List of members of the United Nations Security Council
Membership of the United Nations Security Council is held by the five permanent members and ten elected, non-permanent members. Prior to 1966, there were six elected members, while the permanent members have in essence not changed since the creation of the United Nations in 1945, apart from the representation of China. Elected members hold their place on the Council for a two-year term, and half of these places are contested each year. To ensure geographical continuity, a certain number of members is allocated for each of the five UN regional groupings.
Current membership
- Permanent members
| Country | Regional Group | Member Since |
|---|---|---|
| |
Asia-Pacific Group | 1971, replaced the Republic of China |
| |
Western European and Others Group | 1946 |
| |
Eastern European Group | 1991, replaced the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics |
| |
Western European and Others Group | 1946 |
| |
Western European and Others Group | 1946 |
- Non-permanent members
| Country | Regional Group | Term Began | Term Ends |
|---|---|---|---|
| |
Latin American and Caribbean Group (GRULAC) | 2017 | 2018 |
| |
African Group | 2016 | 2017 |
| |
African Group | 2017 | 2018 |
| |
Western European and Others Group | 2017 | 2017* |
| |
Asia-Pacific Group | 2016 | 2017 |
| |
Asia-Pacific Group | 2017 | 2018 |
| |
African Group | 2016 | 2017 |
| |
Western European and Others Group | 2017 | 2018 |
| |
Eastern European Group | 2016 | 2017 |
| |
Latin American and Caribbean Group (GRULAC) | 2016 | 2017 |
*During the 2016 Security Council elections, Italy and the Netherlands agreed to split a two-year term, in which Italy would serve from 1 January 2017 to 31 December 2017 and the Netherlands would subsequently serve from 1 January 2018 to 31 December 2018.[1][2]
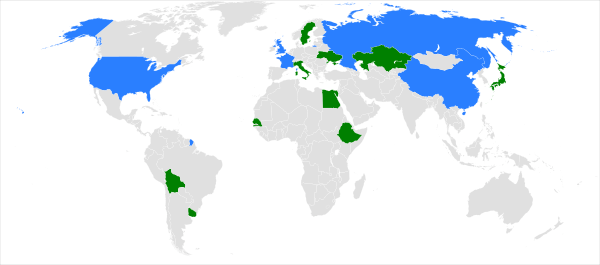
Regional Groups

- African Group: 3 members
- Asia-Pacific Group:[lower-alpha 1] 2 members
- Eastern European Group (CEIT, or Countries with Economies in Transition): 1 member
- Latin American and Caribbean Group (GRULAC): 2 members
- Western European and Others Group (WEOG): 2 members; at least one of these must be from Western Europe[3]
In addition, one of the non-permanent members of the council is an Arab country, alternately from the African or Asia-Pacific groups. This rule was added to the system in 1967 for it to be applied beginning with 1968.
Each year the UN General Assembly elects five new members for a two-year term; these elections always begin in October of the year, and continue until the two-thirds majority for the number of countries for each region has been reached. Re-election is allowed, but the term must not be consecutive.
- Electoral timetable
| Term beginning in years that are: | odd | even |
|---|---|---|
| African Group | one member | two members * |
| Asia-Pacific Group | one member | one member * |
| Eastern European Group | none | one member |
| Latin American and Caribbean Group (GRULAC) | one member | one member |
| Western European and Others Group | two members | none |
* The representative of Arab nations alternates between these two elected spaces.
Previous and future Security Council composition
From 1946 to 1965, the security council included six non-permanent members. The regional grouping at that time was:
- Latin America: 2 members
- Commonwealth of Nations: 1 member
- Eastern Europe: 1 member
- Middle East: 1 member
- Western Europe: 1 member
There were some exceptions to this grouping: Liberia took the place of a Western European country in 1961; the Ivory Coast substituted a member of the Commonwealth in 1964–1965; and the Eastern Europe group included Asian countries from 1956.
