Employment-to-population ratio

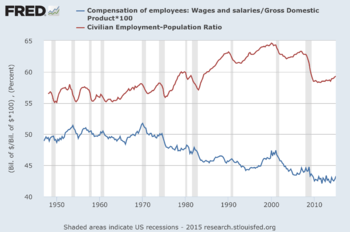
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development defines the employment rate as the employment-to-population ratio. This is a statistical ratio that measures the proportion of the country's working age population (statistics are often given for ages 15 to 64[1][2]) that is employed. This includes people that have stopped looking for work.[3] The International Labour Organization states that a person is considered employed if they have worked at least 1 hour in "gainful" employment in the most recent week.[4]
Background
The employment-population ratio has not always been looked at for labor statistics and where specific areas are economically, but after the recent recession it has been given more attention worldwide, especially by economists. The National Bureau Of Economic Research (NBER) states that the Great Recession ended in June 2009.[5] During 2009 and 2010, however, many areas were still struggling economically, which is the reason the employment-population ratio is still used by both Americans and people around the world.
Key definitions

Key terms that explain the use of the ratio follow:
Employed persons. All those who, (1) do any work at all as paid employees, work in their own business or profession or on their own farm, or work 15 hours or more as unpaid workers in a family-operated enterprise; and (2) all those who do not work but had jobs or businesses from which they were temporarily absent due to illness, bad weather, vacation, childcare problems, labor dispute, maternity or paternity leave, or other family or personal obligations — whether or not they were paid by their employers for the time off and whether or not they were seeking other jobs.
Unemployed persons. All those who, (1) have no employment during the reference week; (2) are available for work, except for temporary illness; and (3) have made specific efforts, such as contacting employers, to find employment sometime during the past 4-week period.
Participant rate This represents the proportion of the population that is in the labor force.
Not in the labor force. Included in this group are all persons in the civilian noninstitutional population who are neither employed nor unemployed. Information is collected on their desire for and availability to take a job at the time of the CPS interview, jobsearch activity in the prior year, and reason for not looking for work in past 4-week period.
Multiple jobholders. These are employed persons who, have two or more jobs as a wage and salary worker, are self-employed and also held a wage and salary job, or work as an unpaid family worker and also hold a wage and salary job.
Use
The ratio is used to evaluate the ability of the economy to create jobs and therefore is used in conjunction with the unemployment rate for a general evaluation of the labour market stance. Having a high ratio means that an important proportion of the population in working age is employed, which in general will have positive effects on the GDP per capita. Nevertheless, the ratio does not give an indication of working conditions, number of hours worked per person, earnings or the size of the black market. Therefore, the analysis of the labour market must be done in conjunction with other statistics.
This measure comes from dividing the civilian noninstitutionalized population who are employed by the total noninstitutionalized population and multiplying by 100.[7]
Employment-to-population ratio in the world
In general, a high ratio is considered to be above 70 percent of the working-age population whereas a ratio below 50 percent is considered to be low. The economies with low ratios are generally situated in the Middle East and North Africa.
Employment-to-population ratios are typically higher for men than for women. Nevertheless, in the past decades, the ratios tended to fall for men and increase in the case of women, which made the differences between both to be reduced.
