next year removed the last two objections to his theory.
However, the problem of infinite charge of the universe remains. Also, as we now know, bosons also have antiparticles, but since bosons do not obey the Pauli exclusion principle (only fermions do), hole theory does not work for them. A unified interpretation of antiparticles is now available in quantum field theory, which solves both these problems.
Particle–antiparticle annihilation
If a particle and antiparticle are in the appropriate quantum states, then they can annihilate each other and produce other particles. Reactions such as
e−
+
e+
→
γ
+
γ
(the two-photon annihilation of an electron-positron pair) are an example. The single-photon annihilation of an electron-positron pair,
e−
+
e+
→
γ
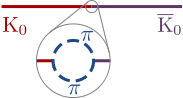
, cannot occur in free space because it is impossible to conserve energy and momentum together in this process. However, in the Coulomb field of a nucleus the translational invariance is broken and single-photon annihilation may occur.[4] The reverse reaction (in free space, without an atomic nucleus) is also impossible for this reason. In quantum field theory, this process is allowed only as an intermediate quantum state for times short enough that the violation of energy conservation can be accommodated by the uncertainty principle. This opens the way for virtual pair production or annihilation in which a one particle quantum state may fluctuate into a two particle state and back. These processes are important in the vacuum state and renormalization of a quantum field theory. It also opens the way for neutral particle mixing through processes such as the one pictured here, which is a complicated example of mass renormalization.
Properties
Quantum states of a particle and an antiparticle can be interchanged by applying the charge conjugation (C), parity (P), and time reversal (T) operators. If denotes the quantum state of a particle (n) with momentum p, spin J whose component in the z-direction is σ, then one has
where nc denotes the charge conjugate state, that is, the antiparticle. This behaviour under CPT symmetry is the same as the statement that the particle and its antiparticle lie in the same irreducible representation of the Poincaré group. Properties of antiparticles can be related to those of particles through this. If T is a good symmetry of the dynamics, then
where the proportionality sign indicates that there might be a phase on the right hand side. In other words, particle and antiparticle must have
- the same mass m
- the same spin state J
- opposite electric charges q and -q.
Quantum field theory
- This section draws upon the ideas, language and notation of canonical quantization of a quantum field theory.
One may try to quantize an electron field without mixing the annihilation and creation operators by writing
where we use the symbol k to denote the quantum numbers p and σ of the previous section and the sign of the energy, E(k), and ak denotes the corresponding annihilation operators. Of course, since we are dealing with fermions, we have to have the operators satisfy canonical anti-commutation relations. However, if one now writes down the Hamiltonian
then one sees immediately that the expectation value of H need not be positive. This is because E(k) can have any sign whatsoever, and the combination of creation and annihilation operators has expectation value 1 or 0.
So one has to introduce the charge conjugate antiparticle field, with its own creation and annihilation operators satisfying the relations
where k has the same p, and opposite σ and sign of the energy. Then one can rewrite the field in the form
where the first sum is over positive energy states and the second over those of negative energy. The energy becomes
where E0 is an infinite negative constant. The vacuum state is defined as the state with no particle or antiparticle, i.e., and . Then the energy of the vacuum is exactly E0. Since all energies are measured relative to the vacuum, H is positive definite. Analysis of the properties of ak and bk shows that one is the annihilation operator for particles and the other for antiparticles. This is the case of a fermion.
This approach is due to Vladimir Fock, Wendell Furry and Robert Oppenheimer. If one quantizes a real scalar field, then one finds that there is only one kind of annihilation operator; therefore, real scalar fields describe neutral bosons. Since complex scalar fields admit two different kinds of annihilation operators, which are related by conjugation, such fields describe charged bosons.
Feynman–Stueckelberg interpretation
By considering the propagation of the negative energy modes of the electron field backward in time, Ernst Stueckelberg reached a pictorial understanding of the fact that the particle and antiparticle have equal mass m and spin J but opposite charges q. This allowed him to rewrite perturbation theory precisely in the form of diagrams. Richard Feynman later gave an independent systematic derivation of these diagrams from a particle formalism, and they are now called Feynman diagrams. Each line of a diagram represents a particle propagating either backward or forward in time. This technique is the most widespread method of computing amplitudes in quantum field theory today.
Since this picture was first developed by Stueckelberg,[5] and acquired its modern form in Feynman's work,[6] it is called the Feynman–Stueckelberg interpretation of antiparticles to honor both scientists.
As a consequence of this interpretation, Villata argued that the assumption of antimatter as CPT-transformed matter would imply that the gravitational interaction between matter and antimatter is repulsive.[7]
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Antiparticles. |
- Gravitational interaction of antimatter
- Parity, charge conjugation and time reversal symmetry.
- CP violations and the baryon asymmetry of the universe.
- Quantum field theory and the list of particles
- Baryogenesis
Notes
- ↑ "Antimatter Atoms Trapped for First Time"
- ↑ Weinberg, Steve. The quantum theory of fields, Volume 1 : Foundations. p. 14. ISBN 0-521-55001-7.
- ↑ Dirac, Paul (1930). "A Theory of Electrons and Protons". Proceedings of the Royal Society A. 126 (801): 360–365. Bibcode:1930RSPSA.126..360D. doi:10.1098/rspa.1930.0013.
- ↑ Sodickson, L.; W. Bowman; J. Stephenson (1961). "Single-Quantum Annihilation of Positrons". Physical Review. 124 (6): 1851–1861. Bibcode:1961PhRv..124.1851S. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.124.1851.
- ↑ Stueckelberg, Ernst (1941), "La signification du temps propre en mécanique ondulatoire." Helv. Phys. Acta 14, pp. 322–323.
- ↑ Feynman, Richard P. (1948). "Space-time approach to non-relativistic quantum mechanics". Reviews of Modern Physics. 20 (2): 367–387. Bibcode:1948RvMP...20..367F. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.20.367.
- ↑ Villata, M. (2011). "CPT symmetry and antimatter gravity in general relativity". EPL. 94 (2): 20001. doi:10.1209/0295-5075/94/20001.
References
- Feynman, R. P. (1987). "The reason for antiparticles". In R. P. Feynman; S. Weinberg. The 1986 Dirac memorial lectures. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-34000-4.
- Weinberg, S. (1995). The Quantum Theory of Fields, Volume 1: Foundations. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-55001-7.