As part of a proposed expansion of the Security Council, Brazil, Germany, India and Japan, collectively the Group of 4 or G4 nations, are seeking permanent representation on this body.
Membership by year
Permanent
| Year | Permanent seats | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1945–1948 | Republic of China |
France |
Soviet Union |
United Kingdom |
United States |
| 1949–1970 | Republic of China (Taiwan) | ||||
| 1971–1991 | People's Republic of China | ||||
| 1992–present | Russian Federation | ||||

Non-permanent (1946–1965)
| Year | Latin American Seats | Commonwealth Seat | Eastern European & Asian Seat[lower-alpha 2] |
Middle Eastern Seat | Western European Seat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1946 | Brazil | Mexico | Australia | Poland | Egypt | Netherlands |
| 1947 | Colombia | Syria | Belgium | |||
| 1948 | Argentina | Canada | Ukraine | |||
| 1949 | Cuba | Egypt | Norway | |||
| 1950 | Ecuador | India | Yugoslavia | |||
| 1951 | Brazil | Turkey | Netherlands | |||
| 1952 | Chile | Pakistan | Greece | |||
| 1953 | Colombia | Lebanon | Denmark | |||
| 1954 | Brazil | New Zealand | Turkey | |||
| 1955 | Peru | Iran | Belgium | |||
| 1956 | Cuba | Australia | Yugoslavia | |||
| 1957 | Colombia | Philippines | Iraq | Sweden | ||
| 1958 | Panama | Canada | Japan | |||
| 1959 | Argentina | Tunisia | Italy | |||
| 1960 | Ecuador | Ceylon | Poland | |||
| 1961 | Chile | Turkey | United Arab Republic | Liberia[lower-alpha 3] | ||
| 1962 | Venezuela | Ghana | Romania | Ireland | ||
| 1963 | Brazil | Philippines | Morocco[lower-alpha 4] | Norway | ||
| 1964 | Bolivia | Ivory Coast[lower-alpha 5] | Czechoslovakia | |||
| 1965 | Uruguay | Malaysia | Jordan | Netherlands | ||
Non-permanent (1966–present)
List by number of years as Security Council member
This list contains the 130 United Nations member states so far elected to the United Nations Security Council, including the five permanent members, all listed by number of years each country has so far spent on the UNSC. Of all the members, 6 have so far ceased to exist, leaving the list with 124 modern nations. These, combined with the 69 modern nations that have never been elected to the UNSC to date (see Non-members, below), make up the entirety of the 193 current members of the UN.
Years on the Security Council, as of 2016, including current year where relevant :
| Years[lower-alpha 8] | Country | First Year | Most Recent Year | Regional Group | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 71 | 1946 | 2017 | WEOG | Permanent member | |
| 71 | 1946 | 2017 | WEOG | Permanent member | |
| 71 | 1946 | 2017 | WEOG | Permanent member | |
| 46 | 1946 | 1991 | E. European | Former permanent member, replaced by Russian Federation | |
| 45 | 1971 | 2017 | Asia-Pacific | Permanent member | |
| 26 | 1946 | 1971 | Asian | Former permanent member, replaced by People's Republic of China | |
| 25 | 1991 | 2017 | E. European | Permanent member | |
| 21 | 1958 | 2017 | Asia-Pacific | Current membership of Security Council expires 31 December 2017 | |
| 20 | 1946 | 2011 | GRULAC | ||
| 18 | 1948 | 2014 | GRULAC | ||
| 14 | 1947 | 2012 | GRULAC | ||
| 14 | 1950 | 2012 | Asia-Pacific | ||
| 14 | 1952 | 2013 | Asia-Pacific | ||
| 12 | 1948 | 2000 | WEOG | ||
| 12 | 1959 | 2008 | WEOG | ||
| 10 | 1946 | 2014 | WEOG | ||
| 10 | 1947 | 2008 | WEOG | ||
| 10 | 1952 | 2015 | GRULAC | ||
| 10 | 1946 | 2017 | African (Arabic) | Includes 2 years with the seat held in the name of the United Arab Republic, of which for more than 15 months UAR served as the name of modern-day Egypt; current membership of Security Council expires 31 December 2017 | |
| 10 | 1977 | 2012 | WEOG | Includes 4 years when the Federal Republic of Germany consisted only of West Germany (but does not include East Germany's 2 years, listed separately below) | |
| 10 | 1966 | 2015 | African | ||
| 10 | 1958 | 2008 | GRULAC | ||
