Electorate of Salzburg
| Electorate of Salzburg | ||||||||||
| Kurfürstentum Salzburg | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
 Flag
 Coat of arms
| ||||||||||
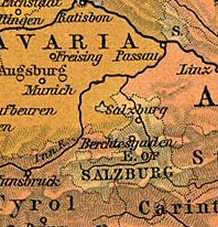 Salzburg between the Bavarian and Habsburg lands | ||||||||||
| Capital | Salzburg | |||||||||
| Government | Principality | |||||||||
| Elector | ||||||||||
| • | 1803–1805 | Ferdinand III | ||||||||
| Historical era | Napoleonic Wars | |||||||||
| • | Archbishopric secularized | February 11, 1803 | ||||||||
| • | Raised to Electorate | April 27, 1803 | ||||||||
| • | Mediatised to Austria | December 26, 1805 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||
The Electorate of Salzburg (German: Kurfürstentum Salzburg or Kursalzburg), occasionally known as the Grand Duchy of Salzburg, was an electoral principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1803–05,[1] the short-lived successor state of the Prince-Archbishopric of Salzburg.
History
In 1800 the territory of the Prince-Archbishopric had been occupied by French forces during the War of the Second Coalition, whereby Archbishop Count Hieronymus von Colloredo fled to Vienna. Augmented by the Berchtesgaden Provostry and parts of the former prince-bishoprics of Eichstätt and Passau, his lands were reorganized as the Electorate of Salzburg, created for Ferdinand III of Habsburg-Lorraine, younger brother of Emperor Francis II.

Ferdinand had held the Grand Duchy of Tuscany until 1801, when Emperor Francis had to cede the rule over Tuscany to France and Louis of Bourbon-Parma according to the Treaty of Lunéville. The Grand Duke, on good terms with Napoleon, reached his compensation with the former Archbishopric in December 1802. The secularisation was accomplished, when Prince-Archbishop Colloredo in his Vienna exile formally resigned in favour of Ferdinand on 11 February 1803. Two weeks later, the episcopal territory was secularized as part of the German Mediatisation (Reichsdeputationshauptschluss).
Ferdinand turned out to be a capable ruler. He established the Faculty of Medicine at the Salzburg University and insatted the distinguished pedagogue Franz Michael Vierthaler to introduce an education reform. He also ordered the improvement of mountain pass roads to Bad Gastein, Sankt Johann im Pongau and Radstadt, while his economic reforms roused opposition by the Salzburg guilds. When in October 1805 French troops again moved in during the War of the Third Coalition, Ferdinand, like his predecessor Archbishop Colloredo, had to leave his residence for his brother's court in Vienna.
Upon the crushing Austrian defeat in the Battle of Austerlitz, the Salzburg electorate was dissolved by the Peace of Pressburg signed on 26 December 1805. The lands of the former Archbishopric with Berchtesgaden passed to the Austrian Empire, while the Eichstätt and Passau territories were annexed by the Kingdom of Bavaria. Ferdinand was again compensated, this time with the newly established Electorate of Würzburg.
With the final dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the Electorate was re-established as the Austrian Duchy of Salzburg and Francis added "Duke of Salzburg" to his title as Emperor of Austria. However, Salzburg remained an object of interests and negotiations during the Napoleonic Wars. After the War of the Fifth Coalition it passed to Bavaria according to the 1809 Treaty of Schönbrunn, incorporated into the Salzach District together with Tyrolean Kitzbühel, Traunstein and Ried im Innkreis in 1810.
The Salzburg region was finally divided between Austria and Bavaria in the 1814 Peace of Paris. From 1816 the major part east of the Salzach River was subsequently administered from Linz within Upper Austria, until the Salzburg duchy was re-established in 1850.
References
- ↑ Gerhard Köbler (2007). Historisches Lexikon der Deutschen Länder: Die deutschen Territorien vom Mittelalter bis zur Gegenwart. C.H.Beck. pp. 41–. ISBN 978-3-406-54986-1. Retrieved 4 July 2012.
