Embraer ERJ 145 family
| ERJ 145 family ERJ 135/ERJ 140/ERJ 145 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| An ERJ-145 of Air France Régional | |
| Role | Twin-engine Regional airliner |
| National origin | Brazil |
| Manufacturer | Embraer |
| First flight | August 11, 1995 |
| Introduction | April 6, 1997 |
| Status | In service |
| Primary users | CommutAir ExpressJet Airlines Envoy Air Trans States Airlines Piedmont Airlines |
| Produced | 1989–present 2003-2016 (China) |
| Number built | 890 as of January 2012[1] |
| Developed from | Embraer EMB 120 Brasilia |
| Variants | R-99 and P-99 Embraer Legacy 600 |
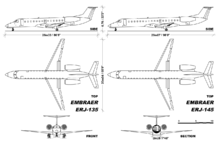
The Embraer ERJ 145 family[lower-alpha 1] is a series of twin-engine regional jets produced by Embraer, a Brazilian aerospace company. Family members include the ERJ 135 (37 passengers), ERJ 140 (44 passengers), and ERJ 145 (50 passengers), as well as the Legacy business jet and the R-99 family of military aircraft. The ERJ 145 is the largest of the group. Each jet in the series is powered by two turbofan engines. The family's primary competition comes from the Bombardier CRJ regional jets.
Development
The ERJ-145 was designed for a perceived new market for regional jet aircraft, where the increased speed, comfort and passenger appeal would outweigh the inherent fuel economy of the turboprop aircraft which were in service and in development.[2] In order to reduce the development cost, it used the EMB120 nose and the same fuselage cross-section.[2]
Early design
The ERJ 145 was launched at the Paris Airshow in 1989 as a stretched and turbofan-powered modification of the EMB 120 Brasilia. Key components of this design included:
- Straight wing (with winglets)
- Rear Fuselage-mounted engines
- Range of 2500 km (1550 miles).
- 75% parts commonality with the EMB 120.
Interim design




By 1990, Embraer engineers found that results from wind-tunnel testing were less than satisfactory, and began considering a significantly different design from the EMB 120. The proposed modified design included a slightly (22.3°) swept wing with winglets, as well as engines mounted in underwing nacelles. This second design showed markedly better aerodynamic performance, but the combination of swept wings and wing-mounted engines required an unusually high (and therefore heavy) undercarriage.[3]
Production design
The design evolved until late 1991, at which time it was frozen. Though the aircraft went through many alterations before it was finalized, it did retain a few of the original influences of the EMB 120 such as the three abreast seating (2+1) configuration which was a similar configuration used for the Embraer/FMA CBA 123 Vector design which never reached production. The key features of the production design included:
- Rear fuselage-mounted engines
- Swept wings (no winglets)
- "T"-tail configuration
- Range of 2500 km
The first design was intended to retain as much commonality as possible with the EMB 120. However, the aircraft has sold well thus overcoming the initial setbacks. Embraer delivered 892 units of all variants through 2006, and predicted that another 102 units would be delivered in the 2007-2016 time period.[4]
Derivatives
The ERJ 140 is based on the ERJ 145 with 96% parts commonality and the same crew type rating. The only significant changes are a shorter fuselage, a slightly derated engine and an increased range. At launch, Embraer estimated the cost of an ERJ 140 to be approximately US$15.2 million. The estimated cost of development of the ERJ 140 was US$45 million. The ERJ 135, with a service entry date of 1999, has 95% parts commonality with the ERJ 145, but is 11.7 feet (3.6 m) shorter.
The ERJ 145 seats 50 passengers, the ERJ 140 seats 44, and the ERJ 135 seats 37. The ERJ 140 was designed with fewer seats in order to meet the needs of some major United States airlines, which have an agreement with the pilots' union to limit the number of 50-seat aircraft that can be flown by their affiliates.