| Country | 1970 | 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | 66.7 | 65.2 | 68.4 | 69.3 | 69.0 | 69.4 | 70.0 | 70.3 | 71.5 | 72.2 | 72.9 | 73.2 | 72.0 | 72.4 | 72.7 | 72.4 | 72.0 |
| Austria | 68.3 | 68.2 | 68.8 | 68.9 | 67.8 | 68.6 | 70.2 | 71.4 | 72.1 | 71.6 | 71.7 | 72.1 | 72.5 | 72.3 | |||
| Belgium | 54.4 | 60.9 | 59.7 | 59.9 | 59.6 | 60.3 | 61.1 | 61.0 | 62.0 | 62.4 | 61.6 | 62.0 | 61.9 | 61.8 | 61.8 | ||
| Canada | 66.1 | 70.3 | 70.9 | 70.8 | 71.4 | 72.2 | 72.5 | 72.4 | 72.8 | 73.5 | 73.6 | 71.5 | 71.5 | 72.0 | 72.2 | 72.5 | |
| Chile | 53.3 | 52.7 | 52.6 | 53.5 | 53.6 | 54.4 | 55.5 | 56.3 | 57.3 | 56.1 | 59.3 | 61.3 | 61.8 | 62.3 | |||
| Czech Republic | 65.2 | 65.3 | 65.7 | 64.9 | 64.2 | 64.8 | 65.3 | 66.1 | 66.6 | 65.4 | 65.0 | 65.7 | 66.5 | 67.7 | |||
| Denmark | 75.4 | 76.4 | 75.9 | 75.9 | 75.1 | 75.7 | 75.9 | 77.4 | 77.0 | 77.9 | 75.3 | 73.3 | 73.1 | 72.6 | 72.5 | ||
| Estonia | 78.2 | 61.0 | 61.4 | 62.0 | 62.8 | 62.9 | 64.2 | 67.9 | 69.2 | 69.7 | 63.5 | 61.0 | 65.2 | 67.2 | 68.5 | ||
| Finland | 70.4 | 70.7 | 74.7 | 67.5 | 68.3 | 68.3 | 67.9 | 67.8 | 68.5 | 69.6 | 70.5 | 71.3 | 68.4 | 68.3 | 69.2 | 69.5 | 68.5 |
| France | 60.8 | 61.7 | 62.7 | 62.9 | 64.0 | 63.7 | 63.7 | 63.6 | 64.3 | 64.8 | 64.0 | 63.9 | 63.9 | 63.9 | 64.1 | ||
| Germany | 66.9 | 65.2 | 64.1 | 65.6 | 65.8 | 65.3 | 64.6 | 65.0 | 65.5 | 67.2 | 69.0 | 70.2 | 70.4 | 71.2 | 72.6 | 72.8 | 73.3 |
| Greece | 54.8 | 55.9 | 55.6 | 57.5 | 58.7 | 59.4 | 60.1 | 61.0 | 61.4 | 61.9 | 61.2 | 59.6 | 55.6 | 51.3 | 49.3 | ||
| Hungary | 56.0 | 56.2 | 56.2 | 57.0 | 56.8 | 56.9 | 57.3 | 57.3 | 56.7 | 55.4 | 55.4 | 55.8 | 57.2 | 58.4 | |||
| Iceland | 84.6 | 84.6 | 82.8 | 84.1 | 82.8 | 84.4 | 85.3 | 85.7 | 84.2 | 78.9 | 78.9 | 79.0 | 80.2 | 81.8 | |||
| Ireland | 52.1 | 65.1 | 65.7 | 65.2 | 65.2 | 65.9 | 67.5 | 68.5 | 69.2 | 67.9 | 62.2 | 60.0 | 59.2 | 58.8 | 60.2 | ||
| Israel | 51.8 | 56.1 | 55.7 | 54.8 | 55.0 | 55.7 | 56.7 | 57.6 | 58.9 | 59.8 | 59.2 | 60.2 | 60.9 | 66.5 | 67.1 | ||
| Italy | 52.0 | 53.9 | 52.6 | 53.9 | 54.9 | 55.6 | 56.2 | 57.4 | 57.5 | 58.4 | 58.7 | 58.7 | 58.3 | 57.7 | 57.8 | 57.6 | 56.4 |
| Japan | 67.9 | 66.8 | 68.6 | 68.9 | 68.8 | 68.2 | 68.4 | 68.7 | 69.3 | 70.0 | 70.7 | 70.7 | 70.0 | 70.1 | 70.3 | 70.6 | 71.7 |
| Korea | 59.2 | 61.2 | 61.5 | 62.1 | 63.3 | 63.0 | 63.6 | 63.7 | 63.8 | 63.9 | 63.8 | 62.9 | 63.3 | 63.9 | 64.2 | 64.4 | |