| 10 | 1969 | 2016 | WEOG | ||
| 10 | 1962 | 2016 | GRULAC | ||
| 9 | 1946 | 2000 | WEOG | ||
| 9 | 1946 | 1997 | E. European | ||
| 8 | 1953 | 2006 | WEOG | ||
| 8 | 1949 | 2002 | WEOG | ||
| 8 | 1955 | 2007 | GRULAC | ||
| 7 | 1965 | 2016 | Asia-Pacific | ||
| 7 | 1946 | 2010 | GRULAC | ||
| 7 | 1954 | 2016 | WEOG | ||
| 7 | 1962 | 2005 | E. European | ||
| 7 | 1947 | 2003 | Asia-Pacific (Arabic) | Includes one year (1961) during which the United Arab Republic was a member, for the greater part of which Syria was a member of that union | |
| 7 | 1951 | 2010 | WEOG | ||
| 7 | 1948 | 2016 | E. European | Includes 4 years of membership under the name of | |
| 7 | 1950 | 1989 | E. European | Predecessor of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia and Slovenia | |
| 6 | 1968 | 1989 | African (Arabic) | ||
| 6 | 1973 | 2010 | WEOG | ||
| 6 | 1966 | 2003 | E. European | ||
| 6 | 1974 | 2009 | GRULAC | ||
| 6 | 1949 | 1991 | GRULAC | ||
| 6 | 1950 | 1992 | GRULAC | ||
| 6 | 1978 | 2011 | African | ||
| 6 | 1962 | 2007 | African | ||
| 6 | 1973 | 2008 | Asia-Pacific | ||
| 6 | 1965 | 2015 | Asia-Pacific (Arabic) | ||
| 6 | 1963 | 2013 | African (Arabic) | ||
| 6 | 1957 | 2004 | Asia-Pacific | ||
| 6 | 1979 | 2012 | WEOG | ||
| 6 | 1957 | 1998 | WEOG | ||
| 6 | 1959 | 2003 | African (Arabic) | ||
| 6 | 1969 | 1988 | African | ||
| 5 | 1962 | 2002 | WEOG | ||
| 5 | 1968 | 2017 | African | Current membership of Security Council expires 31 December 2017 | |
| 5 | 1966 | 2010 | African | ||
| 4 | 2003 | 2016 | African | ||
| 4 | 1979 | 2001 | Asia-Pacific | ||
| 4 | 1976 | 2005 | African | ||
| 4 | 1964 | 1979 | GRULAC | ||
| 4 | 1984 | 2009 | African | For first 7 months of membership of the Security council in 1984 was known as Upper Volta. | |
| 4 | 1974 | 2003 | African | ||
| 4 | 1964 | 1991 | African | ||
| 4 | 1967 | 1990 | African | ||
| 4 | 1969 | 1990 | WEOG | ||
| 4 | 1952 | 2006 | WEOG | ||
| 4 | 1972 | 2003 | African | ||
| 4 | 1975 | 1983 | GRULAC | ||
| 4 | 1968 | 1993 | E. European | ||
| 4 | 1957 | 1975 | Asia-Pacific (Arabic) | ||
| 4 | 1979 | 2001 | GRULAC | ||
| 4 | 1973 | 1998 | African | ||
| 4 | 1953 | 2011 | Asia-Pacific (Arabic) | ||
| 4 | 1976 | 2009 | African (Arabic) | ||
| 4 | 1966 | 2001 | African | ||
| 4 | 1977 | 2002 | African | ||
| 4 | 1969 | 1989 | Asia-Pacific | ||
| 4 | 1970 | 1984 | GRULAC | ||
| 4 | 1986 | 2007 | African | ||
| 4 | 1996 | 2014 | Asia-Pacific | ||
| 4 | 1994 | 2014 | African | ||
| 4 | 2007 | 2012 | African | ||
| 4 | 1975 | 2006 | African | ||
| 4 | 1982 | 2013 | African | ||
| 4 | 1982 | 1991 | African | Now known as Democratic Republic of the Congo | |
| 4 | 1983 | 1992 | African | ||
| 3 | 1964 | 1979 | E. European | Predecessor of Czech Republic and Slovakia | |
| 3 | 1965 | 2016 | GRULAC | Current membership of Security Council expires in December 2017 | |
| 2 | 2012 | 2013 | E. European | Was part of the Soviet Union during its 45 years of Security Council membership | |
| 2 | 1998 | 1999 | Asia-Pacific (Arabic) | ||
| 2 | 2010 | 2011 | E. European | Was also part of the SFR Yugoslavia during its 7 years of Security Council membership | |
| 2 | 1995 | 1996 | African | ||
| 2 | 1970 | 1971 | African | ||
| 2 | 1974 | 1975 | E. European | Now known as Belarus; Byelorussian SSR held its own seat in the General Assembly while being part of the Soviet Union during its 45 years of Security Council membership | |
| 2 | 1992 | 1993 | African | ||
| 2 | 1960 | 1961 | Asia-Pacific | Now known as Sri Lanka | |
| 2 | 2014 | 2015 | African (Arabic) | Was a colony of France from 1900 to 11 August 1960; | |
| 2 | 2008 | 2009 | E. European | Was also part of the SFR Yugoslavia during its 7 years of Security Council membership | |
| 2 | 1994 | 1995 | E. European | Was also part of Czechoslovakia during its 3 years of Security Council membership | |
| 2 | 1993 | 1994 | African | ||
| 2 | 1998 | 1999 | African | ||
