Easter Rising
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Easter Rising (Irish: Éirí Amach na Cásca),[2] also known as the Easter Rebellion, was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter Week, April 1916. The Rising was launched by Irish republicans to end British rule in Ireland and establish an independent Irish Republic while the United Kingdom was heavily engaged in the First World War. It was the most significant uprising in Ireland since the rebellion of 1798, and the first armed action of the Irish revolutionary period.
Organised by a seven-man Military Council of the Irish Republican Brotherhood,[3] the Rising began on Easter Monday, 24 April 1916, and lasted for six days. Members of the Irish Volunteers—led by schoolmaster and Irish language activist Patrick Pearse, joined by the smaller Irish Citizen Army of James Connolly and 200 women of Cumann na mBan—seized key locations in Dublin and proclaimed an Irish Republic. The British Army brought in thousands of reinforcements as well as artillery and a gunboat. There was fierce street fighting on the routes into the city centre, where the rebels put up stiff resistance, slowing the British advance and inflicting heavy casualties. Elsewhere in Dublin, the fighting mainly consisted of sniping and long-range gun battles. The main rebel positions were gradually surrounded and bombarded with artillery. There were isolated actions in other parts of Ireland, with attacks on the Royal Irish Constabulary barracks at Ashbourne, County Meath, County Cork and in County Galway, and the seizure of the town of Enniscorthy, County Wexford. Germany had sent a shipment of arms to the rebels, but the British had intercepted it just before the Rising began. Volunteer leader Eoin MacNeill had then issued a countermand in a bid to halt the Rising, which greatly reduced the number of rebels who mobilised.
With much greater numbers and heavier weapons, the British Army suppressed the Rising. Pearse agreed to an unconditional surrender on Saturday 29 April, although sporadic fighting continued until Sunday, when word reached the other rebel positions. After the surrender the country remained under martial law. About 3,500 people were taken prisoner by the British, many of whom had played no part in the Rising, and 1,800 of them were sent to internment camps or prisons in Britain. Most of the leaders of the Rising were executed following courts-martial. The Rising brought physical force republicanism back to the forefront of Irish politics, which for nearly 50 years had been dominated by constitutional nationalism. It, and the British reaction to it, led to increased popular support for Irish independence. In December 1918, republicans, represented by the reconstituted Sinn Féin party, won a landslide victory in the general election to the British Parliament. They did not take their seats, but instead convened the First Dáil and declared the independence of the Irish Republic. The Soloheadbeg ambush started the War of Independence.
485 people were killed in the Easter Rising. About 54% were civilians, 30% were British military and police, and 16% were Irish rebels. More than 2,600 were wounded. Many of the civilians were killed as a result of the British using artillery and heavy machine guns, or mistaking civilians for rebels. Others were caught in the crossfire in a crowded city. The shelling and the fires it caused left parts of inner city Dublin in ruins.
Background

The Acts of Union 1800 united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland as the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, abolishing the Irish Parliament and giving Ireland representation in the British Parliament. From early on, many Irish nationalists opposed the union and the ensuing exploitation and impoverishment of the island, which led to a high level of depopulation.[4][5] Opposition took various forms: constitutional (the Repeal Association; the Home Rule League), social (disestablishment of the Church of Ireland; the Land League) and revolutionary (Rebellion of 1848; Fenian Rising).[6] The Irish Home Rule movement sought to achieve self-government for Ireland, within the United Kingdom. In 1886, the Irish Parliamentary Party (IPP) under Charles Stewart Parnell succeeded in having the First Home Rule Bill introduced in the British parliament, but it was defeated. The Second Home Rule Bill of 1893 was passed by the House of Commons but rejected by the House of Lords.
After the fall of Parnell, younger and more radical nationalists became disillusioned with parliamentary politics and turned toward more extreme forms of separatism. The Gaelic Athletic Association, the Gaelic League and the cultural revival under W. B. Yeats and Lady Augusta Gregory, together with the new political thinking of Arthur Griffith expressed in his newspaper Sinn Féin and organisations such as the National Council and the Sinn Féin League, led many Irish people to identify with the idea of an independent Gaelic Ireland.[7][8] This was sometimes referred to by the generic term Sinn Féin.[9]
The Third Home Rule Bill was introduced by British Prime Minister H. H. Asquith in 1912. Unionists, who were Protestant, opposed it, as they did not want to be ruled by a Catholic-dominated Irish government. Led by Sir Edward Carson and James Craig, they formed the Ulster Volunteers (UVF) in January 1913.[10] In response, Irish nationalists formed a rival paramilitary group, the Irish Volunteers, in November 1913. The Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB) was a driving force behind the Irish Volunteers and attempted to control it. Its leader was Eoin MacNeill, who was not an IRB member.[11] The Irish Volunteers' stated goal was "to secure and to maintain the rights and liberties common to all the people of Ireland". It included people with a range of political views, and was open to "all able-bodied Irishmen without distinction of creed, politics or social group".[12] Another militant group, the Irish Citizen Army, was formed by trade unionists as a result of the Dublin Lock-out of that year.[13] When the Irish Volunteers smuggled rifles into Dublin, the British Army attempted to stop them and fired into a crowd of civilians. British Army officers then threatened to resign if they were ordered to take action against the UVF. By 1914, Ireland seemed to be on the brink of a civil war.[14] The crisis was ended in August that year by the outbreak of World War I[15] and Ireland's involvement in it. The Home Rule Bill was enacted, but its implementation was postponed by a suspensory act until the end of the war.
