Ibiza
| Native name: Eivissa | |
|---|---|
 Flag of Ibiza | |
 Ibiza Ibiza is midway between Spain's coastline and the larger island of Majorca.  Ibiza (west of Majorca) in Balearic Islands | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Balearic Sea |
| Coordinates | 38°59′N 1°26′E / 38.98°N 1.43°ECoordinates: 38°59′N 1°26′E / 38.98°N 1.43°E |
| Archipelago | Balearic Islands, Pityusic Islands |
| Area | 571.6 km2 (220.7 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 475 m (1,558 ft) |
| Highest point | Sa Talaia |
| Administration | |
| Autonomous Community | Balearic Islands |
| Province | Balearic Islands |
| Capital city | Ibiza Town |
| Largest settlement | Ibiza Town (pop. 49,768) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 132,637 (1 January 2010) |
| Pop. density | 231.6 /km2 (599.8 /sq mi) |
| Additional information | |
|
Official languages:  Ibiza Insular Council Emblem | |
| Official name | Ibiza, Biodiversity and Culture |
| Type | Mixed |
| Criteria | ii, iii, iv, ix, x |
| Designated | 1999 (23rd session) |
| Reference no. | 417 |
| State Party | Spain |
| Region | Southern Europe |
Ibiza (Catalan: Eivissa) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea off the east coast of Spain. It is 150 kilometres (93 miles) from the city of Valencia. It is the third largest of the Balearic Islands, an autonomous community of Spain. Its largest settlements are Ibiza Town (Catalan: Vila d'Eivissa, or simply Vila), Santa Eulària des Riu, and Sant Antoni de Portmany. Its highest point, called Sa Talaiassa (or Sa Talaia), is 475 metres (1,558 feet) above sea level.
Ibiza has become well known for its association with nightlife, electronic music that originated on the island, and for the summer club scene, all of which attracts large numbers of tourists drawn to that type of holiday. Several years before 2010, the island's government and the Spanish Tourist Office had been working to promote more family-oriented tourism, with the police closing down clubs that played music at late night hours, but by 2010 this policy was reversed.[1] Around 2015 it was resumed.[2]
The port in Ibiza Town is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[3]
Ibiza and the nearby island of Formentera to its south are called the Pine Islands, or "Pityuses".
Toponymy
The official name of the island is in Catalan Eivissa (pronounced [əjˈvisə]). Its name in Spanish is Ibiza (pronounced [iˈβiθa]). In British English, the name is usually pronounced in an approximation of the Spanish /ɪˈbiːθə/,[4] whereas in American English the pronunciation is closer to Latin American Spanish (/ɪˈbiːzə/,[5] /iːˈbiːsə/[6]).[7][8]
Phoenician colonists called the island Ibossim (from the Phoenician iboshim, meaning dedicated to the Egyptian god Bes).[9][10] It was later known to Romans as Ebusus. The Greeks called the two islands of Ibiza and Formentera the Pityûssai (Greek: Πιτυοῦσσαι, "pine-covered islands").[11]
In the 18th and 19th centuries the island was known to the British, and especially to the Royal Navy, as Ivica.[12]
History
.jpg)



In 654 BC, Phoenician settlers founded a port on Ibiza. With the decline of Phoenicia after the Assyrian invasions, Ibiza came under the control of Carthage, also a former Phoenician colony. The island produced dye, salt, fish sauce (garum), and wool.
A shrine with offerings to the goddess Tanit was established in the cave at Es Cuieram, and the rest of the Balearic Islands entered Eivissa's commercial orbit after 400 BC. Ibiza was a major trading post along the Mediterranean routes. Ibiza began establishing its own trading stations along the nearby Balearic island of Majorca, such as Na Guardis, where numerous Balearic mercenaries hired on, no doubt as slingers,[13] to fight for Carthage.
