Eastern Area Command (RAAF)
| Eastern Area Command | |
|---|---|
|
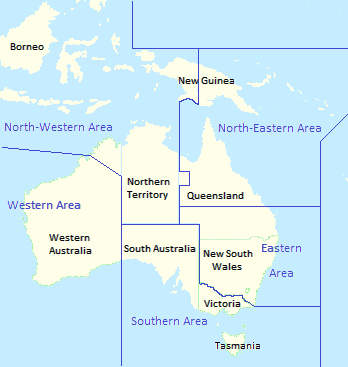
RAAF area commands, November 1942. Eastern Area's boundaries remained in place until it re-formed as Home Command in October 1953, beginning the supersession of the area command system. | |
| Active | 1942–53 |
| Allegiance | Australia |
| Branch | Royal Australian Air Force |
| Role |
Air defence Aerial reconnaissance Protection of adjacent sea lanes |
| Garrison/HQ |
Sydney (1942–49) Glenbrook (1949–53) |
| Engagements | World War II |
| Commanders | |
| Notable commanders |
William Anderson (1942–43) Alan Charlesworth (1943–44, 1946) Leon Lachal (1945, 1946–47) Frank Lukis (1945–46) Frank Bladin (1947–48) John McCauley (1949–53) |
Eastern Area Command was one of several geographically based commands raised by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) during World War II. It was formed in May 1942, and controlled units based in New South Wales and southern Queensland. Headquartered in Sydney, Eastern Area Command was primarily responsible for air defence, aerial reconnaissance and protection of the sea lanes within its boundaries. The area continued to function following the end of the war, transferring its headquarters to Glenbrook, in the Blue Mountains, in 1949. By this time most of the RAAF's operational units were based within Eastern Area's boundaries. It was re-formed in October 1953 as Home Command (renamed Operational Command in 1959, and Air Command in 1987) under the RAAF's new functional command-and-control system.
History
World War II
Prior to World War II, the Royal Australian Air Force was small enough for all its elements to be directly controlled by RAAF Headquarters in Melbourne. When war broke out, the RAAF began to decentralise its command structure, commensurate with expected increases in manpower and units.[1][2] Between March 1940 and May 1941, Australia and Papua were divided into four geographically based command-and-control zones: Central Area, Southern Area, Western Area, and Northern Area.[3] The roles of the area commands were air defence, protection of adjacent sea lanes, and aerial reconnaissance. Each was led by an Air Officer Commanding (AOC) who controlled the administration and operations of all air bases and units within his boundary.[2][3]
Central Area was disbanded in August 1941 and its responsibilities divided between Southern Area, Northern Area, and the newly formed No. 2 (Training) Group.[4] The outbreak of the Pacific War resulted in Northern Area being split in January 1942 into North-Western and North-Eastern Areas, to counter separate Japanese threats to Northern Australia and New Guinea.[1][5] Southern Area was also considered appropriate for division owing to its size, so the Air Board proposed assigning responsibility for operational and maintenance units within New South Wales to a new area command, Eastern Area, which would also assume control of units in southern Queensland from North-Eastern Area.[6]
Headquartered in the Sydney suburb of Edgecliff, Eastern Area Command was formed on 15 May 1942 under the leadership of Air Vice Marshal Bill Anderson. Staff numbered 114, including forty-five officers.[7] Training units in New South Wales remained part of No. 2 (Training) Group. No. 5 (Maintenance) Group was formed in Sydney on 1 June, and took responsibility for all maintenance units initially controlled by Eastern Area Command.[6][8] In September, the Allied Air Forces commander in the South West Pacific Area, Major General George Kenney, formed the majority of his US flying units into the Fifth Air Force, and most of their Australian counterparts into RAAF Command, led by Air Vice Marshal Bill Bostock.[9][10] Bostock exercised control of Australian air operations through the area commands, although RAAF Headquarters continued to hold overarching administrative authority, meaning that Bostock and his area commanders were ultimately dependent on the Chief of the Air Staff, Air Vice Marshal George Jones, for supplies and equipment.[11]