| 2 | 1980 | 1981 | E. European | Now subsumed into Germany, which has 5 years of Security Council membership since it has included the former territory of East Germany | |
| 2 | 2012 | 2013 | GRULAC | ||
| 2 | 1996 | 1997 | African | ||
| 2 | 1995 | 1996 | GRULAC | ||
| 2 | 1955 | 1956 | Asia-Pacific | ||
| 2 | 1978 | 1979 | Asia-Pacific (Arabic) | ||
| 2 | 2014 | 2015 | E. European | Was part of the Soviet Union from 3 August 1940 to 11 March 1990; Membership of Security Council expired in December 2015 | |
| 2 | 2013 | 2014 | WEOG | ||
| 2 | 1985 | 1986 | African | ||
| 2 | 1983 | 1984 | WEOG | ||
| 2 | 1974 | 1975 | African | ||
| 2 | 1999 | 2000 | African | ||
| 2 | 1980 | 1981 | African | ||
| 2 | 1994 | 1995 | Asia-Pacific (Arabic) | ||
| 2 | 1968 | 1969 | GRULAC | ||
| 2 | 1970 | 1971 | African | ||
| 2 | 2001 | 2002 | Asia-Pacific | Was also part of Malaysia for several months of 1965 during its membership of the Security Council | |
| 2 | 2006 | 2007 | E. European | Was also part of Czechoslovakia during its 3 years of Security Council membership | |
| 2 | 1998 | 1999 | E. European | Was also part of the SFR Yugoslavia during its 7 years of Security Council membership | |
| 2 | 1971 | 1972 | African | ||
| 2 | 1972 | 1973 | African (Arabic) | ||
| 2 | 1985 | 1986 | Asia-Pacific | ||
| 2 | 1985 | 1986 | GRULAC | ||
| 2 | 2006 | 2007 | Asia-Pacific (Arabic) | ||
| 2 | 1986 | 1987 | Asia-Pacific (Arabic) | ||
| 2 | 1961 | 1962 | African (Arabic) | Predecessor of Syria and Egypt | |
| 2 | 2008 | 2009 | Asia-Pacific | ||
| 2 | 1990 | 1991 | Asia-Pacific (Arabic) | The entity elected, and which held the Security Council seat for the first five months of membership, was South Yemen: unification with North Yemen occurred during the time of membership. | |
| 1 | 1961 | 1961 | African | Served only one year[lower-alpha 9] | |
| 1 | 2017 | 2017 | Asia-Pacific | Was part of the Soviet Union from 26 April 1920 to 25 December 1991. |
Future candidacies
The following countries have made known their applications for future United Nations Security Council membership:
| Africa | Asia-Pacific | Eastern Europe | GRULAC | WEOG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | ? | Indonesia,[5][6] Maldives[5][7] | – | ? | Belgium,[8][9][10] Germany,[9][10] Israel[9][10] |
| 2019 | ? | India,[11][12] Vietnam[6][13] | Estonia[14] | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines[5] | – |
| 2020 | ? | Afghanistan[12] | – | ? | Ireland,[15] Norway,[16] San Marino,[17] Canada[18] |
| 2021 | ? | Bahrain,[19] United Arab Emirates[12] | Albania[20] | ? | – |
| 2022 | ? | Mongolia[21][12] | – | ? | Switzerland,[22] Malta[5] |
| 2023 | ? | Tajikistan[23] | ? | Guyana[5] | – |
| 2024 | ? | Pakistan[5] | – | ? | Greece,[24] Denmark[17] |
| 2025 | ? | ? | Latvia,[25] Montenegro[26] | ? | – |
| 2026 | ? | The Philippines[6] | – | ? | Portugal,[27] Austria[17] |
| 2027 | ? | Republic of Korea[28] | ? | ? | – |
| 2028 | ? | Iran[29] | – | ? | Australia,[30] Finland[17] |
| 2029 | ? | ? | Croatia[31] | ? | – |
| 2031 | ? | ? | Armenia[32] | ? | – |
Serbia[33] as a member of the Eastern European Group has also expressed their wish to apply for United Nations Security Council membership in the future, but did not specify any term.
Non-members
As of July 2011, there are currently 193 members of the United Nations and five permanent members of the Security Council. The other ten seats are assigned amongst the remaining 188 members. As a result, many members have never been on the Security Council. The following list is a summary of all countries, currently 68 modern nations[34] and three historical ones, that have never been a member of the United Nations Security Council. The three historical UN members listed are Tanganyika, Zanzibar, and the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.
| UN Member state | Regional Group | Security Council membership as part of another entity |
