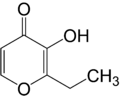
Ethyl maltol
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Ethyl-3-hydroxy-4-pyranone | |
| Other names
2-Ethyl pyromeconic acid, 2-ethyl-3-hydroxy-4-pyrone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.023.256 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 140.14 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 85 to 95 °C (185 to 203 °F; 358 to 368 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 161 °C (322 °F; 434 K) |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R22 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S36 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethyl maltol is an organic compound that is a common flavourant in some confectioneries. It is related to the more common flavorant maltol by replacement of the methyl group by an ethyl group.[2] It is a white solid with a sweet smell that can be described as caramelized sugar and cooked fruit.
The conjugate base derived from ethylmaltol, again like maltol, has a high affinity for iron, forming a red coordination complex. In such compounds, the heterocycle is a bidentate ligand.
References
- ↑ Ethyl maltol at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Erich Lück and Gert-Wolfhard von Rymon Lipinski "Foods, 3. Food Additives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi: 10.1002/14356007.a11_561
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.