Falling (accident)
| Falling | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Falling is a normal experience for young children, but falling from a significant height or onto a hard surface can be dangerous. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-10 | W00-W19, X80, X81 |
Falling is the second leading cause of accidental death worldwide and is a major cause of personal injury, especially for the elderly.[1] Falls in older adults are an important class of preventable injuries. Builders, electricians, miners, and painters are occupations with high rates of fall injuries.
About 155 million new cases of a significant fall occurred in 2013.[2] These unintentional falls resulted in 556,000 deaths up from 341,000 deaths in 1990.[3]
Causes
Accidents
The most common cause of falls in healthy adults is accidents. It may be by slipping or tripping from stable surfaces or stairs, improper footwear, dark surroundings, uneven ground, or lack of exercise. Studies suggest that women are more prone to falling than men in all age groups.[4]
Age
Older people and particularly older people with dementia are at greater risk than young people to injuries due to falling.[5][6] Older people are at risk due to accidents, gait disturbances, balance disorders, changed reflexes due to visual, sensory, motor and cognitive impairment, medications and alcohol consumption, infections, and deyhdration.[7][8][9][10]
Illness
People who have experienced stroke are at risk for falls due to gait disturbances, reduced muscle tone and weakness, side effects of drugs to treat MS, low blood sugar, low blood pressure, and loss of vision.[11][12]
People with Parkinson's disease are at risk of falling due to gait disturbances, loss of motion control including freezing and jerking, autonomic system disorders such as orthostatic hypotension, fainting, and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome; neurological and sensory disturbances including muscle weakness of lower limbs, deep sensibility impairment, epileptic seizure, cognitive impairment, visual impairment, balance impairment, and side effects of drugs to treat PD.[13][14]
People with multiple sclerosis are at risk of falling due to gait disturbances, drop foot, ataxia, reduced proprioception, improper or reduced use of assistive devices, reduced vision, cognitive changes, and medications to treat MS.[15][16][17][18]
Workplace

In the occupational setting, falling incidents are commonly referred to as slips, trips, and falls (STFs).[19] Falls from elevation hazards are present at almost every jobsite, and many workers are exposed to these hazards daily. As such, falls are an important topic for occupational safety and health services. Any walking/working surface could be a potential fall hazard. An unprotected side or edge which is 6 feet (1.8 m) or more above a lower level should be protected from falling by the use of a guard rail system, safety net system, or personal fall arrest system.[20] These hazardous exposures exist in many forms, and can be as seemingly innocuous as changing a light bulb from a step ladder to something as high-risk as installing bolts on high steel at 200 feet (61 m) in the air. In 2000, 717 workers died of injuries caused by falls from ladders, scaffolds, buildings, or other elevations.[21] More recent data in 2011, found that STFs contributed to 14% of all workplace fatalities in the United States that year.[22]
Companies must make sure that they follow the applicable safety legislation (e.g., the Occupational Safety and Health Act in the United States) to keep their work environments safe.
Risk factors
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health has compiled certain known risk factors that have been found responsible for STFs in the workplace setting.[19] While falling can occur at any time and by any means in the workplace, these factors have been known to cause same-level falls, which are less likely to occur than falls to a lower level.[19]
Workplace factors: spills on walking surfaces, ice, precipitation (snow/sleet/rain), loose mats or rugs, boxes/containers, poor lighting, uneven walking surfaces
Work organization factors: fast work pace, work tasks involving liquids or greases
Individual factors: age; employee fatigue; failing eyesight / use of bifocals; inappropriate, loose, or poor-fitting footwear
Preventive measures: warning signs
Intentionally caused falls
Injurious falls can be caused intentionally, as in cases of defenestration or deliberate jumping.