During the Second Punic War, the island was assaulted by the two Scipio brothers in 209 BC but remained loyal to Carthage. With the Carthaginian military failing on the Iberian mainland, Ibiza was last used by the fleeing Carthaginian General Mago to gather supplies and men before sailing to Minorca and then to Liguria. Ibiza negotiated a favorable treaty with the Romans, which spared Ibiza from further destruction and allowed it to continue its Carthaginian-Punic institutions well into the Empire days, when it became an official Roman municipality. For this reason, Ibiza today contains excellent examples of late Carthaginian-Punic civilization. During the Roman Empire, the island became a quiet imperial outpost, removed from the important trading routes of the time.
After the fall of the Western Roman Empire and a brief period of first Vandal and then Byzantine rule, the island was conquered by the Moors in 990, the few remaining locals converted to Islam and Berber settlers came in. Under Islamic rule, Ibiza came in close contact with the city of Dénia—the closest port in the nearby Iberian peninsula, located in the Valencian Community—and the two areas were administered jointly by the Taifa of Dénia.
Ibiza together with the islands of Formentera and Minorca were invaded by the Norwegian King Sigurd I of Norway in the spring of 1110 on his crusade to Jerusalem. The king had previously conquered the cities of Sintra, Lisbon, and Alcácer do Sal and given them over to Christian rulers, in an effort to weaken the Muslim grip on the Iberian peninsula. King Sigurd continued to Sicily where he visited King Roger II of Sicily.
The island was conquered by Aragonese King James I in 1235. The local Muslim population got deported as was the case with neighboring Majorca and elsewhere, and Christians arrived from Girona. The island maintained its own self-government in several forms until 1715, when King Philip V of Spain abolished the local government's autonomy. The arrival of democracy in the late 1970s led to the Statute of Autonomy of the Balearic Islands. Today, the island is part of the Balearic Autonomous Community, along with Majorca, Minorca, and Formentera.
Geography
Ibiza is a rock island covering an area of 572.56 square kilometres (221.07 sq mi), almost six times smaller than Majorca, but over five times larger than Mykonos (in the Greek Isles) or 10 times larger than Manhattan in New York City.
Ibiza is the larger of a group of the western Balearic archipelago called the "Pityuses" or "Pine Islands" composed of itself and Formentera. The Balearic island chain includes over 50 islands, many of which are uninhabited. The highest point of the island is Sa Talaiassa, at 475 metres (1,558 ft).
Administration
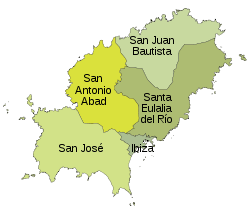
Ibiza is administratively part of the autonomous community of the Balearic Islands, whose capital is Palma, on the island of Majorca. Ibiza comprises 5 of the community's 67 municipalities. Clockwise from the south coast, these are:
- Sant Josep de sa Talaia (Spanish: San José)
- Sant Antoni de Portmany (San Antonio Abad)
- Sant Joan de Labritja (San Juan Bautista)
- Santa Eulària des Riu (Santa Eulalia del Río)
- Vila d'Eivissa ("Ibiza Town"; known simply as Vila, "Town")
| Municipality | Area in square km |
Census population 1 November 2001 |
Estimated population 1 January 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sant Josep de sa Talaia | 159.4 | 14,267 | 22,871 |
| Sant Antoni de Portmany | 126.8 | 15,081 | 22,136 |
| Sant Joan de Labritja | 121.7 | 4,094 | 5,477 |
| Santa Eulària des Riu | 153.6 | 19,808 | 32,637 |
| Vila d'Eivissa (Ibiza) | 11.1 | 34,826 | 49,516 |
| Totals | 572.6 | 88,076 | 132,637 |
At the 2001 census these municipalities had a total population of 88,076 inhabitants, which had risen to an estimated 132,637 by the start of 2010, and have a land area of 572.56 km2 (221.07 sq mi).