|---|---|---|
| Asia-Pacific | ||
| E. European | ||
| WEOG | ||
| GRULAC | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1632 to 1 November 1980 | |
| E. European | Was part of the Soviet Union from 29 November 1920 to 25 December 1991 | |
| GRULAC | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1717 to 10 July 1973 | |
| GRULAC | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1625 to 30 November 1966 | |
| GRULAC | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1862 to 21 September 1981 | |
| Asia-Pacific | ||
| Asia-Pacific | Was a protectorate of the United Kingdom from 1888 to 1984, and was occupied by Japan from 1941 to 1945 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was a colony of France from 1863 to 9 November 1953 | |
| African | Was a colony of France from 1894 to 13 August 1960 | |
| African | Was a colony of France from 1841 to 6 July 1975 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 5 November 1914 to 16 August 1960 | |
| Asia-Pacific | ||
| GRULAC | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1783 to 3 November 1978 | |
| GRULAC | ||
| GRULAC | ||
| African | Equatorial Guinea was a colony of Spain until 1968, but Spain's first term on the UNSC was in 1969 | |
| African | Was under the administration of the United Kingdom from 1941 to 1947, then a United Nations Trust Territory from 1947 to 1952, then part of Ethiopia from 1952 to 24 May 1993 | |
| E. European | Was part of the Soviet Union from 1944 to 20 August 1991 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1874 to 10 October 1970 | |
| E. European | Was part of the Soviet Union from 25 February 1921 to 25 December 1991 | |
| GRULAC | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1763 to 7 February 1974 | |
| GRULAC | ||
| WEOG | ||
| None / WEOG[lower-alpha 10] | Part of a League of Nations mandate under United Kingdom administration from 25 April 1920 to 14 May 1948 | |
| Asian / None[lower-alpha 11] | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1892 to 12 July 1979 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was part of the Soviet Union from 1 February 1926 to 25 December 1991 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was a colony of France from 1893 to 19 July 1949 | |
| E. European | Was part of the Soviet Union from 5 August 1940 to 21 August 1991 | |
| African | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1884 to 4 October 1966 | |
| WEOG | ||
| E. European | Was part of Yugoslavia from 29 November 1943 to 3 April 1993 | |
| African | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1891 to 6 July 1964 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1887 to 26 July 1965 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was part of the League of Nations South Pacific Mandate under Japanese administration from 28 June 1919 to 17 July 1947, then part of the United Nations Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands under the administration of the United States from 17 July 1947 to 21 October 1986 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was part of the League of Nations South Pacific Mandate under Japanese administration from 28 June 1919 to 17 July 1947, then part of the United Nations Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands under the administration of the United States from 17 July 1947 to 3 November 1986 | |
| E. European | Was part of the Soviet Union from 28 June 1940 to 25 December 1991 | |
| WEOG | ||
| Asia-Pacific | ||
| E. European | Was part of Yugoslavia from 29 November 1943 to 28 April 1992[lower-alpha 12] | |