Of necessity, the RAAF's two northerly area commands were primarily responsible for bombing and air defence, while the other commands focussed on maritime patrol and anti-submarine warfare.[11] Aircraft from Eastern Area flew over 400 patrol, anti-submarine, and convoy escort missions in January 1943.[12] By April, the command was operating seven combat units: No. 5 Squadron, flying army cooperation missions with CAC Wirraways out of Kingaroy, Queensland; No. 23 Squadron, flying dive-bombing missions with Wirraways from Lowood, Queensland; No. 24 Squadron, flying dive-bombing missions with Wirraways from Bankstown, New South Wales; No. 32 Squadron, flying reconnaissance and bombing missions with Lockheed Hudsons from Camden, New South Wales; No. 71 Squadron, flying maritime reconnaissance and anti-submarine missions with Avro Ansons from Lowood; No. 73 Squadron, flying maritime reconnaissance and anti-submarine missions with Ansons from Nowra, New South Wales; and No. 83 Squadron, flying fighter missions with Wirraways from Strathpine, Queensland.[13] Area headquarters staff numbered 626, including ninety-nine officers.[14] Bristol Beauforts of No. 32 Squadron were credited with damaging a Japanese submarine on 19 June, but neither the RAAF nor the Royal Australian Navy was able to destroy any enemy submarines in coastal waters during 1943.[15]
Anderson handed over command of Eastern Area to Air Commodore John Summers in July 1943.[16][17] Group Captain Alister Murdoch became senior air staff officer (SASO).[18] On 22 October, Avro Lancaster Q-for-Queenie, piloted by Flight Lieutenant Peter Isaacson, "buzzed" the Eastern Area headquarters building in Edgecliff before flying under the Sydney Harbour Bridge, flouting regulations and becoming the largest aircraft to pull such a stunt.[19] The same month, the Air Board proposed carving a new area command out of Eastern Area, which by then was considered too large to be controlled by one headquarters and therefore ripe for division. The new command, to be known as Central Area, would have been responsible for training and operational units in southern Queensland; the War Cabinet deferred its decision on the proposal. The concept was raised again in August 1944, and this time Central Area Command was to control maintenance units, as well as training and operations, in southern Queensland; once again, nothing came of the proposal.[20]
Air Commodore Alan Charlesworth was appointed AOC Eastern Area in December 1943.[16] Japanese submarine activity had decreased in the months prior to Charlesworth taking command, and he was concerned that Allied ships were becoming complacent. He observed "a general slackening off in procedure; ships are seldom where they should be, and a minority of merchant ships identify themselves to aircraft". The RAAF's patrols had also settled into a predictable pattern that an observant submarine captain could easily avoid.[21][22] Charlesworth relinquished command in September 1944 to take over North-Western Area.[23][24] In December, aircraft from Eastern Area took part in the search for the German submarine U-862, but could not prevent it sinking the Liberty ship Robert J. Walker on Christmas; a Beaufort of No. 15 Squadron, based at Camden, located the wreck. No. 32 Squadron lost a Beaufort with its crew shortly after takeoff from Lowood during the search for U-862, which was called off in January 1945.[25][26] That month, Air Commodore Leon Lachal became AOC Eastern Area, and held command for the duration of the Pacific War.[23]
Post-war activity and reorganisation
Following the end of the Pacific War in August 1945, South West Pacific Area was dissolved and RAAF Headquarters again assumed full control of all its operational elements, including the area commands.[27] According to the official history of the post-war Air Force, the AOC Eastern Area was considered "Australia's senior operational airman" and delegated by the Chief of the Air Staff with day-to-day responsibility for the nation's air defence.[28] Most of the RAAF's bases and aircraft employed in operations were situated within Eastern Area's sphere of control in New South Wales and southern Queensland.[29] Air Commodore Frank Lukis succeeded Lachal as AOC in December 1945. By the end of the month, headquarters staff numbered 1,122, including 104 officers.[30] No. 82 (Bomber) Wing came under the control of Eastern Area Command in April 1946, when it moved to RAAF Station Amberley, Queensland; initially operating B-24 Liberators, the wing re-equipped with Avro Lincolns soon after.[31][32] By this time Eastern Area headquarters occupied seven mansions in Point Piper, Sydney; it subsequently relocated to Bradfield Park.[33][34] Lukis retired from the Air Force in May, and Charlesworth took over command.[35][36]
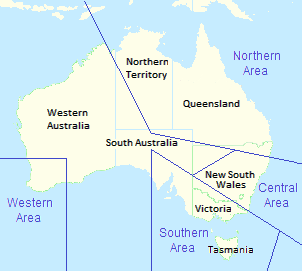