Planning the Rising

The Supreme Council of the IRB met on 5 September 1914, just over a month after the British government had declared war on Germany. At this meeting, they decided to stage an uprising before the war ended and to secure help from Germany.[16] Responsibility for the planning of the rising was given to Tom Clarke and Seán MacDermott (Mac Diarmada).[17] The Irish Volunteers—the smaller of the two forces resulting from the September 1914 split over support for the British war effort[18]—set up a "headquarters staff" that included Patrick Pearse[19] as Director of Military Organisation, Joseph Plunkett as Director of Military Operations and Thomas MacDonagh as Director of Training. Éamonn Ceannt was later added as Director of Communications.[20]
In May 1915, Clarke and MacDermott established a Military Committee or Military Council within the IRB, consisting of Pearse, Plunkett and Ceannt, to draw up plans for a rising.[21] Clarke and MacDermott joined it shortly after. The Military Council was able to promote its own policies and personnel independently of both the Volunteer Executive and the IRB Executive. Although the Volunteer and IRB leaders were not against a rising in principle, they were of the opinion that it was not opportune at that moment.[22] Volunteer Chief-of-Staff Eoin MacNeill supported a rising only if the British government attempted to suppress the Volunteers or introduce conscription, and if such a rising had some chance of success. IRB President Denis McCullough and prominent IRB member Bulmer Hobson held similar views.[23] The Military Council kept its plans secret, so as to prevent the British authorities learning of the plans, and to thwart those within the organisation who might try to stop the rising. IRB members held officer rank in the Volunteers throughout the country and took their orders from the Military Council, not from MacNeill.[24]
After the war began, Roger Casement and Clan na Gael leader John Devoy met the German ambassador to the United States, Johann Heinrich von Bernstorff, to discuss German backing for an uprising. Casement went to Germany and began negotiations with the German government and military. He persuaded the Germans to announce their support for Irish independence in November 1914.[25] Casement also attempted to recruit an Irish Brigade, made up of Irish prisoners of war, which would be armed and sent to Ireland to join the uprising.[26][27] However, only 56 men volunteered. Plunkett joined Casement in Germany the following year. Together, Plunkett and Casement presented a plan (the 'Ireland Report') in which a German expeditionary force would land on the west coast of Ireland, while a rising in Dublin diverted the British forces so that the Germans, with the help of local Volunteers, could secure the line of the River Shannon, before advancing on the capital.[28] The German military rejected the plan, but agreed to ship arms and ammunition to the Volunteers.[29]
James Connolly—head of the Irish Citizen Army (ICA), a group of armed socialist trade union men and women—was unaware of the IRB's plans, and threatened to start a rebellion on his own if other parties failed to act. If they had done it alone, the IRB and the Volunteers would possibly have come to their aid;[30] however, the IRB leaders met with Connolly in January 1916 and convinced him to join forces with them. They agreed that they would launch a rising together at Easter and made Connolly the sixth member of the Military Council. Thomas MacDonagh would later become the seventh and final member.
The death of the old Fenian leader Jeremiah O'Donovan Rossa in New York in August 1915 was an opportunity to mount a spectacular demonstration. His body was sent to Ireland for burial in Glasnevin Cemetery, with the Volunteers in charge of arrangements. Huge crowds lined the route and gathered at the graveside. Pearse made a dramatic funeral oration, a rallying call to republicans, which ended with the words "Ireland unfree shall never be at peace".[31]
Build-up to Easter Week

In early April, Pearse issued orders to the Irish Volunteers for three days of "parades and manoeuvres" beginning on Easter Sunday. He had the authority to do this, as the Volunteers' Director of Organisation. The idea was that IRB members within the organisation would know these were orders to begin the rising, while men such as MacNeill and the British authorities would take it at face value.
