Eyke
| Eyke | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Population | 362 (2011 Census) |
| OS grid reference | TM 31702 51796 |
| Civil parish |
|
| District |
|
| Shire county |
|
| Region | |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | Woodbridge |
| Dialling code | 01394 |
| Police | Suffolk |
| Fire | Suffolk |
| Ambulance | East of England |
| EU Parliament | East of England |


Eyke is a village and a civil parish in the Suffolk Coastal District, in the English county of Suffolk. It is located on the A1152 road near the town of Woodbridge. Eyke has a primary school, the manor house of Lord and Lady Lucas with scenic pond and horse paddock, and a pub. The mediaeval parish church of All Saints was restored in the 1860s. Services are normally held on the first and third Sundays of the month. The Eyke Parish Council "consists of seven parish Councillors." and they hold regular meetings "on the second Monday of every other month, at 7 pm " these are held in the Eyke village hall. From the Vision of Britain website, a 19th-century description described Eyke like this "Eyke, a village and a parish in Plomesgate district, Suffolk. The village stands near the river Deben, 1½ mile ENE of Melton r. station, and 3 NE by E of Woodbridge; and has a post office under Woodbridge. The parish comprises 2, 749 acres. Pop., 486. Houses, 109, the population reducing to 362 at the 2011 Census.[1] The church is Norman, has a brass of the 15th century, and was repaired in 1859."[2]
A brief history of early Eyke
The name 'Eyke' previously derived from the world 'Oak' had a number of changes and various spellings to its name, some earlier names for the small settlement where "Eike, Ike, Yke, Eyck, as it has been variously spelt." Eyke was first mentioned during the reign of Henry II, "when the King held Staverton Manor from 1171–1185. Adam de Eik had to pay a fine of three marks" but for what, this is not known. Eyke has quite a strong history of revolt and rebelling against authority figures within the local community. one account of this was during the year of "1310" when "they attacked the Manor House of Eyke Rectory, burst open the gates and rifled a chest, in order to destroy the records of the services due to Robert de Redenhale." Thirty-one years later, in the June 1381, there was a peasants' revolt: "they broke down the home of John Staverton, destroyed various records and carried away booty to the value of 100 shillings." Whether this was politically sparked of just a mindless act of theft is unclear. It was reputed that in "In 1589, 1590 and 1591, Eyke people were fined because they persisted in wearing German felt hats on festivals and Sundays instead of the English hats made of pile." The last reported act of rebellion from this time period was yet again in relation to "John Staverton", where in "1644 some testified against John Stoneham, the rector, for the way he conducted the church services and his behaviour generally". There is no recorded evidence that any sort of resolution came from this testimony. Eyke has been mostly dependent on agriculture and its related trades; they seemed to be generally quite a self-sufficient village. It is recorded that up until the First World War "there were six separate farms, and several small holdings. In addition, most families kept chickens and a pig, and grew their own vegetables." Other local trades and businesses included "two shoemakers, a blacksmith, a hurdlemaker, a thatcher, a builder and a carpenter/wheelwright who was also the undertaker". The majority of the land the farms where located on where reported to be "part of the Rendlesham Estate until it was sold in 1920."[3]
Eyke population through time
The first detailed census data that has been recorded for the Civil Parish of Eyke was in 1801; this shows that the population at the time was 308. The population continued to rise at a steady pace: in 1811 the population was 337 and in 1821 it was recorded at 396. However, in 1831 the population of Eyke had grown significantly in the last ten years since the last census was taken. In 1831 the population had grown by almost 100 people; it now stood at 485,[4] a significant increase compared to previous years. According to "Dr Marjorie Bloy" he estimated that there was a "population increase between 1801–31 was as much as 50%" in England; this could explain the sudden population boom. One could assume another reason for the increased population could have been due to: during this time period, children where seen as an economic asset; this would therefore encourage increased reproduction.[5] In 1851 Eyke reached its highest recorded population at 529. Even to this day it has not exceeded that number. However, once again there was a significant change in the population. The next recorded census was only thirty years later in 1881, and here it shows us that the population has dropped by 149 people between 1851 and 1881. You could speculate that this could have been due to the 1954 Cholera outbreak that occurred throughout England, as there is no significant boundary change or any other aspects that could have caused such a dramatic drop in the population. After this dramatic drop the population once again grew to 489. However, from 1891 onwards the population continued to decline at a relatively steady rate up until the 1960s, where it was 280.[6] "It had a population of 362 according to the 2011 Census"[7] Comparing this to the Suffolk Coastal region where the population is "124,298"[8] This shows us that Eyke holds only 0.29% of the population of Suffolk in 2011.