Height and severity
The severity of injury increases with the height of the fall but also depends on body and surface features and the manner of the body's impacts against the surface.[23] The chance of surviving increases if landing on a highly deformable surface (a surface that is easily bent, compressed, or displaced) such as snow or water.[23]
Injuries caused by falls from buildings vary depending on the building's height and the age of the person. Falls from a building's second floor/story (American English) or first floor/storey (British English and equivalent idioms in continental European languages) usually cause injuries but are not fatal. Overall, the height at which 50% of children die from a fall is between four and five storey heights (around 12 to 15 metres or 40 to 50 feet) above the ground.[24]
Prevention

Rates of falls in hospital can be reduced with a number of interventions together by 0.72 from baseline in the elderly.[25] In nursing homes fall prevention problems that involve a number of interventions prevent recurrent falls.[26]
Epidemiology
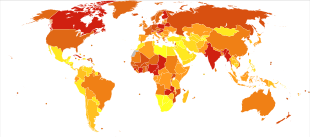

In 2013 unintentional falls resulted in 556,000 deaths up from 341,000 deaths in 1990.[3] They are the second most common cause of death from unintentional injuries after motor vehicle collisions.[28] They were the most common cause of injury seen in emergency departments in the United States. One study found that there were nearly 7.9 million emergency department visits involving falls, nearly 35.7% of all encounters.[29]
See also
References
- ↑ "Fact sheet 344: Falls". World Health Organization. October 2012. Retrieved 3 December 2012.
- ↑ Global Burden of Disease Study 2013, Collaborators (22 August 2015). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.". Lancet (London, England). 386 (9995): 743–800. PMC 4561509
 . PMID 26063472. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(15)60692-4.
. PMID 26063472. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(15)60692-4. - 1 2 GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators (17 December 2014). "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.". Lancet. 385: 117–71. PMC 4340604
 . PMID 25530442. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2.
. PMID 25530442. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. - ↑ Talbot, L. A., Musiol, R. J., Witham, E. K., & Metter, E. J. (2005). Falls in young, middle-aged and older community dwelling adults: perceived cause, environmental factors and injury. BMC public health, 5(1), 86.
- ↑ Gillespie, L. D. (2013). Preventing falls in older people: the story of a Cochrane review. Cochrane database of systematic reviews, 3, ED000053-ED000053.
- ↑ Yoshikawa, T. T., Cobbs, E. L., & Brummel-Smith, K. (1993). Ambulatory geriatric care. Mosby Inc.
- ↑ O'Loughlin, J. L., Robitaille, Y., Boivin, J. F., & Suissa, S. (1993). Incidence of and risk factors for falls and injurious falls among the community-dwelling elderly. American journal of epidemiology, 137(3), 342-354
- ↑ Winter DA, Patla AE, Frank JS, Walt SE. Biomechanical walking pattern changes in the fit and healthy elderly. Phys Ther. 1990;70(6):340–347.
- ↑ Elble RJ, Thomas SS, Higgins C, Colliver J. Stride-dependent changes in gait of older people. J Neurol. 1991;238(1):1–5
- ↑ Snijders AH, van de Warrenburg BP, Giladi N, Bloem BR. Neurological gait disorders in elderly people: clinical approach and classification. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6(1):63–74.
- ↑ Tsur, A., & Segal, Z. (2010). Falls in stroke patients: risk factors and risk management. IMAJ-Israel Medical Association Journal, 12(4),216
- ↑ Vivian Weerdesteyn PhD, P. T., de Niet MSc, M., van Duijnhoven MSc, H. J., & Geurts, A. C. (2008). Falls in individuals with stroke. Journal of rehabilitation research and development, 45(8), 1195.
- ↑ C.W. Olanow, R.L. Watts, W.C. Koller An algorithm for the management of Parkinson's disease: treatment guidelines Neurology, 56 (11 Suppl 5) (2001), pp. S1–S88
- ↑ McNeely, M. E., Duncan, R. P., & Earhart, G. M. (2012). Medication improves balance and complex gait performance in Parkinson disease. Gait & posture, 36(1), 144-148.
- ↑ Finlayson, M. L., Peterson, E. W., & Cho, C. C. (2006). Risk factors for falling among people aged 45 to 90 years with multiple sclerosis. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation, 87(9), 1274-1279.