Climate
The summer climate of Ibiza typically ranges in the upper 20s °C (70s–80s °F), often reaching 30.0 °C (86 °F), with overnight lows below 22.2 °C (72 °F). The winter, off-season temperature reaches lows of 8.1–14.2 °C (46.6–57.6 °F), with highs in the upper-teens °C (60s °F). On average it snows once every ten years.
| Climate data for Eivissa Airport 6 metres (20 feet) (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 23.8 (74.8) |
23.5 (74.3) |
26.5 (79.7) |
27.8 (82) |
31.0 (87.8) |
36.5 (97.7) |
36.6 (97.9) |
36.6 (97.9) |
38.4 (101.1) |
32.0 (89.6) |
28.4 (83.1) |
23.8 (74.8) |
38.4 (101.1) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 15.7 (60.3) |
15.9 (60.6) |
17.7 (63.9) |
19.7 (67.5) |
22.7 (72.9) |
26.8 (80.2) |
29.7 (85.5) |
30.3 (86.5) |
27.7 (81.9) |
24.0 (75.2) |
19.6 (67.3) |
16.7 (62.1) |
22.2 (72) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 11.9 (53.4) |
12.1 (53.8) |
13.7 (56.7) |
15.6 (60.1) |
18.6 (65.5) |
22.6 (72.7) |
25.6 (78.1) |
26.3 (79.3) |
23.8 (74.8) |
20.2 (68.4) |
15.9 (60.6) |
13.1 (55.6) |
18.3 (64.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 8.1 (46.6) |
8.3 (46.9) |
9.6 (49.3) |
11.4 (52.5) |
14.6 (58.3) |
18.4 (65.1) |
21.4 (70.5) |
22.2 (72) |
19.9 (67.8) |
16.5 (61.7) |
12.3 (54.1) |
9.5 (49.1) |
14.3 (57.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −1.2 (29.8) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
0.8 (33.4) |
3.4 (38.1) |
6.8 (44.2) |
10.0 (50) |
14.0 (57.2) |
11.0 (51.8) |
11.4 (52.5) |
6.3 (43.3) |
1.0 (33.8) |
0.4 (32.7) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 37 (1.46) |
36 (1.42) |
27 (1.06) |
31 (1.22) |
27 (1.06) |
11 (0.43) |
5 (0.2) |
18 (0.71) |
57 (2.24) |
58 (2.28) |
53 (2.09) |
52 (2.05) |
413 (16.26) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1 mm) | 5 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 45 |
| Average snowy days | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 162 | 166 | 211 | 246 | 272 | 299 | 334 | 305 | 236 | 205 | 157 | 151 | 2,744 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 52 | 54 | 57 | 63 | 63 | 67 | 72 | 70 | 66 | 60 | 52 | 54 | 60.8 |
| Source #1: Agencia Estatal de Meteorología[14] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: Agencia Estatal de Meteorología,[15] Met Office for snow days[16] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Ibiza | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average sea temperature °C (°F) | 14.7 (58.5) |
14.3 (57.7) |
14.5 (58.0) |
16.3 (61.4) |
19.1 (66.3) |
22.5 (72.6) |
25.1 (77.1) |
26.2 (79.1) |
25.2 (77.4) |
22.7 (72.9) |
19.6 (67.3) |
16.6 (61.8) |
19.7 (67.5) |
| Mean daily daylight hours | 10.0 | 11.0 | 12.0 | 13.0 | 14.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 14.0 | 12.0 | 11.0 | 10.0 | 9.0 | 12.2 |
| Average Ultraviolet index | 2 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 5.4 |
| Source #1: seatemperature.org [17] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: Weather Atlas [18] | |||||||||||||
People
Demographically, Ibiza displays a very peculiar configuration, as census agencies diverge on exact figures. According to the 2001 national census, Ibiza had 88,076 inhabitants (against 76,000 in 1991, 64,000 in 1981, 45,000 in 1971, and 38,000 in 1961). However, two years later, this figure jumped to 108,000 (Govern de les Illes Balears – IBAE 2004), and by the start of 2010 had reached 132,637. This rapid growth stems from the amnesty which incorporated a number of unregistered foreign migrants. In terms of origin, about 55 percent of island residents were born in Ibiza, 35 percent are domestic migrants from mainland Spain (mostly working-class families from Andalusia, and the remainder from Catalonia, Valencia and Castile), and the remaining 10 to 15 percent are foreign, dual and multi-national citizens of the EU and abroad (Govern de les Illes Balears – IBAE 1996). In decreasing order, the most commonly visiting foreigners are German, British, Latin American, French, Italian and Dutch, in addition to a myriad of other nationalities. This mosaic reflects the fluidity of foreigners living and moving across the island, in ways that render impossible to exactly quantify the expatriate population (Rozenberg 1990).