In July–August 1946, Eastern Area Command oversaw the establishment of No. 86 (Transport) Wing, operating C-47 Dakotas, at RAAF Station Schofields, New South Wales, displacing No. 78 (Fighter) Wing, which moved to RAAF Station Williamtown, and began operating P-51 Mustangs.[37] The following month, Air Vice Marshal Jones proposed reducing the five mainland area commands (North-Western, North-Eastern, Eastern, Southern, and Western Areas) to three: Northern Area, covering Queensland and the Northern Territory; Eastern Area, covering New South Wales; and Southern Area, covering Western Australia, South Australia, Victoria and Tasmania. The proposal was part of a much larger plan to restructure the post-war RAAF; the Federal government rejected the plan and the wartime area command boundaries largely remained in place.[38][39] Lachal succeeded Charlesworth as AOC Eastern Area in October, and held command until his retirement from the Air Force in July 1947.[40][41]

Lachal's successor as AOC Eastern Area, Air Vice Marshal Frank Bladin, was responsible for preparing the transfer of its headquarters from Bradfield Park to the former Lapstone Hotel at Glenbrook in the Lower Blue Mountains, a process that was completed in 1949.[42][43] As well as commanding a view of the surrounding countryside, the property was within five kilometres (three miles) of the City of Penrith and thirty kilometres (twenty miles) of RAAF Station Richmond, and incorporated a disused railway tunnel that offered, according to government correspondence, "complete protection from Atom Bomb attack". An adjoining property, "Briarcliffe", was purchased soon afterwards to augment the new headquarters' accommodation facilities.[43] Bladin completed his term as AOC Eastern Area in October 1948.[42] Air Vice Marshal John McCauley was appointed AOC in March the following year.[44] McCauley commanded Eastern Area during the early years of the Malayan Emergency, and oversaw the deployment of No. 90 (Composite) Wing to administer RAAF units stationed there—a Lincoln squadron detached from No. 82 Wing and a Dakota squadron from No. 86 Wing.[45][46] Having re-equipped with de Havilland Vampire jets, No. 78 Wing departed Williamtown for garrison duties with the RAF on Malta in July 1952.[47][48] In May 1953, Eastern Area's SASO, Group Captain Frank Headlam, announced that the Air Force was planning to re-equip No. 82 Wing with English Electric Canberra jet bombers, and also procure CAC Sabre swept-wing jet fighters.[49]
The Federal government retired Air Marshal Jones in 1952 and replaced him with Air Marshal Donald Hardman, RAF, who proceeded to re-organise the RAAF command-and-control system along functional lines, establishing Home (operational), Training, and Maintenance Commands in October 1953. The first was re-formed from Eastern Area Command as it was considered the RAAF's de facto operational organisation. The second was re-formed from Southern Area Command, as it was the hub of training services, controlling those in New South Wales and Queensland as well as Victoria and South Australia. The third and last functional command was formed from the extant Maintenance Group headquarters in Melbourne. The transition to a functional system was completed in February 1954, when the three new commands assumed control of operations, training and maintenance from Western, North-Western, and North-Eastern Areas.[50][51]
Aftermath
The functional commands established in 1953–54 were revised in 1959. Home Command was renamed Operational Command, and Training and Maintenance Commands merged to become Support Command.[52] Operational Command was renamed Air Command in 1987, and three years later Support Command split into Logistics Command and Training Command.[53] Throughout the evolution from Home to Operational to Air Command, the headquarters remained at Glenbrook in the Blue Mountains.[43] In 1997, logistics management became the responsibility of Support Command (Air Force), the RAAF component of the Defence-wide Support Command Australia (later subsumed by the Defence Materiel Organisation).[54][55][56] Training Command was re-formed as Air Force Training Group, a force element group under Air Command, in 2006.[57] Air Command thus became the sole command-level organisation in the RAAF.[58]
Order of battle
As at May 1944, Eastern Area controlled the following squadrons:[59]
- No. 11 Squadron, equipped with Consolidated PBY Catalinas, based in Rathmines
- No. 21 Squadron, equipped with Vultee Vengeances, based at Camden
- No. 32 Squadron, equipped with Bristol Beauforts, based at Lowood
- No. 107 Squadron, equipped with Vought Kingfishers, based at St. George's Basin
Notes
- 1 2 Stephens, The Royal Australian Air Force, pp. 111–112
- 1 2 "Organising for War: The RAAF Air Campaigns in the Pacific". Pathfinder. No. 121. Air Power Development Centre. October 2009. Retrieved 10 July 2015.