- ↑ Severini, G., Manca, M., Ferraresi, G., Caniatti, L. M., Cosma, M., Baldasso, F., ... & Basaglia, N. (2017). Evaluation of Clinical Gait Analysis parameters in patients affected by Multiple Sclerosis: Analysis of kinematics. Clinical Biomechanics.
- ↑ D. Cattaneo, C. De Nuzzo, T. Fascia, M. Macalli, I. Pisoni, R. Cardini Risks of falls in subjects with multiple sclerosis Arch Phys Med Rehabil, 83 (2002), pp. 864–867
- ↑ L.B. Krupp, C. Christodoulou Fatigue in multiple sclerosis Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep, 1 (2001), pp. 294–298
- 1 2 3 "Preventing Slips, Trips, and Falls in Wholesale and Retail Trade Establishments" (Press release). DHHS (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) Publication No. 2013-100. October 2012. Retrieved 7 January 2013.
- ↑ "NIOSH Falls from Elevations". United States National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Retrieved 4 November 2007.
- ↑ "STRATEGIC PRECAUTIONS AGAINST FATAL FALLS ON THE JOB ARE RECOMMENDED BY NIOSH" (Press release). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. 2 January 2001. Retrieved 4 November 2007.
- ↑ "Census of Fatal Occupational Injuries, 2011" (PDF). US Bureau of Labor Statistics, US Department of Labor. Retrieved 7 January 2013.
- 1 2 Atanasijević, T; Nikolić, S; Djokić, V (2004). "Level of total injury severity as a possible parameter for evaluation of height in fatal falls". Srpski arhiv za celokupno lekarstvo. 132 (3–4): 96–8. PMID 15307311. doi:10.2298/sarh0404096a.
- ↑ Barlow, B.; Niemirska, M.; Gandhi, R. P.; Leblanc, W. (1983). "Ten years of experience with falls from a height in children". Journal of pediatric surgery. 18 (4): 509–511. PMID 6620098. doi:10.1016/S0022-3468(83)80210-3.
- ↑ Martinez, F; Tobar, C; Hill, N (March 2015). "Preventing delirium: should non-pharmacological, multicomponent interventions be used? A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature.". Age and ageing. 44 (2): 196–204. PMID 25424450. doi:10.1093/ageing/afu173.
- ↑ Vlaeyen, E; Coussement, J; Leysens, G; Van der Elst, E; Delbaere, K; Cambier, D; Denhaerynck, K; Goemaere, S; Wertelaers, A; Dobbels, F; Dejaeger, E; Milisen, K; Center of Expertise for Fall and Fracture Prevention, Flanders (February 2015). "Characteristics and effectiveness of fall prevention programs in nursing homes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.". Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 63 (2): 211–21. PMID 25641225. doi:10.1111/jgs.13254.
- ↑ "WHO Disease and injury country estimates". World Health Organization. 2009. Retrieved 11 November 2009.
- ↑ Lozano, R; Naghavi, M; Foreman, K; Lim, S; Shibuya, K; Aboyans, V; Abraham, J; Adair, T; et al. (15 December 2012). "Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010". Lancet. 380 (9859): 2095–128. PMID 23245604. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0.
- ↑ Villaveces A, Mutter R, Owens PL, Barrett ML. "Causes of Injuries Treated in the Emergency Department, 2010". HCUP Statistical Brief #156. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. May 2013. Retrieved 27 June 2013.
External links
- Falls Among Older Adults: Brochures and Posters (in English, Spanish, and Chinese) US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Falls Among Older Adults: An Overview US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Costs of Falls Among Older Adults US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Hip Fractures Among Older Adults US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Falls in Nursing Homes US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- CDC Fall Prevention Activities US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Preventing Falls: What Works―A CDC Compendium of Effective Community-based Interventions from Around the World US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (PDF)
- Preventing Falls: How to Develop Community-based Fall Prevention Programs for Older Adults US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Public Health Grand Rounds: Help Older Adults Live Better, Longer: Prevent Falls and Traumatic Brain Injuries US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- CDC's Division of Unintentional Injury – Podcasts US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention