European Theater of Operations, United States Army
| European Theater of Operations, United States Army (ETOUSA) | |
|---|---|
| Active | 1942–45 |
| Country |
|
| Branch |
|
| Type | Theater Army |
| Role | Headquarters |
| Part of |
War Department Allied Expeditionary Force |
| Nickname(s) | "ETOUSA" |
| Anniversaries | V-E Day (8 May) |
| Campaigns | World War II |
| Commanders | |
| Notable commanders |
Dwight D. Eisenhower Frank Andrews Jacob Devers |
The European Theater of Operations, United States Army (ETOUSA) was a United States Army formation which directed US Army operations in parts of Europe from 1942 to 1945. It referred to Army Ground Forces, United States Army Air Forces, and Army Service Forces operations north of Italy and the Mediterranean coast, in the European Theater of World War II. It was bordered to the south by the North African Theater of Operations, US Army (NATOUSA), which later became the Mediterranean Theater of Operations (MTOUSA).
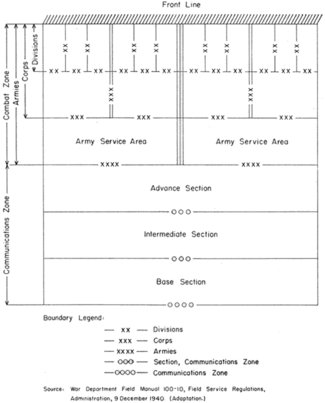
The term theater of operations was defined in the US Army field manuals as the land and sea areas to be invaded or defended, including areas necessary for administrative activities incident to the military operations. In accordance with the experience of World War I, it was usually conceived of as a large land mass over which continuous operations would take place and was divided into two chief areas-the combat zone, or the area of active fighting, and the Communications Zone, or area required for administration of the theater. As the armies advanced, both these zones and the areas into which they were divided would shift forward to new geographic areas of control.[1]
History
British–American military staffs agreed during their meetings in Washington in January–March 1941 (the ABC-1 Conversations) to exchange military missions to facilitate planning for the eventuality of American entry in the war.[2] Major General James E. Chaney, an Army Air Corps officer, arrived in the United Kingdom on 18 May 1941, and on the following day, Headquarters, Special Observer Group (SPOBS), was established in London.[3] SBOPS also had the role of studying British use of Lend Lease supplies. His formal title was the Special Army Observer in the United Kingdom and head of SPOBS. After the United States entered the war, SPOBS was succeeded by United States Army Forces in the British Isles (USAFBI), actually SPOBS under a new name. At the time of the ARCADIA Conference, December 1941 – January 1942, the decision was made to place the MAGNET forces (U.S. Forces for Northern Ireland) under the command of Maj. Gen. E.L. Daley, and make him in turn responsible to General Chaney, designated as CG, USAFBI. On 5 May 1942, Maj. Gen. John C. H. Lee became Commanding General, Services of Supply, U.S. Army Forces British Isles, and later deputy theater commander, ETOUSA.[4] On 8 June 1942, the United States Department of War officially established ETOUSA in its place. Its mission was to conduct planning for the eventual retaking of Europe and to exercise administrative and operational control over U.S. forces.
The 133rd Infantry Regiment of the 34th Infantry Division was the first United States Army unit sent to Europe in World War II. The first battalion arrived in Belfast in late January 1942, followed by the rest of the regiment in February. These units were designated as U.S. Army Northern Ireland Forces, later incorporated within the European Theater of Operations. The 133rd and 168th Infantry Regiments trained in the peat bogs, and performed border guard patrols between British Northern Ireland and the neutral Irish Free State. The remaining unit of the division, the 135th Infantry Regiment, arrived in May 1942.
From February 1944 the operational command was the Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force (SHAEF) which as an Allied command also had operational control of British and all other allied land forces and tactical airforces in the European theatre. Until SHAEF was operational ETOUSA liaised closely with the British in the planning and organising of Operation Overlord.
U.S. General Dwight D. Eisenhower had multiple command appointments; he replaced Chaney in late June 1942, but in November he also commanded the Allied forces in Operation Torch through AFHQ. He then relinquished command of ETOUSA to Lt. Gen. Frank M. Andrews in February 1943, who was killed in an air crash in May. He was replaced by Lt. Gen. Jacob L. Devers, former Chief of the Armored Force. In December 1943 it was announced that Eisenhower would be Supreme Allied Commander in Europe. In January 1944 he resumed command of ETOUSA and the following month was officially designated as the Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionary Forces. (Note that Supreme Headquarters of the Allied Expeditionary Forces (SHAEF) was the headquarters of the Commander of the Allied Expeditionary Forces, whereas the AFHQ was the headquarters of only the Allied forces.) He served in a dual role until the end of hostilities in Europe in May 1945. From February 1944, SHAEF was the operational command and ETOUSA administrative command.
Some units were transferred between operational commands and administrative commands at different times. For example, the American 6th Army Group, which was set up under the Mediterranean Theater of Operations to oversee Operation Dragoon, the invasion of Southern France between Toulon and Cannes, was passed to SHAEF (and into ETO) a month after the invasion which took place on 15 August 1944.
By the end of 1944, Eisenhower, through SHAEF, commanded three powerful Allied army groups. In the north British 21st Army Group commanded by Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery ("Monty"), in the middle the American 12th Army Group commanded by General Omar N. Bradley, and in the South the American 6th Army Group commanded by Devers. The British 21st Army Group and French elements of the 6th Army Group were not part of ETOUSA, but by that stage of the war most of the operational forces under the command of SHAEF were American.
The ETOUSA planning staff in London was usually referred to by its Army Post Office number, "APO 887". After the war in Europe ended, ETOUSA became briefly U.S. Armed Forces Europe, then U.S. Forces, European Theater (USFET), and then, eventually, United States Army Europe.
Campaigns and operations
Operation Torch—the invasion of French North Africa—involving the 9th, 3rd Infantry and the 2nd Armored Divisions, initiated on 8 November 1942, was the first ground combat operations for the United States in World War II.[5]
Albert Coady Wedemeyer was chief author of the Victory Program, published three months before the U.S. entered the war in 1941, which advocated the defeat of the German armies on the European continent. When the U.S. entered the war after the Japanese bombed Pearl Harbor on 7 December 1941 and the U.S. was at war with both Japan and Germany, a "Europe first" a modified version of his plan was adopted by U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt and British Prime Minister Winston Churchill. Under the German first policy, the plan was expanded to include the blueprint for the Normandy landings.
- List of air operations during the Battle of Europe 1 September 1939 – 7 May 1945
- Normandy Campaign 6 June 1944 – 24 July 1944
- Northern France Campaign 25 July 1944 – 14 September 1944
- Southern France Campaign
- Rhineland Campaign
- Lorraine Campaign (unofficial) 1 September 1944 – 18 December 1944
- Ardennes–Alsace Campaign 16 December 1944 – 25 January 1945 ("Battle of the Bulge")
- Central Europe Campaign 22 March 1945 – 11 May 1945
See also
- China Burma India Theater of Operations
- Mediterranean Theater of Operations
- Pacific Theater of Operations
- United States Army Europe
Notes
- ↑ Blanche B. Armfield, M.A., Prepared and published in 1963 under the direction of Lieutenant General Leonard D. Heaton The Surgeon General, United States Army. "Medical department United States Army in World War II: Chapter VII: Prewar Army Doctrine for Theater". history.amedd.army.mil.
- ↑ Ray S. Cline, Washington Command Post: The Operations Division, Appendix B: U.S. Army Commanders in Major Theater Commands, December 1941 – September 1945, via HyperWar, accessed March 2012
- ↑ James E. Chaney 1908
- ↑ "CHAPTER XV Command Reorganization, June–October 1944". ibiblio.org.
- ↑ American "observers" had participated in the Dieppe Raid in August 1942
References
- "The European Theater of Operations". history.army.mil.
Further reading
- ORDER OF BATTLE OF THE UNITED STATES ARMY WORLD WAR II – EUROPEAN THEATER OF OPERATIONS. Office of the Theater Historian. Paris, France: Office of the Theater Historian Paris, France. December 1945. Retrieved 9 June 2010.