The Spanish composer and music theorist Miguel Roig-Francolí was born in Ibiza,[19] as was the politician and Spain's former Minister of Foreign Affairs, Abel Matutes.[20] Notable former residents of Ibiza include: English punk musician John Simon Ritchie (Sid Vicious),[21] the psychedelic rock band Philiac, comic actor Terry-Thomas,[22] Hungarian master forger Elmyr de Hory,[23] American fraudster Clifford Irving, and film director/actor Orson Welles.[24]
Language
Eivissenc is the native dialect of Catalan that is spoken on Ibiza and nearby Formentera. Catalan shares co-official status with Spanish.[25] Additionally, because of the influence of tourism and expatriates living in or maintaining residences on the island, other languages like German, English and Italian, are widely spoken.
Tourism
Nightlife

.jpg)
_(190294471).jpg)
Ibiza is considered to be a popular tourist destination, especially due to its legendary and at times riotous nightclub based nightlife centered on two areas: Ibiza Town, the island's capital on the southern shore and Sant Antoni to the West.[3]
Night life in Ibiza has undergone several changes since the island's opening to international tourism in the late 1950s. Origins of today's club culture may be traced back to the hippie gatherings held during the 1960s and 1970s. During these, people of various nationalities sharing the hippie ethos would regroup, talk, play music and occasionally take drugs. These would most often happen on beaches during the day, with nude bathing a common sight, and in rented fincas in the evenings or at nights. Apart from this confidential scene, which nevertheless attracted many foreigners to the island, local venues during the 1960s consisted mostly of bars, which would be the meeting points for Ibicencos, ex-pats, seafarers and tourists alike. The Estrella bar on the port and La Tierra in the old city of Eivissa were favourites.[26]
During the 1970s, a decade that saw the emergence of the contemporary nightclub, several places opened and made a lasting impact on Ibiza's nightlife. Four of these original clubs are still in operation today : Pacha, Privilege (formerly Ku), Amnesia and Es Paradís. These four clubs mainly defined nightlife on the White Island, which has evolved and developed from several distinctive elements : open-air parties (Es Paradis, Privilege, Amnesia), held in isolated places, eventually old fincas (Pacha, Amnesia), that mixed in nudity and costume party (Es Paradis, Privilege, Pacha) and enabled people from various backgrounds to blend (all). The hippie ethos served as a common factor that infused all these venues and catalyzed the experience of a certain kind of freedom, accentuated by the holiday nature of most of the stays on the White Island.
During the 1980s, the music played in these clubs gained in reputation and became known as Balearic beat, a precursor of the British Acid house scene. As rave parties blossomed all over Europe, a DJ-driven club culture took hold of Ibizenca nightlife. It was the time when Space opened, thanks to Pepe Rosello, which found a niche in the after-hour parties : basically, the club would close at 6 AM and open again at 7 AM, when all the other clubs were still closed, enabling party-goers to flock from the other clubs to Space and continue dancing in broad daylight.
At the end of the 1990s, the after-hour parties held firm root on the island. In 1999, the Circoloco parties made their debut at DC10, with some of the original elements of Ibiza nightlife at the forefront.[3]
Nowadays, during the summer, top producers and DJs in dance music come to the island and play at the various clubs, in between touring to other international destinations. Some of the most famous DJs run their own weekly nights around the island. Many of these DJs use Ibiza as an outlet for presenting new songs within the house, trance and techno genres of electronic dance music. The city has achieved renowned worldwide fame as a cultural center for house and trance in particular, with its name often being used as a partial metonym for the particular flavor of electronic music originating there, much like Goa in India.
