Fasciculus Medicinae
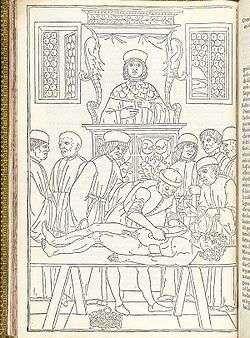
Fasciculus Medicinae is a “bundle” of six independent and quite different medieval medical treatises. The collection, which existed only in two manuscripts (handwritten copies), was first printed in 1491 in Latin and came out in numerous editions over the next 25 years. Johannes de Ketham, the German physician routinely associated with the Fasciculus, was neither the author nor even the original compiler but merely an owner of one of the manuscripts. The topics of the treatises cover a wide spectrum of medieval European medical knowledge and technique, including uroscopy, astrology, bloodletting, the treatment of wounds, plague, anatomical dissection, and women’s health. The book is remarkable as the first illustrated medical work to appear in print; notable illustrations include: a urine chart, a diagram of the veins for phlebotomy, a pregnant woman, Wound Man, Disease Man and Zodiac Man. In 1495, it appeared in Italian under the title Fasiculo de Medicina.
The ten handsome full-page woodcut illustrations influenced artists for some time - even as late as 1751 when the last of William Hogarth's Four Stages of Cruelty seems to borrow from the dissection scene (above).
References

- Choulant, L. History and bibliography of anatomic illustration. Trans. and annotated by Mortimer Frank. (New York: Hafner, 1962). Pp. 115-119.
- Ketham, J. de. The Fasciculus Medicinae of Johannes de Ketham, Alemanus : facsimile of the first (Venetian) edition of 1491. With English translation by Luke Demaitre ; commentary by Karl Sudhoff ; trans. and adapted by Charles Singer. (Birmingham, Ala.: The Classics of Medicine Library, 1988).
- Morton's Medical Bibliography (Garrison and Morton). Ed. By Jeremy Norman. Fifth ed. (Aldershot, Hants, England : Scolar Press ; Brookfield, Vt., USA : Gower Pub. Co., 1991). No. 363.1.
External links
- Edition review
- Johannes de Ketham: Fasiculo de medicina (Venice, 1495). Selected pages scanned from the original work. Historical Anatomies on the Web. US National Library of Medicine.
- Turn the pages of a virtual copy of Fasiculo de Medicina at the National Library of Medicine's website Click your mouse on the right side of the book cover to start.
- Images from Fasciculus Medicinae (Milan, 1516) From The College of Physicians of Philadelphia Digital Library