Production
In 2003, Embraer entered a partnership with the Harbin Aircraft Industry Group of Harbin, China. The resulting joint-venture company Harbin Embraer Aircraft Industry began producing the ERJ 145 for the Chinese market by assembling complete knock down kits prepared by other worldwide Embraer operations. After 13 years, its last delivery was done in March 2016; more than 40 ERJ-145 and 5 Embraer Legacy 650 were assembled.[5]
Design
Engine
The EMB-145 Family of aircraft generally come equipped with two Rolls-Royce AE 3007 series turbofan engines. The engines have a bypass ratio of 5:1. The engines are controlled by two FADECs (Full Authority Digital Engine Controls). The FADECs control virtually all aspects of the engine and send engine data to be displayed on the EICAS for the pilot.
Avionics
The Embraer ERJ 145 Family typically comes equipped with the Honeywell Primus 1000 Avionics suite. The suite normally consists of five CRT display units (DUs) or screens. From left to right, the system consists of a Primary Flight Display (PFD), Multi-Function Display (MFD), Engine Indication and Crew Alerting System (EICAS), Multi-Function Display (MFD) (Co-pilot) and Primary Flight Display (PFD) (Co-pilot). The DUs are normally CRTs but can be upgraded to lighter LCD displays. These upgraded DUs also have added functionality.
Operations
The first flight of the ERJ 145 occurred on August 11, 1995, with the first delivery in December 1996 to ExpressJet Airlines (then the regional division of Continental Airlines flying as Continental Express). ExpressJet is the largest operator of the ERJ 145, with 270 of the nearly-1,000 ERJ 145s in service. The second largest operator is Envoy Air, with 206 ERJ 145 aircraft. Trans States operates 47 ERJ 145s through alliances with United Express and Envoy Air. Chautauqua Airlines also operates 38 ERJ 145s through an alliance with Delta Connection.

By some accounts, the ERJ 145 has a cost of ownership of about $2,500,000 per year.
In March 2007 ExpressJet entered into a short-term agreement to operate some regional routes for JetBlue Airways using its ERJ 145 aircraft.
The ERJ 140 was introduced in September 1999, first flew on June 27, 2000 and entered commercial service in July 2001. Envoy Air, the regional jet subsidiary of American Airlines flying as American Eagle, operates the majority of the ERJ 140s built, including the first to be delivered (N800AE).
As of early 2005, 74 ERJ 140s had been delivered.
This version is marketed as ERJ 140, but on the company's internal documents and on Federal Aviation Administration certification, the version is designated EMB 135KL.
Variants
Civilian models

_Mar_2006.jpeg)

- ERJ 135ER - Extended range, although this is the Baseline 135 model. Simple shrink of the ERJ 145, seating thirteen fewer passengers, for a total of 37 passengers.
- ERJ 135LR - Long Range - increased fuel capacity and upgraded engines.
- ERJ 140ER - Simple shrink of the ERJ 145, seating six fewer passengers for a total of 44 passengers.
- ERJ 140LR - Long Range (increased fuel capacity (5,187 kg) and upgraded engines.
- ERJ 145STD - The baseline original, seating for a total of 50 passengers.
- ERJ 145EU - Model optimized for the European market. Same fuel capacity as 145STD (4,174 kg) but an increased MTOW[6] 19,990 kg
- ERJ 145ER - Extended Range, although this is the Baseline 145 model.
- ERJ 145EP - Same fuel capacity as 145ER (4,174 kg) but an increased MTOW 20,990 kg.
- ERJ 145LR - Long Range - increased fuel capacity (5,187 kg) and upgraded engines.
- ERJ 145LU - Same fuel capacity as 145LR (5,187 kg) but an increased MTOW 21,990 kg.
- ERJ 145MK - Same fuel capacity (4,174 kg), landing weight (MLW) and MTOW as in the 145STD, but a changed MZFW[7] (17,700 kg).