Since 2005, the live music event Ibiza Rocks has helped to redefine the Ibiza party landscape. Bands such as Arctic Monkeys, Kasabian, The Prodigy, and the Kaiser Chiefs have played in the courtyard of the Ibiza Rocks Hotel.
The season traditionally begins at the start of June with Space and DC10's opening parties and finishes on the first weekend of October with the Closing Parties. A typical schedule for clubbers going to Ibiza includes waking at noon, early evening naps, late night clubbing, and "disco sunrises." Due to Ibiza's notable tolerance toward misbehaviour from young adult tourists, it has acquired the sobriquet "Gomorrah of the Med." Also well-known is Café del Mar, a long-standing bar where many tourists traditionally view the sunset made famous by José Padilla, who has released more than a dozen eponymous album compilations of ambient music played at the location. That and other bars nearby have become an increasingly popular venue for club pre-parties after sunset, hosting popular DJ performers.
The island's government is trying to encourage a more cultured and quieter tourism scene, passing rules including the closing of all nightclubs by 6 a.m. at the latest, and requiring all new hotels to be 5-star.[27] The administration wants to attract a more international mixture of tourists.[28]
In popular culture
A number of novels and other books have been written using Ibiza as the setting, including "The White Island" by Stephen Armstrong, Joshua Then and Now by Mordecai Richler, Soma Blues by Robert Sheckley,[29] Vacation in Ibiza by Lawrence Schimel,[30] A Short Life on a Sunny Isle: An Alphonse Dantan Mystery by Hannah Blank,[31] They Are Ruining Ibiza by A. C. Greene,[32] and The Python Project by Victor Canning.[33]
World Heritage Site
Though primarily known for its party scene, large portions of the island are registered as UNESCO World Heritage Sites,[34] and thus protected from the development and commercialization of the main cities. A notable example includes "God's Finger" in the Benirràs Bay as well as some of the more traditional Ibizan cultural sites such as the remains of the first Phoenician settlement at Sa Caleta. Other sites are still under threat from the developers, such as Ses Feixes Wetlands,[35] but this site has now been recognised as a threatened environment, and it is expected that steps will be taken to preserve this wetland.
Because of its rustic beauty, companies and artists alike frequently use the island for photographic and film shoots. A monument ("The Egg") erected in honour of Christopher Columbus can be found in Sant Antoni; Ibiza is one of several places purporting to be his birthplace.
Development
Since the early days of mass tourism on the island, there have been a large number of development projects ranging from successful ventures, such as the super clubs at Space and Privilege, to failed development projects, such as Josep Lluís Sert's abandoned hotel complex at Cala D'en Serra,[36] the half-completed and now demolished "Idea" nightclub in Sant Antoni,[37] and the ruins of a huge restaurant/nightclub in the hills near Sant Josep called "Festival Club" that only operated for three summer seasons in the early 1970s.[38] The transient nature of club-oriented tourism is most obvious in these ruins scattered all over the island. Local artist Irene de Andrès has tackled the difficult issue of the impact of mass tourism on the island local landscapes, both natural and cultural, in an ongoing project called "Donde nada ocurre" (Where nothing happens).[39] In 2013, Ibiza property prices generally remained above market value, and many of the development projects on the island have now been completed or continue, as well as some new projects announced at the end of 2012. Since 2009, Ibiza has seen an increase in tourist numbers every year, with nearly 6 million people traveling through Ibiza Airport in 2012. The summer season has become concentrated between June and September, focusing on the "clubbing calendar"[40] which is currently booming. In recent years, the luxury market has dramatically improved, with new restaurants, clubs, and improvements to the marina in Ibiza Town.[41]
Ibiza's increased popularity has led to problems with potable water shortages and overrun infrastructure. This has led to imposition of a "Sustainable Tourism Tax" which went into effect in July 1, 2016.[42] Minister of Tourism Vincente Torres stated in an interview in 2016 that the government has instituted a moratorium and building in certain areas. He said that with almost 100,000 legal touristic beds and about 132,000 inhabitants on the island's 572 square kilometres (221 sq mi) not much more tourism can be supported.[42]
Transport
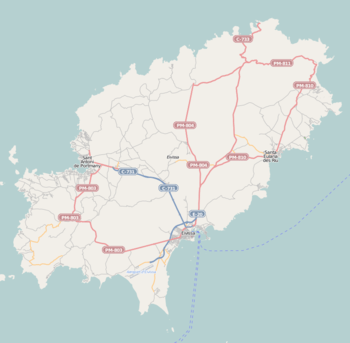
Ibiza is served by Ibiza Airport, which has many international flights during the summer tourist season, especially from the European Union.