| African | Mozambique was a colony of Portugal from 1498 to 25 June 1975, but Portugal's first term on the UNSC was in 1979 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1824 to 4 January 1948 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was a United Nations Trust Territory administered by the United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand from 1 January 1946 to 31 January 1968 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was part of the League of Nations South Pacific Mandate under Japanese administration from 28 June 1919 to 17 July 1947, then part of the United Nations Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands under the administration of the United States from 17 July 1947 to 1 October 1994 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was administered by Australia in the case of the Territory of Papua from 1905, the Territory of New Guinea as a League of Nations mandate from 1919 and as a unified Territory of Papua and New Guinea from 1949 until 16 September 1975 | |
| GRULAC | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1713 to 19 September 1983 | |
| GRULAC | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1803 to 22 February 1979 | |
| GRULAC | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1783 to 27 October 1979 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was a League of Nations mandate under the administration of New Zealand from 17 December 1920 to 25 January 1947, then a United Nations Trust Territory under the administration of New Zealand from 25 January 1947 to 1 January 1962 | |
| WEOG | ||
| African | São Tomé and Príncipe was a colony of Portugal from 1471 to 12 July 1975, but Portugal's first term on the UNSC was in 1979 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Saudi Arabia was elected in the 2013 election, but declined the seat.[35] | |
| E. European | Was part of Yugoslavia from 31 January 1946 to 27 April 1992[lower-alpha 13] | |
| African | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1801 to 29 June 1976 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1893 to 7 July 1978 | |
| African | Was part of Sudan from the country's independence from the United Kingdom and Egypt on 1 January 1956 to 9 July 2011 | |
| GRULAC | Was a colony of the Netherlands from 1667 to 25 November 1975 | |
| African | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1902 to 6 September 1968 | |
| WEOG | ||
| Asia-Pacific | Was part of the Soviet Union from 14 October 1924 to 25 December 1991 | |
| Commonwealth Seat | Was a League of Nations mandate under the administration of the United Kingdom from 20 July 1922 to 11 December 1946, then a United Nations Trust Territory under the administration of the United Kingdom until 9 December 1962, then independent until federation with Zanzibar to form Tanzania | |
| Asia-Pacific | During the existence of the United Nations, Timor Leste has been a colony of Portugal (until 28 November 1975) and occupied by Indonesia (until 1999); Indonesia was a Security Council member in 1995-6. | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was a protectorate of the United Kingdom from 18 May 1900 to 4 June 1970 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was part of the Soviet Union from 13 May 1925 to 8 December 1991 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 1892 to 1 October 1978 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was part of the Soviet Union from 13 May 1925 to 25 December 1991 | |
| Asia-Pacific | Was a Condominium under joint sovereignty of the United Kingdom and France from 1906 to 30 July 1980 | |
| Commonwealth Seat | Was a colony of the United Kingdom from 27 August 1896 to 10 December 1963, then independent until federation with Tanganyika to form Tanzania on 26 April 1964. | |
| E. European | Was part of Yugoslavia from 29 November 1943 to 27 April 1992 |
See also
- United Nations Regional Groups
- Member states of the United Nations
- List of members of the United Nations Economic and Social Council
- List of members of the United Nations Commission on Human Rights
Notes
- ↑ "Asian group of nations at UN changes its name to Asia-Pacific group", Radio New Zealand International, 2011-08-31.