| Luxembourg | 59.2 | 62.7 | 63.0 | 63.6 | 62.2 | 62.5 | 63.6 | 63.6 | 64.2 | 63.4 | 65.2 | 65.2 | 64.6 | 65.8 | 65.7 | ||
| Mexico | 60.1 | 59.4 | 59.3 | 58.8 | 59.9 | 59.6 | 61.0 | 61.1 | 61.3 | 59.4 | 60.3 | 59.8 | 61.3 | 61.0 | |||
| Netherlands | 54.5 | 61.8 | 72.1 | 72.6 | 73.0 | 71.6 | 71.1 | 71.5 | 72.5 | 74.4 | 75.9 | 75.6 | 74.7 | 74.9 | 75.1 | 74.3 | |
| New Zealand | 67.5 | 70.4 | 71.4 | 72.2 | 72.2 | 73.2 | 74.3 | 74.9 | 75.2 | 74.7 | 72.9 | 72.3 | 72.6 | 72.1 | 73.1 | ||
| Norway | 72.2 | 73.0 | 77.9 | 77.5 | 77.1 | 75.8 | 75.6 | 75.2 | 75.5 | 76.9 | 78.1 | 76.5 | 75.4 | 75.3 | 75.8 | 75.5 | |
| Poland | 55.0 | 53.5 | 51.7 | 51.4 | 51.9 | 53.0 | 54.5 | 57.0 | 59.2 | 59.3 | 58.9 | 59.3 | 59.7 | 60.0 | |||
| Portugal | 64.3 | 65.6 | 68.3 | 68.9 | 68.7 | 68.0 | 67.8 | 67.5 | 67.9 | 67.8 | 68.2 | 66.3 | 65.6 | 64.2 | 61.8 | 60.6 | |
| Slovak Republic | 56.8 | 56.9 | 56.9 | 57.7 | 57.0 | 57.7 | 59.4 | 60.7 | 62.3 | 60.2 | 58.8 | 59.5 | 59.7 | 59.9 | |||
| Slovenia | 63.4 | 62.6 | 65.3 | 66.0 | 66.6 | 67.8 | 68.6 | 67.5 | 66.2 | 64.4 | 64.1 | 63.3 | |||||
| Spain | 52.7 | 51.8 | 57.4 | 58.8 | 59.5 | 60.7 | 62.0 | 64.3 | 65.7 | 66.6 | 65.3 | 60.6 | 59.4 | 58.5 | 56.2 | 55.6 | |
| Sweden | 72.3 | 79.8 | 83.1 | 74.3 | 75.4 | 75.2 | 74.4 | 73.7 | 74.0 | 74.6 | 74.2 | 74.3 | 72.2 | 72.1 | 73.6 | 73.8 | 74.4 |
| Switzerland | 78.4 | 79.2 | 78.9 | 77.9 | 77.4 | 77.2 | 77.9 | 78.6 | 79.5 | 79.0 | 78.6 | 79.3 | 79.4 | 79.6 | |||
| Turkey | 54.5 | 48.9 | 47.8 | 46.7 | 45.5 | 44.1 | 44.4 | 44.6 | 44.6 | 44.9 | 44.3 | 46.3 | 48.4 | 48.9 | 49.5 | ||
| United Kingdom | 72.5 | 72.2 | 72.5 | 72.3 | 72.6 | 72.7 | 72.7 | 72.6 | 72.4 | 72.7 | 70.6 | 70.3 | 70.4 | 70.9 | 71.3 | ||
| United States | 57.4[8] | 59.2[8] | 62.8[8] | 74.1 | 73.1 | 71.9 | 71.2 | 71.2 | 71.5 | 72.0 | 71.8 | 70.9 | 67.6 | 66.7 | 66.6 | 67.1 | 67.4 |
| Brazil | 64.3 | 65.4 | 65.0 | 66.5 | 67.0 | 67.4 | 67.4 | 68.3 | 67.7 | 66.9 | 67.2 | 66.7 | |||||
| China | 79.3 | 75.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Colombia | 57.5 | 57.0 | 58.5 | 57.5 | 58.1 | 56.7 | 56.9 | 58.9 | 60.2 | 61.4 | 62.5 | 62.7 | |||||
| India | 54.8 | 53.3 | |||||||||||||||
| Russian Federation | 63.3 | 63.2 | 64.5 | 64.1 | 65.5 | 66.3 | 66.8 | 68.5 | 68.6 | 66.9 | 67.3 | 68.0 | 69.0 | 68.8 | |||