- 1 2 Gillison, Royal Australian Air Force, pp. 91–92
- ↑ Gillison, Royal Australian Air Force, p. 112
- ↑ Gillison, Royal Australian Air Force, p. 311
- 1 2 Ashworth, How Not to Run an Air Force! Volume One, pp. xxi, 134–135
- ↑ Eastern Area Headquarters, Operations Record Book, p. 1
- ↑ Ashworth, How Not to Run an Air Force! Volume Two, p. 212
- ↑ Gillison, Royal Australian Air Force, pp. 585–588
- ↑ Odgers, Air War Against Japan, pp. 4–6
- 1 2 Stephens, The Royal Australian Air Force, pp. 144–145
- ↑ Stevens, A Critical Vulnerability, pp. 221–222
- ↑ Odgers, Air War Against Japan, p. 141
- ↑ Eastern Area Headquarters, Operations Record Book, p. 292
- ↑ Odgers, Air War Against Japan, pp. 152–153
- 1 2 Ashworth, How Not to Run an Air Force! Volume One, p. 303
- ↑ "Summers, John Hamilton". World War 2 Nominal Roll. Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- ↑ Dennis et al, The Oxford Companion to Australian Military History, p. 412
- ↑ "Lancaster bomber made illegal pass under Sydney Harbour Bridge". Air Power Development Centre. Retrieved 6 April 2016.
- ↑ Ashworth, How Not to Run an Air Force! Volume One, pp. 214–217, 227–228
- ↑ Odgers, Air War Against Japan, p. 349
- ↑ Stevens, A Critical Vulnerability, p. 258
- 1 2 Ashworth, How Not to Run an Air Force! Volume One, p. 304
- ↑ "New Air Member for Personnel". The Sydney Morning Herald. 13 September 1944. p. 3. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- ↑ Stevens, A Critical Vulnerability, pp. 269–272
- ↑ Odgers, Air War Against Japan, pp. 350–351
- ↑ Ashworth, How Not to Run an Air Force! Volume One, p. 262
- ↑ Stephens, Going Solo, p. 344
- ↑ Stephens, Going Solo, pp. 72–73
- ↑ Eastern Area Headquarters, Operations Record Book, pp. 1101, 1105
- ↑ Bennett, Highest Traditions, pp. 250–251
- ↑ "Order of Battle – Air Force – Headquarters". Department of Veterans' Affairs. Retrieved 12 July 2015.
- ↑ "RAAF units for Bradfield". The Sydney Morning Herald. 27 May 1946. p. 4. Retrieved 6 August 2015.
- ↑ "RAAF to leave Point Piper". The Sydney Morning Herald. 12 June 1946. p. 4. Retrieved 6 August 2015.
- ↑ "Lukis, Francis William Fellowes". World War 2 Nominal Roll. Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- ↑ "All Air Force cottages seized". The Sydney Morning Herald. 1 June 1946. p. 5. Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- ↑ No. 78 Wing Headquarters (1943–59). Operations Record Book. RAAF Unit History sheets. National Archives of Australia. pp. 106–108. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ↑ Helson, The Private Air Marshal, pp. 321–325
- ↑ Stephens, Going Solo, pp. 68, 462
- ↑ "Air chief on tour of inspection". The Newcastle Herald. 25 October 1946. p. 2. Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- ↑ "Lachal, Leon Victor". World War 2 Nominal Roll. Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- 1 2 Dalkin, R.N. "Bladin, Francis Masson (1898–1978)". Australian Dictionary of Biography. Australian National University. Retrieved 6 August 2015.