- ↑ The Eastern Europe group included Asian countries from 1956 onwards.
- ↑ Liberia took the place of the Western European country in 1961
- ↑ Morocco took the place of the Middle Eastern country in 1963–1964.
- ↑ Côte d'Ivoire took the place of a member of the Commonwealth in 1964–1965.
- ↑ At the time of election, and until August 1984, the country was known as Republic of Upper Volta.
- ↑ The election was secured by South Yemen, and in May 1990, during its membership of the Security Council, it unified with North Yemen to form the single country of Yemen.
- ↑ Table shows years completed or in progress. Each term on the Council consist of 2 years. Any odd number of years are countries currently serving the first year of a term, countries with terms between 1956 and 1967, when the order of the council changed, or the three countries (Mexico, Egypt and the Netherlands) who had the first terms in 1946 and changed in 1947.
- ↑ Liberia retired after one year following an agreement reached on the 15th Session. Ireland was elected for the remainder of the two-year term.[4]
- ↑ Not a member of any regional group until joining the WEOG in 2000. Crossette, Barbara (3 December 1999). "Membership in Key Group Within U.N. Eludes Israel". The New York Times. Retrieved 17 April 2011.
- ↑ As of May 2006, Kiribati is not a member of any regional group.
- ↑ Montenegro was also part of FR Yugoslavia and of Serbia and Montenegro from 27 April 1992 to 5 June 2006, but these entities were not members of the Security Council.
- ↑ Serbia was also part of FR Yugoslavia and of Serbia and Montenegro from 27 April 1992 to 5 June 2006, but these entities were not members of the Security Council.
References
- ↑ "Republic of Italy and Kingdom of the Netherlands agree to split membership of UN Security Council 2017-2018". Government of the Netherlands. Retrieved January 1, 2017.
- 1 2 "Italy, Netherlands ask to share Security Council seat". Al Jazeera. June 28, 2016. Retrieved January 1, 2017.
- ↑ The United Nations Security Council, The Green Papers Worldwide
- ↑ Commonwealth Bureau of Census and Statistics. Official Year Book of the Commonwealth of Australia No. 47 – 1961. Aust. Bureau of Statistics. p. 1143. GGKEY:5SX8QTW3P5T. Retrieved 21 August 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Candidature Chart of the Commonwealth Countries". Commonwealth of Nations. 20 February 2014. Retrieved 1 November 2015.
- 1 2 3 "46th ASEAN Foreign Ministers’ Meeting Joint Communiqué". VietnamPlus. 1 July 2013. Retrieved 19 October 2013.
- ↑ "India – Maldives Relations" (PDF). Ministry of External Affairs of India. January 2012. Retrieved 20 August 2013.