| South Africa | 44.1 | 42.8 | 41.5 | 41.6 | 43.4 | 44.9 | 44.4 | 44.8 | 42.7 | 40.8 | 40.8 | 41.0 | 42.7 | ||||
| Latvia | 63.3 | 66.3 | 68.1 | 68.2 | 60.3 | 58.5 | 60.8 | 63.0 | 65.0 | ||||||||
| EU-21 | 61.0 | 59.5 | 61.7 | 62.6 | 63.0 | 63.0 | 63.2 | 63.5 | 64.1 | 64.9 | 65.9 | 66.4 | 65.2 | 64.8 | 65.0 | 64.8 | 64.8 |
| EU-15 | 61.0 | 59.5 | 61.6 | 63.6 | 64.3 | 64.4 | 64.6 | 65.0 | 65.5 | 66.3 | 67.0 | 67.4 | 66.1 | 65.8 | 65.9 | 65.6 | 65.4 |
| Europe | 61.0 | 59.7 | 60.9 | 61.3 | 61.5 | 61.3 | 61.2 | 61.4 | 61.9 | 62.7 | 63.4 | 63.9 | 62.8 | 62.7 | 63.1 | 63.0 | 63.0 |
| G7 Countries | 63.9 | 65.2 | 67.7 | 69.0 | 68.9 | 68.3 | 68.2 | 68.4 | 68.7 | 69.3 | 69.7 | 69.5 | 67.7 | 67.3 | 67.5 | 67.9 | 68.2 |
| OECD Countries | 64.2 | 64.2 | 65.7 | 65.4 | 65.2 | 64.9 | 64.7 | 65.0 | 65.3 | 66.0 | 66.5 | 66.5 | 64.8 | 64.6 | 64.8 | 65.1 | 65.3 |
| Country | 1970 | 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 |
Source: OECD.StatExtracts, except as noted
See also
- Dependency ratio
- Female labor force in the Muslim world
- Labor-force participation rate
- List of countries by employment rate
References
- ↑ OECD. "LFS by sex and age – indicators".
- ↑ "File:Employment rates for selected population groups, 2004–14 (%) YB16.png – Statistics Explained".
- ↑ Employment/Population Ratios for the 50 Largest Metropolitan Statistical Areas: 2008, 2009, and 2010. (2011, September). Retrieved December 10, 2012, from United States Census Bureau website: http://www.census.gov/prod/2011pubs/ acsbr10-09.pdf
- ↑ OECD Factbook 2007 (pdf), Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, 2007, ISBN 978-92-64-02946-0, retrieved 2008-01-31
- ↑ Employment/Population Ratios for the 50 Largest Metropolitan Statistical Areas: 2008, 2009, and 2010. (2011, September). Retrieved December 10, 2012, from United States Census Bureau website: http://www.census.gov/prod/2011pubs/ acsbr10-09.pdf
- ↑ BLS Handbook Of Methods. (2003, April 17). Retrieved December 6, 2012, from Bureau Of Labor Statistics website: http://www.bls.gov/opub/hom/ homch1_c.htm
- ↑ Employment/Population Ratios for the 50 Largest Metropolitan Statistical Areas: 2008, 2009, and 2010. (2011, September). Retrieved December 10, 2012, from United States Census Bureau website: http://www.census.gov/prod/2011pubs/ acsbr10-09.pdf
- 1 2 3 http://data.bls.gov/timeseries/LNS12300000