Etelcalcetide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Parsabiv |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | UK Drug Information |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous injection |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Biological half-life | 3–5 days in dialysis patients |
| Excretion | 60% in dialysate, 7% in urine and faeces |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | Velcalcetide, telcalcetide, AMG-416, KAI-4169, ONO-5163 |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C38H73N21O10S2 |
| Molar mass | 1,048.26 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Etelcalcetide (formerly velcalcetide, trade name Parsabiv) is a calcimimetic drug for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients undergoing hemodialysis. It is administered intravenously at the end of each dialysis session.[1][2] Etelcalcetide functions by binding to and activating the calcium-sensing receptor in the parathyroid gland.[1]
Medical uses
Etelcalcetide is used for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on hemodialysis.[3] Hyperparathyroidism is the condition of elevated parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels and is often observed in patients with CKD.[4]
Contraindications
The drug is of course contraindicated in people with blood serum calcium levels below the norm.[3][5]
Side effects
Common side effects (in more than 10% of people) are nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, muscle spasms, and hypocalcaemia (too low blood calcium levels). In clinical studies, the latter side effect was usually mild to moderate and without symptoms. An increase of the QT interval of more than 60 ms was detected in 1.2% of people receiving etelcalcetide.[3][5]
Interactions
No interaction studies in humans were conducted. Studies in vitro showed no affinity of etelcalcetide to cytochrome P450 enzymes or common transport proteins. Therefore, no relevant pharmacokinetic interactions are expected.[3][5]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Etelcalcetide functions by binding to and activating the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) in the parathyroid gland as an allosteric activator, resulting in PTH reduction and suppression.[1]
Chemistry
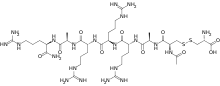
The substance is a peptide consisting mostly of D-amino acids instead of the common L-amino acids. More specifically, it is the disulfide of N-acetyl-D-cysteinyl-D-alanyl-D-arginyl-D-arginyl-D-arginyl-D-alanyl-D-argininamide with L-cysteine.[6]
History
On 25 August 2015 Amgen Inc. announced its submission of a new drug application to the Food and Drug Administration for etelcalcetide.[1] The European Medicines Agency approved the drug in November 2016.[3]
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Amgen Submits New Drug Application For Novel Intravenous Calcimimetic Etelcalcetide (AMG 416)”
- ↑ Martin, K. J.; Bell, G; Pickthorn, K; Huang, S; Vick, A; Hodsman, P; Peacock, M (2014). "Velcalcetide (AMG 416), a novel peptide agonist of the calcium-sensing receptor, reduces serum parathyroid hormone and FGF23 levels in healthy male subjects". Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 29 (2): 385–92. PMC 3910343
 . PMID 24235081. doi:10.1093/ndt/gft417.
. PMID 24235081. doi:10.1093/ndt/gft417. - 1 2 3 4 5 "Parsabiv: EPAR – Product Information" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. 24 November 2016.
- ↑ Wu, Q; Lai, X; Zhu, Z; Hong, Z; Dong, X; Wang, T; Wang, H; Lou, Z; Lin, Q; Guo, Z; Chai, Y (2015). "Evidence for Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder Associated With Metabolic Pathway Changes". Medicine. 94 (32): e1273. PMC 4616673
 . PMID 26266360. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000001273.
. PMID 26266360. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000001273. - 1 2 3 Haberfeld, H, ed. (2016). Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag.
- ↑ "Etelcalcetide". ChemSpider. Retrieved 7 January 2016.