- ERJ 145XR - Extra-long Range (numerous aerodynamic improvements, including winglets, strakes, etc. for lower cruise-configuration drag; a ventral fuel tank (aft location) in addition to the two main larger capacity wing tanks (same tanks as in the LR models); increased weight capacity; higher top speed and up-rated engines.
- Legacy 600 (EMB 135BJ) - Business jet variant based on the ERJ 135.
- Legacy 650 (EMB 135BJ) - Business jet variant based on the ERJ 135.
- Harbin Embraer ERJ145 - joint venture with Harbin Aircraft Manufacturing Corporation
The physical engines are the same (Rolls-Royce AE 3007), however, the FADEC (Full Authority Digital Engine/Electronic Control) logic is what differs between the various models in regards to total thrust capability.
The extended range version, the ERJ 145ER, has Rolls Royce AE 3007A engines rated at 31.3 kN(7,036 lb) thrust, with the option of more powerful AE 3007A1 engines. A, A1, A1P models are mechanically identical but differ in thrust due to variations in FADEC software. The A1E engine, however, has not only new software, but significantly upgraded mechanical components.
The long-range ERJ 145LR aircraft is equipped with Rolls Royce AE 3007A1 engines which provide 15% more power. The engines are flat rated at 33.1 kN (7,440 lb) thrust to provide improved climb characteristics and improved cruise performance in high ambient temperatures.
The extra-long-range ERJ 145XR aircraft is equipped with Rolls-Royce AE 3007A1E engines. The high performance engines provide lower specific fuel consumption (SFC) and improved performance in hot and high conditions. The engines also yield a higher altitude for one-engine-inoperable conditions."[8] CommutAir and ExpressJet are the only two operators of the ERJ 145XR. February 2011 Embraer presented its new EMB-145 AEW&C for India.

Despite the multiple variants, pilots need only one type rating to fly any variant of the ERJ aircraft. Companies like American Eagle and ExpressJet Airlines utilize this benefit with their mixed fleet of ERJ135ER/LR and ERJ145EP/LR/XR. Shared type ratings allows operators to utilize a single pilot pool for any ERJ aircraft.
Military models
- C-99A - Transport model
- EMB 145SA (R-99A) - Airborne Early Warning model
- EMB 145RS (R-99B) - Remote sensing model
- EMB 145MP/ASW (P-99) - Maritime patrol model
Operators
Civilian operators
The main civilian operators, with ten units or more, as of May 2017 are:

.jpg)
- CommutAir: 13
- ExpressJet Airlines: 124
- Envoy Air: 109
- Trans States Airlines: 56
- Tianjin Airlines: 17
- Airlink: 21
- bmi Regional: 18
- Komiaviatrans: 6
- JETGO Australia: 5
- HOP!: 17
- Dniproavia: 15
- Novoair: 3
- TAR Aerolineas: 11
- Air Mandalay: 2
- Piedmont Airlines: 21
- Via Air: 6
Military operators

- Belgian Air Component (operates two ERJ 135 and two ERJ 145 since 2001 in passenger transport and VIP roles)
Notable accidents
The ERJ 145 family of aircraft has no reported crashes or fatalities due to mechanical malfunction in over 15 million hours (as of June 2009) of flight time for the fleet.[10]
- On February 11, 1998 a Continental Express ERJ-145ER registered N14931 crashed on takeoff at Jefferson County Airport in Beaumont, Texas during a training flight. The NTSB reported that after the incorrect application of rudder during a V1 cut maneuver, the left wing stalled. The aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
- On December 28, 1998, a Rio-Sul flight crew, approaching Curitiba, Brazil's Afonso Pena Airport, descended beyond the normal rates and landed at a speed significantly higher than the normal landing speed. The aircraft tail section cracked and was dragged along the runway.[11] The aircraft involved, an ERJ 145ER registered as PT-SPE, was damaged beyond economical repair.
