Ecology Flag
The Ecology Flag is a cultural symbol used primarily in the 1970s by American environmentalists.
Description
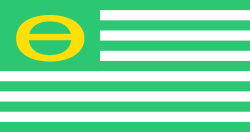
Ron Cobb created an ecology symbol which he published on November 7, 1969, in the Los Angeles Free Press and then placed it in the public domain. The symbol was formed by taking the letters "e" and "o", taken from the words "environment" and "organism", and putting them in superposition, thereby forming a shape reminiscent of the Greek letter Θ (Theta). Look magazine incorporated the symbol into an image of a flag in their April 21, 1970 issue. It widely popularized the theta symbol, which it associated with the Greek word thanatos (death) in light of human threats to the environment and atmosphere of the earth.[1] The flag was patterned after the flag of the United States, and had thirteen stripes alternating green and white. Its canton was green with the ecology symbol where the stars would be in the United States flag
History
One of the earliest recorded flyings of the Ecology Flag was in 1971. As a 16-year-old high school student, Betsy Boze (Betsy Vogel), an environmental advocate and social activist that enjoyed sewing costumes and unique gifts, made a 3 x 5 foot green and white "theta" ecology flag to commemorate the first Earth Day. Initially denied permission to fly the flag at C.E. Byrd High School in Shreveport, Louisiana, Vogel sought and received authorization from the Louisiana Legislature and Louisiana Governor John McKeithen in time to display the flag for Earth Day.
See also
References
- ↑ http://flagsinternational.com (12 July 2012). "Ecology Flag".
External links
- Ecology Flags (U.S.) at Flags of the World
- Artwork of original symbol at Ron Cobb's website (2011 snapshot at archive.org)