There are also ferries from the harbour of Sant Antoni and Ibiza Town to Barcelona, Majorca, Dénia, and Valencia. There are also ferries to Formentera leaving Sant Antoni Harbour (normally every Wednesday), and daily from Ibiza Town, Santa Eulària, and Figueretes–Platja d'en Bossa.
Several public busses also travel between Sant Antoni and Ibiza Town—every 15 minutes in summer and every half-hour in winter. In addition, there are buses from Sant Antoni to Cala Bassa, Cala Conta and Cala Tarida, and to the Airport. From Ibiza there are buses to the Platja d'en Bossa, Ses Salines, the Airport, and Santa Eulària.
Cuisine
Ibiza's local cuisine is typically Mediterranean. Of the most common culinary products of the island are sweets known as flaons. Other savory dishes include sofrit pagès, bullit de peix (fish stew), arròs de matança (rice with pork) and arròs a la marinera.
Gallery
- Sun set across Sant Antoni Bay
 Eivissa, Cala Salada, at north of Sant Antoni de Portmany
Eivissa, Cala Salada, at north of Sant Antoni de Portmany- Staircase in Ibiza Town
.jpg) Cala d'Hort, Ibiza
Cala d'Hort, Ibiza Sant Antoni de Portmany from afar
Sant Antoni de Portmany from afar- The Egg of Columbus in Sant Antoni
 The Platja d'en Bossa looking north towards Ibiza Town
The Platja d'en Bossa looking north towards Ibiza Town- Puig de Missa in Santa Eulària
- Marina of Santa Eulària des Riu
- Sunset San Antonio
- s'Arenal Gros Bay in Portinatx
- Private bay
- Clear water
- Cala Tarida
 Ibiza boat cruises
Ibiza boat cruises- Phoenician settlement remains on the headland at Sa Caleta
 Es Cubells
Es Cubells Platja de Comte
Platja de Comte Old country house
Old country house Port
Port
See also
- Eivissa Town (Vila d'Eivissa or Vila)
- Balearic Islands
- Pityusic Islands
- Formentera
- Majorca
- Minorca
- List of municipalities in Balearic Islands
- Electronic Dance Music
- International Music Summit
References
Notes
- ↑ Ibiza renews its party spirit, Luke Bainbridge, June 27, 2010 (The Guardian)
- ↑ Inside the police crackdown on Ibizas endless party culture Michelle Lhooqe, November 13, 2015 (Vice TV website)
- 1 2 3 Armstrong, Stephen (2006-07-01). "Ibiza unplugged". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 2010-05-04.
- ↑ "Ibiza". Oxford English Dictionary (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. September 2005. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- ↑ Random House dictionary
- ↑ American Heritage dictionary
- ↑ Jones, Daniel; Peter Roach; et al. (2003). English Pronouncing Dictionary (16th ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- ↑ Wells, John C. (2000). Longman Pronunuciation Dictionary (2nd ed.). Harlow: Pearson Education Limited.
- ↑ "Ibiza Literature, Literature in Ibiza". Liveibiza.com. Retrieved 2013-03-26.