- On September 29, 2006, an ExcelAire Embraer Legacy EMB 135BJ, Civil Registration N600XL[12], collided with Gol Transportes Aéreos Flight 1907, a Boeing 737-800, while flying over the northern state of Mato Grosso en route to Manaus from São José dos Campos. The Legacy made an emergency landing at Cachimbo Airport near Serra do Cachimbo, Pará, Brazil, with significant damage and with its 5 passengers and 2 crew members uninjured. The Gol 737 crashed in the Amazon forest east of Peixoto de Azevedo, killing all 148 passengers and 6 crew members.[13]
- On 7 December 2009, an ERJ 135 operated by South African Airlink (registration:ZS-SJW) on a scheduled flight SA-8625 from Cape Town, overshot the runway when trying to land in wet weather at George Airport; no fatalities were reported. It was determined that the aircraft touched down in the area of the fourth landing marker. According to the air traffic controller (ATC) on duty at the time, the landing appeared normal, however the aircraft did not vacate the runway but instead veered to the right and slid past the ILS localizer. The aircraft collided with eleven approach lights and burst through the aerodrome's perimeter fence; it came to rest in a nose-down attitude on a public road. A preliminary investigation showed that the landing gear tyres did display some evidence of aquaplaning. The plane was damaged beyond economical repair.
- On August 25, 2010, an ERJ 145 operated by Passaredo, crash-landed on approach to Vitória da Conquista. The plane touched-down short of the runway and the crew lost control, resulting in the aircraft sustaining severe damage before coming to a stop away from the runway. Two of the 27 people on board were injured. The airline said the plane was unable to lower landing gear, although observers said the landing gear was lowered while the aircraft was landing.[14]
- On September 4, 2011, a United Express Embraer 145 slid off the runway upon landing at Ottawa Macdonald–Cartier International Airport in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. All 44 passengers aboard were uninjured. The plane sustained substantial damage to its gear and wing on the right-hand side; it was damaged beyond economic repair.
Specifications
| Variant | ERJ135[15][16] | ERJ140[17][18] | ERJ145 LR[19][20]/ XR[21][22] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crew | 3 (2 pilots + flight attendant) | ||
| Seating | 37 | 44 | 50 |
| Length | 26.33 m (86 ft 5 in) | 28.45 m (93 ft 4 in) | 29.87 m (98 ft 0 in) |
| Wing span | 20.04 m (65 ft 9 in) | ||
| Height | 6.76 m (22 ft 2 in) | ||
| MTOW | ER: 19,000 kg (41,887 lb) LR: 20,000 kg (44,092 lb) |
ER: 20,100 kg (44,312 lb) LR: 21,100 kg (46,517 lb) |
LR: 22,000 kg (48,501 lb) XR: 24,100 kg (53,131 lb) |
| BOW | ER: 11,402kg / 25,137 lb LR: 11,501kg / 25,355lb |
ER: 11,816kg / 26,049 lb LR: 11,808kg / 26,032lb |
LR: 12,114kg / 26,706lb XR: 12,591kg / 27,758lb |
| Max payload | ER: 4,198 kg (9,255 lb) LR: 4,499 kg (9,918 lb) |
ER: 5,284 kg (11,649 lb) LR: 5,292 kg (11,666 lb) |
LR: 5,786 kg (12,755 lb) XR: 5,909 kg (13,027 lb) |
| Fuel capacity | ER: 5,146l / 1,359gal, LR: 6,396l / 1,690gal, XR: 7,438l / 1,965gal | ||
| Engines (2x) | ER: AE 3007-A3 / LR: -A1/3 | AE 3007-A1/3 | LR: AE 3007-A1 / XR: -A1E |
| Takeoff Thrust | A3: 33.71 kN / 7580 lbf; A1, A1/3 : 33.71 kN / 7580 lbf; A1E: 39.67 kN / 8917 lbf[23] | ||
| Maximum cruise | Mach 0.78 (450 kn; 833 km/h) / 145XR: Mach 0.8 (461 kn; 854 km/h) | ||
| Service ceiling | 37,000 ft / 11,278m | ||
| Range | ER: 1,300 nmi (2,400 km) LR: 1,750 nmi (3,240 km) |
ER: 1,250 nmi (2,320 km) LR: 1,650 nmi (3,060 km) |
LR: 1,550 nmi (2,870 km) XR: 2,000 nmi (3,700 km) |
See also
- Related development
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Related lists
References
- Notes
- ↑ ERJ or Embraer Regional Jet is a marketing name. The type is officially the Embraer EMB 135 and EMB 145.