- 1 2 3 Stephens, Going Solo, pp. 69–71
- ↑ Clark, Chris. "McCauley, Sir John Patrick Joseph (1899–1989)". Australian Dictionary of Biography. Australian National University. Retrieved 6 August 2015.
- ↑ Stephens, Going Solo, pp. 246–247
- ↑ "RAAF wing takes over a new important job". The Examiner. Launceston, Tasmania: National Library of Australia. 20 April 1951. p. 2. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ↑ Stephens, Going Solo, pp. 202–203
- ↑ "DHA Vampire". RAAF Museum. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- ↑ "Re-equipping bomber wing". The Canberra Times. Canberra: National Library of Australia. 20 May 1953. p. 4. Retrieved 6 April 2016.
- ↑ "Sir Donald Hardman’s Reorganisation of the RAAF". Pathfinder. No. 106. Air Power Development Centre. March 2009. Retrieved 10 July 2015.
- ↑ Stephens, Going Solo, pp. 73–76, 462–463
- ↑ Stephens, Going Solo, pp. 76–77
- ↑ Dennis et al, The Oxford Companion to Australian Military History, pp. 150–151
- ↑ Stephens, The Royal Australian Air Force, p. 307
- ↑ "Program 6: Support Command" (PDF). Defence Annual Report 1997–98. Department of Defence. 1998. p. 224. Retrieved 10 July 2015.
- ↑ Horner, Making the Australian Defence Force, pp. 278–279
- ↑ "Air Force Training Group". Royal Australian Air Force. Retrieved 10 July 2015.
- ↑ "Air Command". Royal Australian Air Force. Archived from the original on 20 July 2008. Retrieved 10 July 2015.
- ↑ Gogler, We Never Disappoint, p. 105
References
- Ashworth, Norman (2000). How Not to Run an Air Force! Volume One – Narrative. Canberra: RAAF Air Power Studies Centre. ISBN 0-642-26550-X.
- Ashworth, Norman (2000). How Not to Run an Air Force! Volume Two – Documents. Canberra: RAAF Air Power Studies Centre. ISBN 0-642-26551-8.
- Bennett, John (1995). Highest Traditions: The History of No. 2 Squadron, RAAF. Canberra: Australian Government Publishing Service. ISBN 0-644-35230-2.
- Dennis, Peter; Grey, Jeffrey; Morris, Ewan; Prior, Robin (2008) [1995]. The Oxford Companion to Australian Military History. South Melbourne: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-551784-2.
- Eastern Area Headquarters (1942–45). Operations Record Book. RAAF Unit History Sheets. Canberra: National Archives of Australia.
- Gillison, Douglas (1962). Australia in the War of 1939–1945: Series Three (Air) Volume I – Royal Australian Air Force 1939–1942. Canberra: Australian War Memorial. OCLC 2000369.
- Gogler, Kevin (2012). We Never Disappoint: A History of 7 Squadron RAAF 1940–1945. Canberra: Air Power Development Centre. ISBN 978-1-920800-68-0.
- Helson, Peter (2010). The Private Air Marshal. Canberra: Air Power Development Centre. ISBN 978-1-920800-50-5.
- Horner, David (2001). The Australian Centenary History of Defence Volume IV: Making the Australian Defence Force. Melbourne: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-554117-5.
- Odgers, George (1968) [1957]. Australia in the War of 1939–1945: Series Three (Air) Volume II – Air War Against Japan 1943–1945. Canberra: Australian War Memorial. OCLC 246580191.
- Stephens, Alan (1995). Going Solo: The Royal Australian Air Force 1946–1971. Canberra: Australian Government Publishing Service. ISBN 0-644-42803-1.
- Stephens, Alan (2006) [2001]. The Royal Australian Air Force: A History. London: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-555541-4.
- Stevens, David (2005). A Critical Vulnerability: The Impact of the Submarine Threat on Australia's Maritime Defence 1915–1954. Canberra: Sea Power Centre – Australia. ISBN 0-642-29625-1.