1,2-Ethanedithiol
| | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethane-1,2-dithiol | |
| Other names
Dimercaptoethane 1,2-Ethanedithiol | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.958 |
| RTECS number | KI3325000 |
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H6S2 | |
| Molar mass | 94.19 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.123 g/cm³ |
| Melting point | −41 °C (−42 °F; 232 K) |
| Boiling point | 146 °C (295 °F; 419 K) 46 mmHg |
| Slightly sol | |
| Solubility in other solvents | Good solubility in most organic solvents |
| Acidity (pKa) | ~11 |
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.5589 (D-line, 25 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| EU classification (DSD) (outdated) |
Toxic (T) |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R10 R22 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S16 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 50 °C (122 °F; 323 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related thiols |
1,1-Ethanedithiol; Ethanethiol; 1,3-Propanedithiol; 1,2-Benzenedithiol; Thiophenol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
1,2-Ethanedithiol, also known as EDT[1], is a colorless liquid with the formula C2H4(SH)2. It has a very characteristic odor which is compared by many people to rotten cabbage. It is a common building block in organic synthesis and an excellent ligand for metal ions.
Preparation
1,2-Ethanedithiol is prepared commercially by the reaction of 1,2-dichloroethane with aqueous sodium bisulfide. In the laboratory, it can also be prepared by the action of 1,2-dibromoethane on thiourea followed by hydrolysis.[2]
Applications
As a 1,2-dithiol, this compound is widely used in organic chemistry because it reacts with aldehydes and ketones to give 1,3-dithiolanes, which are useful intermediates. [3]
- C2H4(SH)2 + RR'CO → C2H4S2CRR' + H2O
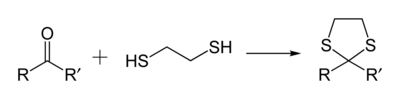
Other 1,2- and 1,3-dithiols undergo this reaction to give related 1,3-dithiolanes and 1,3-dithianes (six-membered rings). Diols such as ethylene glycol undergo analogous reactions to 1,3-dioxolanes and 1,3-dioxanes. One distinguishing feature of the dithiolanes and dithianes derived from aldehydes is that the methyne group can be deprotonated and the resulting carbanion alkylated.
1,2-Ethanedithiol is commonly used as a scavenger in peptide cleavage synthesis.
See also
References
- ↑ Choi, H.; Aldrich, J.v. (1993-07-01). "Comparison of methods for the Fmoc solid-phase synthesis and cleavage of a peptide containing both tryptophan and arginine". International Journal of Peptide and Protein Research. 42 (1): 58–63. ISSN 1399-3011. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3011.1993.tb00350.x.
- ↑ Speziale, A. J. (1963). "Ethanedithiol". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol., 4, p. 401
- ↑ R. E. Conrow "Ethanedithiol" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (Ed: L. Paquette) 2004, J. Wiley & Sons, New York. doi:10.1002/047084289