- ↑ "Embraer Delivers 105 Commercial and 99 Executive Jets in 2011" (PDF) (Press release). São José dos Campos: Embraer. 11 January 2012. Retrieved 28 January 2012.
- 1 2 Resende, O.C. The evolution of the aerodynamic design tools and transport aircraft wings at Embraer, J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. & Eng. vol.26 no.4 Rio de Janeiro Oct./Dec. 2004 Retrieved 8 November 2015.
- ↑ ERJ 145 information at Airliners.net. Retrieved September 3, 2009.
- ↑ Aviation Week & Space Technology, 29 October 2007 issue, p. 66
- ↑ Trautvetter, Chad (6 June 2016). "Embraer To Close Legacy 650 Assembly Facility in China". AINonline. Retrieved 7 June 2016.
- ↑ MTOW - Maximum TakeOff Weight
- ↑ MZFW - Maximum Zero Fuel Weight
- ↑ Aerospace-Technology.com ERJ145
- ↑ "Embraer Signs Contracts with the Royal Thai Army and the Royal Thai Navy" (Press release). São José dos Campos: Embraer. 5 November 2007. Retrieved 3 December 2008.
- ↑ "Embraer ERJ 145 Jet Family Surpasses 15 Million Flight-Hours" (Press release). São José dos Campos: Embraer. 12 June 2009. Retrieved 25 June 2009.
- ↑ Flight recorder video of Rio-Sul incident YouTube. Retrieved July 18, 2007.
- ↑ "FAA Registry". Federal Aviation Administration.
- ↑ Harro Ranter (29 September 2006). "ASN Aircraft accident Embraer EMB-135BJ Legacy 600 N600XL Novo Progresso-Cachimbo Air Base, PA (SBCC)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- ↑ "Accident: Passaredo E145 at Vitoria da Conquista on Aug 25th 2010, landed short of runway". The Aviation Herald. 26 August 2010. Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ↑ "E135 Weights" (PDF). Embraer. June 2013.
- ↑ "E135 Performance" (PDF). Embraer. June 2013.
- ↑ "E140 Weight" (PDF). Embraer. June 2013.
- ↑ "E140 Performance" (PDF). Embraer. June 2013.
- ↑ "E145 LR Weight" (PDF). Embraer. June 2013.
- ↑ "E145 LR Performance" (PDF). Embraer. June 2013.
- ↑ "E145 XR Weight" (PDF). Embraer. June 2013.
- ↑ "E145 XR Performance" (PDF). Embraer. June 2013.
- ↑ "Rolls-Royce AE3007" (PDF). type certificate data sheet. EASA. 5 May 2015.
- Bibliography
- ERJ 145 information at Airliners.net
- Embraer Legacy Super Mid-Size Corporate Jet Aerospace-Technology website
- Information on Harbin Embraer
- EMB-145 Press Release for Rio-Sul Crash
- Endres, Gunter and Gething, Mike. (2002). Aircraft Recognition Guide, (2nd Ed.). New York: Harper Collins Publishers. ISBN 0-00-713721-4
- Aviation Week & Space Technology, 29 October 2007 issue, p. 66
- New Embraer-145 AEWC for India
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Embraer ERJ. |