- ↑ Kuhbier, Heinrich; Alcover, Josep Antoni; Guerau d'Arellano Tur, Cristòfol, eds. (1984). Biogeography and Ecology of the Pityusic Islands. Monographiae Biologicae, Volume 52. The Hague, The Netherlands: Dr. W. Junk (Kluwer). p. 1. ISBN 978-90-6193-105-8.
- ↑ Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon
- ↑ "Ivica". Encyclopaedia Metropolitana, Or, Universal Dictionary of Knowledge. 21. London. 1845. p. 167.
- ↑ Strab. xiv. p. 654; Plin. l. c "The Rhodians, like the Baleares, were celebrated slingers"
Sil. Ital. iii. 364, 365: "Iam cui Tlepolemus sator, et cui Lindus origo, Funda bella ferens Balearis et alite plumbo." (Latin). - ↑ "Valores climatológicos normales. Ibiza, Aeropuerto". March 2016.
- ↑ "Valores extremos. Ibiza, Aeropuerto". March 2016.
- ↑ "Ibiza weather".
- ↑ "Ibiza Sea Temperature". seatemperature.org. Retrieved 15 March 2017.
- ↑ "Ibiza, Spain - Climate data". Weather Atlas. Retrieved 15 March 2017.
- ↑ Enciclopèdia d'Eivissa i Formentera. "Roig-Francoli Costa, Miguel Angel"
- ↑ Who's Who at NATO. "Abel Matutes"
- ↑ "Sid Vicious - Life History Part 1".
- ↑ Bounder! The Biography of Terry-Thomas by Graham McCann, serialised in The Times
- ↑ Clark, Thomas G. (18 May 2011). "Sant Agustí".
- ↑ "Ibiza Literature, Literature in Ibiza".
- ↑ "Introduction to Ibiza". Frommer's. 2006-11-20. Retrieved 2010-05-04.
- ↑ "Bares y cafés de la Marina". Diario de Ibiza. 23 December 2016.
- ↑ Robbins, Tom (2007-11-18). "Is the party over in Ibiza?". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 2010-05-04.
- ↑ "Is Ibiza changing??". Bbs.clubplanet.com. Retrieved 2013-03-26.
- ↑ Sheckley, Robert (1997). Soma Blues. New York: Forge/Tom Doherty Associates. p. 222. ISBN 0-312-86273-3.
- ↑ Schimel, Lawrence (2003). Vacation in Ibiza. Eurotica. ISBN 1-56163-377-1.
- ↑ Blank, Hannah (2002). A Short Life on a Sunny Isle: An Alphonse Dantan Mystery. New York: Hightrees/Prism Corporation. p. 221. ISBN 0-9652778-4-4.
- ↑ Greene, A. C. (1998). They Are Ruining Ibiza. Denton, TX: University of North Texas Press. p. 123. ISBN 1-57441-042-3.
- ↑ Canning, Victor (1967). The Python Project. London, UK: Heinemann. p. 284.
- ↑ Centre, UNESCO World Heritage. "Ibiza, Biodiversity and Culture".
- ↑ Ibiza Preservation Fund
- ↑ Clark, Thomas G. (7 July 2011). "Josep Lluís Sert's abandoned hotel at Cala D'en Serra.".
- ↑ Clark, Thomas G. (29 May 2011). "An abandoned Idea".
- ↑ "Ibiza Party". TravelnTourism. Retrieved 2016-06-18.
- ↑ "Irene de Andrès website". 24 December 2016.
- ↑ "Clubbing calendar", Ibiza-spotlight.com, August 2013.
- ↑ "Ibiza – a hedonist's paradise whatever your poison". Ibiza Traveller. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- 1 2 Shortlidge, Chadler (17 July 2016). "Ibiza "Cannot Support Much More Increase in Tourism" Says Govt". Pulse. Retrieved 23 July 2016.
External links
- Consell Insular d'Eivissa (local government) (in Catalan)
- "Official tourism portal of Ibiza" – Consell Insular d'Eivissa
- "Ibiza and the Historic Town of Eivissa" by The Guardian