Tayra
| Tayra | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Mustelidae |
| Subfamily: | Mustelinae |
| Genus: | Eira Hamilton Smith, 1842 |
| Species: | E. barbara |
| Binomial name | |
| Eira barbara (Linnaeus, 1758) | |
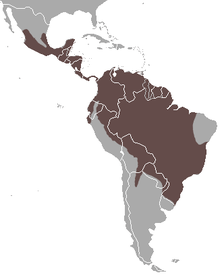 | |
| Tayra range | |
The tayra (Eira barbara), is an omnivorous animal from the weasel family, native to the Americas. It is the only species in the genus Eira.
Tayras are also known as the tolomuco or perico ligero in Central America, motete in Honduras, irara in Brazil, san hol or viejo de monte in the Yucatan Peninsula, and high-woods dog (or historically chien bois) in Trinidad.[2] The genus name Eira is derived from the indigenous name of the animal in Bolivia and Peru, while barbara means "strange" or "foreign".[3]
Description
Tayras are long, slender animals with an appearance similar to weasels and martens. They range from 56 to 71 cm (22 to 28 in) in length, not including a 37 to 46 cm (15 to 18 in) long bushy tail, and weigh 2.7 to 7 kg (6.0 to 15.4 lb). Males are larger, and slightly more muscular, than females. They have short, dark brown to black fur which is relatively uniform across the body, limbs, and tail, except for a yellow or orange spot on the chest. The fur on the head and neck is much paler, typically tan or greyish in color. Albino or yellowish individuals are also known, and are not as rare among tayras as they are amongst other mustelids.[3]
The feet have toes of unequal length with tips that form a strongly curved line when held together. The claws are short and curved, but strong, being adapted for climbing and running rather than digging. The pads of the feet are hairless, but are surrounded by stiff sensory hairs. The head has small, rounded, ears, long whiskers and black eyes with a blue-green shine. Like most other mustelids, tayras possess anal scent glands, but these are not particularly large, and their secretion is not as pungent as in other species, and is not used in self-defence.[3]
Range and habitat
Tayras are found across most of South America east of the Andes, except for Uruguay, eastern Brazil, and all but the most northerly parts of Argentina. They are also found across the whole of Central America, in Mexico as far north as southern Veracruz, and on the island of Trinidad.[1] They are generally found only in tropical and subtropical forests, although they may cross grasslands at night to move between forest patches,[4] and they also inhabit cultivated plantations and croplands.[1]
Subspecies
At least seven subspecies are currently recognised:[3]
- Eira barbara barbara (northern Argentina, Paraguay, western Bolivia and central and southern Brazil)
- Eira barbara biologiae (central Costa Rica and Panama)
- Eira barbara inserta (South Guatemala to central Costa Rica)
- Eira barbara madeirensis (west Ecuador and northern Brazil)
- Eira barbara peruana (the eastern Andes in Peru and Bolivia)
- Eira barbara poliocephala (eastern Venezuela, the Guianas, and northeastern Brazil)
- Eira barbara senex (central Mexico to northern Honduras)
- Eira barbara senilis (northern Ecuador)
- Eira barbara sinuensis (Colombia, western Venezuela, northern Ecuador, and Panama)
Behavior and diet
Tayras are solitary diurnal animals, although occasionally active during the evening or at night.[4] They are opportunistic omnivores, hunting rodents and other small mammals, as well as birds, lizards, and invertebrates, and climbing trees to get fruit and honey.[3][5] They locate prey primarily by scent, having relatively poor eyesight, and actively chase it once located, rather than stalking or using ambush tactics.[4]
They are expert climbers, using their long tails for balance. On the ground or on large horizontal tree limbs, they use a bounding gallop when moving at high speeds.[6] They can also leap from treetop to treetop when pursued. They generally avoid water, but are capable of swimming across rivers when necessary.[3]
They live in hollow trees, or burrows in the ground. Individual animals maintain relatively large home ranges, with areas of up to 24 km2 (9.3 sq mi) having been recorded. They may travel at least 6 km (3.7 mi) in a single night.[3]
An interesting instance of caching has been observed among tayras: a tayra will pick unripe green plantains, which are inedible, and leave them to ripen in a cache, coming back a few days later to consume the softened pulp.[7]
Reproduction
Tayras breed year-round, with the females entering estrus several times each year for anything from 3 to 20 days at a time. Unlike some other mustelids, tayras do not exhibit embryonic diapause, and gestation lasts from 63 to 67 days. The female gives birth to from one to three young, which she cares for alone.[3][8]
The young are altricial, being born blind and with closed ears, but are already covered in a full coat of black fur; they weigh about 100 g (3.5 oz) at birth. Their eyes open at 35 to 47 days, and they leave the den shortly thereafter. They begin to take solid food at around 70 days of age, and are fully weaned by 100 days. Hunting behavior begins as early as three months, and the mother initially brings her young wounded or slow prey to practice on as they improve their killing technique. The young are fully grown at around six months, and leave their mother to establish their own territory by ten months.[3]

Interaction with humans
Tayras are playful and easily tamed. Indigenous people, who often refer to the tayra as "cabeza del viejo", or old man's head, due to their wrinkled facial skin, have kept them as household pets to control vermin. Sometimes, they attack domestic animals, such as chickens.
Conservation
Wild tayra populations are slowly shrinking, especially in Mexico, due to habitat destruction for agricultural purposes. The species is listed as being of Least Concern.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Eira |
- 1 2 3 Cuarón, A. D., et al. 2008. Eira barbara. In: IUCN 2012. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. Downloaded on 2 June 2013.
- ↑ http://www2.ine.gob.mx/publicaciones/libros/360/yuc.html
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Presley, S.J. (2000). "Eira barbara" (PDF). Mammalian Species. 636: 1–6. doi:10.1644/1545-1410(2000)636<0001:eb>2.0.co;2.
- 1 2 3 Defler, T.R. (1980). "Notes on interactions between tayra (Eira barbara) and the white-fronted capuchin (Cebus albifrons)". Journal of Mammalogy. 61 (1): 156. doi:10.2307/1379979.
- ↑ Galef, B.G.; et al. (1976). "Predation by the tayra (Eira barbara)". Journal of Mammalogy. 57 (4): 760–761. doi:10.2307/1379450.
- ↑ Kavanau, J.L. (1971). "Locomotion and activity phasing of some medium-sized mammals". Journal of Mammalogy. 52 (2): 396–403. doi:10.2307/1378681.
- ↑ Soley, F.G. & Alvarado-Díaz, I. (8 July 2011). "Prospective thinking in a mustelid? Eira barbara (Carnivora) cache unripe fruits to consume them once ripened". Naturwissenschaften. 98 (8): 693–698. doi:10.1007/s00114-011-0821-0.
- ↑ Vaughan, R. (1974). "Breeding the tayra (Eira barbara) at Antelope Zoo, Lincoln". International Zoo Yearbook. 14: 120–122. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1090.1974.tb00791.x.
Further reading
- Nowak, Ronald M. (2005). Walker's Carnivores of the World. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Press. ISBN 0-8018-8032-7
- Emmons, L.H. (1997). Neotropical Rainforest Mammals, 2nd ed. University of Chicago Press ISBN 0-226-20721-8