- ↑ http://www.diplomatie.be/newyorkun/default.asp?id=105&mnu=105
- 1 2 3 "Surprise UN attack: Germany v. Israel". New York Post. 16 May 2013. Retrieved 20 August 2013.
- 1 2 3 "Is Germany Preventing Israel from Joining the Security Council?". Jewish Voice. 22 May 2013. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ↑ "India’s troubled Security Council bid". The Daily Star. 22 October 2013. Retrieved 28 April 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 Ankit Kumar. "CHOOSING BETWEEN ALLIES AND UNSC SEAT: INDIA’S CATCH 22 SITUATION" (PDF). Centre for Air Power studies. Retrieved 28 April 2014.
- ↑ "Viet Nam makes bilateral leap with Ukraine towards prosperity". Viet Nam News. 17 November 2012. Retrieved 21 August 2013.
- ↑ "Estonian Security Policy". Estonian Embassy in Stockholm. 1 March 2011. Retrieved 21 August 2013.
- ↑ "Department of Foreign Affairs". Irelandunnewyork.org.
- ↑ "Norway and the United Nations: Common Future, Common Solutions". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Norway. Retrieved 21 August 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 "Switzerland's candidature for a non-permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council for the 2023-2024 term" (PDF). Swiss Federal Council. 5 June 2015. Retrieved 1 November 2015.
- ↑ "Trudeau unveils Canada's plan to seek 2021 UN Security Council seat". Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. 16 March 2016. Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- ↑ "Security Council Elections: Options after Saudi Arabia Rejects its Seat". What's in Blue?. 18 October 2013. Retrieved 18 October 2013.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 22 March 2012. Retrieved 2017-05-22.
- ↑ "Secretary-General, Opening Annual General Debate, Urges World Leaders to Tackle Global Challenges Decisively for Sake of Future Generations". United Nations. 21 September 2011. Retrieved 7 September 2013.
- ↑ "Swiss aim for UN Security Council in 2023–24. – swissinfo". Swissinfo.ch. 12 January 2011.
- ↑ "Speech of the Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Tajikistan H.E. Mr. Sirodjidin Aslov at the 41st session of the Council of the OIC Member States Foreign Ministers". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Tajikistan. 20 June 2014. Retrieved 1 November 2015.
- ↑
- ↑ "Dombrovskis and UN secretary general discuss UN priorities and Latvia's interests". The Baltic Course. 16 May 2013. Retrieved 28 September 2013.
- ↑ "Minister Describes Use of Force to Address Problems as ‘Ineffective, Meaningless and Destructive’, on Fourth Day of General Assembly’s Annual Debate". United Nations. 27 September 2013. Retrieved 1 November 2015.
- ↑ "Non-Permanent Member of the Security Council 2027-2028". Permanent Mission of Portugal to the United Nations. Retrieved 1 November 2015.
- ↑ "Seoul to push to win nonpermanent UNSC seat for 2028-29". Yonhap New Agency. 19 February 2014. Retrieved 1 May 2014.
- ↑ "RESOLUTION NO.6/42-ORG ON CANDIDACIES SUBMITTED BY OIC MEMBER STATES FOR POSTS IN INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATIONS". Organization of Islamic Cooperation. 28 May 2015. Retrieved 23 September 2016.
- ↑ "General Debate Statement by The Hon Julie Bishop MP Minister of Foreign Affairs of Australia" (PDF). United Nations. 29 September 2015. Retrieved 1 November 2015.
- ↑ "MVP RH". Un.mfa.hr.
- ↑ "Uruguay and Armenia support each other at UN Security Council". News.am. 8 December 2014. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- ↑ Tadić: Kandidovaćemo se za poziciju u Savetu bezbednosti Archived 6 April 2009 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Countries never elected members of the Security Council". United Nations. Retrieved 13 December 2013.
- ↑ United Nations, General Assembly, Letter dated 12 November 2013 from the Permanent Representative of Saudi Arabia to the United Nations addressed to the Secretary-General, A/68/599 (14 November 2013), available from undocs.org/A/68/599