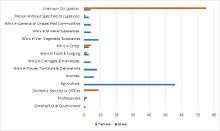
Occupational structure in 1881
The occupational structure of Eyke in 1881, the graph shows us the number of occupational orders in both the male and female sector in 1881. The first notable differences the data suggests is the number of females in the Domestic services which is "9” compared to the men "0”. This is as expected as during this time period. Women tended to be employed to care for the children and look after the general upkeep of a household, either by being employed as a maid, servant or similar occupation. If you compare this number "9" to the total female population in 1881 "179" you could assume the general houses of Eyke were not that large, as the majority of households did not have the need to employ persons in the domestic services. Agriculture was the leading employer in 1881 with "56 males" employed within this sector and "0" Females. This was due to agriculture being a manual labour-intensive job, and you can assume from the data this would have discouraged females from both wanting and being employed in this field.[9] If we compare the 1881 data to modern day data from 2011 you can see that employment in the agricultural sector has decreased significantly. According to the 2011 Census data there are as little as "18" people employed with in "agriculture or agriculture related trades". This suggests that the majority of the population have moved away from conventional employment and moved towards modern day jobs, this could be assumed to be due to the rise in technology with better-paying and less labour-intensive jobs available. It can be seen from the 2011 Census data that this could be true as the highest sector for employment is now "Managers, Directors and Senior Officials" at "27" Another assumption could be due to a higher range and more diversity of jobs available.
Coordinates: 52°06′N 1°23′E / 52.100°N 1.383°E
Housing in Eyke
From looking at the 2011 Census data we can see there are a total of "154" houses holds in Eyke, these range from people living on their own to groups and family. We can presume that the Area of Eyke is generally well-off, as "81" out of the "154" households are detached houses and "52" semi-attached. there no recorded shared dwellings and only "1" recorded "Caravan or Other Mobile Temporary Structure" By looking at the General health of the people of Eyke as according to the 2011 Census data, the majority of the population are either in "good health or very good health" with ""192" in very good health and "114" in good health.[10] This data suggests that overall Eyke has good public health and therefore you can assume a good level of health services are available. This often helps "create a happier community and strengthens social relationships"[11] within the Civil Parish.
All Saints Church
"The church is a Norman structure of the 12th century, and is dedicated to All Saints"[12] The Church was "founded in 1538."[13] From Suffolk Churches, an online journey though the churches of Suffolk one travellers account of the All Saints Church in Eyke was this, "All Saints sits quietly, with no tower to lead you to it from afar. At first sight, this is a simple, if uneven, little church, somewhat barnlike in its ancient graveyard. Tall elm trees around it are home to jackdaws and rooks; their cries fill the air as they wheel above you. The modern little porch gives no indication that you are about to enter one of the more interesting churches in this part of Suffolk." Sam' Mortlock a former Norfolk county librarian argues that "All Saints was probably a cruciform church."[14] Cruciform churches were common in the Middle Ages and "Generally form the shape of a latin cross they are formed through the intersection of two halls of similar heights that meet at right angles."[15] When the church was originally built by "the Manor of Staverton" it was valued at the price of "£6.00, which works out at 2d an acre."[16]
References
- ↑ "Parish population 2011". Retrieved 15 September 2015.
- ↑ Wilson, John. "Eyke Suffolk Location". http://www.visionofbritain.org.uk. Retrieved 13 April 2015. External link in
|website=(help) - ↑ Hatcher, Phyllis. "Our Village". http://eyke.onesuffolk.net. Eyke Millennium Group. Retrieved 9 March 2015. External link in
|website=(help) - ↑ "Total Population, A Vision of Britain through Time.". http://www.visionofbritain.org.uk. Retrieved 14 April 2015. External link in
|website=(help) - ↑ Bloy, Marjorie. "Population Growth in the Age of Peel". http://www.historyhome.co.uk. Retrieved 14 April 2015. External link in
|website=(help) - ↑ "Eyke through time Total Population". http://www.visionofbritain.org.uk. Retrieved 14 April 2015. External link in
|website=(help) - ↑ "Eyke (Parish) key figures for 2011 Census: Key Statistics". Neighbourhood Statistics. Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ↑ "Key Figures for 2011 Census: Key Statistics (Eyke)". www.neighbourhood.statistics.gov.uk. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ↑ "1881 Occupational Orders". http://www.visionofbritain.org.uk. GB Historical GIS / University of Portsmouth. Retrieved 23 March 2015. External link in
|website=(help) - ↑ "General Health, 2011". https://neighbourhood.statistics.gov.uk. Retrieved 15 April 2015. External link in
|website=(help) - ↑ "HEALTHY VILLAGES: A GUIDE FOR COMMUNITIES AND COMMUNITY HEALTH WORKERS" (PDF). http://www.who.int/. Retrieved 15 April 2015. External link in
|website=(help) - ↑ "Eyke". GENUKI UK and Ireland Genealogy. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ↑ "All Saints, Eyke- Church of England". http://www.genuki.org.uk/. Retrieved 6 February 2015. External link in
|website=(help) - ↑ Knott, Simon. "All Saints, Eyke". www.suffolkchurches.co.uk. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ↑ "CRUCIFORM" (PDF). http://www.heritagetrust.on.ca. Retrieved 8 February 2015. External link in
|website=(help) - ↑ Hatcher, Phyllis. "Our Village". http://eyke.onesuffolk.net. Retrieved 9 March 2015. External link in
|website=(help)