On 9 April, the German Navy dispatched a ship for County Kerry. Disguised as a Norwegian ship called the Aud, it was loaded with 20,000 rifles, one million rounds of ammunition, and explosives. Casement also left for Ireland aboard the German submarine U-19. He was disappointed with the level of support offered by the Germans and he intended to stop or at least postpone the rising.[32]
On Wednesday 19 April, Alderman Tom Kelly, a Sinn Féin member of Dublin Corporation, read out at a meeting of the Corporation a document supposedly leaked from Dublin Castle, revealing that the British authorities planned to shortly arrest leaders of the Irish Volunteers, Sinn Féin and the Gaelic League, and occupy their premises.[33] Although the British authorities said the "Castle Document" was fake, MacNeill ordered the Volunteers to prepare to resist.[34] Unbeknownst to MacNeill, the document had been forged by the Military Council to persuade moderates of the need for their planned uprising. It was an edited version of a real document outlining British plans in the event of conscription.[35] That same day, the Military Council informed senior Volunteer officers that the rising would begin on Easter Sunday. However, it chose not to inform the rank-and-file, or moderates such as MacNeill, until the last minute.[36]
The following day, MacNeill got wind that a rising was about to be launched and threatened to do everything he could to prevent it, short of informing the British.[37] MacNeill was briefly persuaded to go along with some sort of action when Mac Diarmada revealed to him that a German arms shipment was about to land in County Kerry. MacNeill believed that when the British learned of the shipment they would immediately suppress the Volunteers, thus the Volunteers would be justified in taking defensive action, including the planned manoeuvres.[38]
The Aud and the U-19 reached the coast of Kerry on Good Friday, 21 April. This was earlier than the Volunteers expected and so none were there to meet the vessels. The Royal Navy had known about the arms shipment and intercepted the Aud, prompting the captain to scuttle the ship. Furthermore, Casement was captured shortly after he landed at Banna Strand.[39]
When MacNeill learned that the arms shipment had been lost, he reverted to his original position. With the support of other leaders of like mind, notably Bulmer Hobson and The O'Rahilly, he issued a countermand to all Volunteers, cancelling all actions for Sunday. This countermanding order was relayed to Volunteer officers and printed in the Sunday morning newspapers. It succeeded in putting the rising off for only a day, although it greatly reduced the number of Volunteers who turned out.
British Naval Intelligence had been aware of the arms shipment, Casement's return, and the Easter date for the rising through radio messages between Germany and its embassy in the United States that were intercepted by the Royal Navy and deciphered in Room 40 of the Admiralty.[40] The information was passed to the Under-Secretary for Ireland, Sir Matthew Nathan, on 17 April, but without revealing its source, and Nathan was doubtful about its accuracy.[41] When news reached Dublin of the capture of the Aud and the arrest of Casement, Nathan conferred with the Lord Lieutenant, Lord Wimborne. Nathan proposed to raid Liberty Hall, headquarters of the Citizen Army, and Volunteer properties at Father Matthew Park and at Kimmage, but Wimborne insisted on wholesale arrests of the leaders. It was decided to postpone action until after Easter Monday, and in the meantime Nathan telegraphed the Chief Secretary, Augustine Birrell, in London seeking his approval.[42] By the time Birrell cabled his reply authorising the action, at noon on Monday 24 April 1916, the Rising had already begun.[43]
On the morning of Easter Sunday, 23 April, the Military Council met at Liberty Hall to discuss what to do in light of MacNeill's countermanding order. They decided that the Rising would go ahead the following day, Easter Monday, and that the Irish Volunteers and Irish Citizen Army would go into action as the 'Army of the Irish Republic'. They elected Pearse as president of the Irish Republic, and also as Commander-in-Chief of the army; Connolly became Commandant of the Dublin Brigade.[44] Messengers were then sent to all units informing them of the new orders.[45]
The Rising in Dublin
Easter Monday


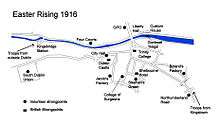
On the morning of Monday 24 April, about 1,200 members of the Irish Volunteers and Irish Citizen Army mustered at several locations in central Dublin. Among them were members of the all-female Cumann na mBan. Some wore Irish Volunteer and Citizen Army uniforms, while others wore civilian clothes with a yellow Irish Volunteer armband, military hats, and bandoliers.[46][47] They were armed mostly with rifles (especially 1871 Mausers), but also with shotguns, revolvers, a few Mauser C96 semi-automatic pistols, and grenades.[48] The number of Volunteers who mobilised was much smaller than expected. This was due to MacNeill's countermanding order, and the fact that the new orders had been sent so soon beforehand. However, several hundred Volunteers joined the Rising after it began.[49]
Shortly before midday, the rebels began to seize important sites in central Dublin. The rebels' plan was to hold Dublin city centre. This was a large, oval-shaped area bounded by two canals: the Grand to the south and the Royal to the north, with the River Liffey running through the middle. On the southern and western edges of this district were five British Army barracks. Most of the rebel's positions had been chosen to defend against counter-attacks from these barracks.[50] The rebels took the positions with ease. Civilians were evacuated and policemen were ejected or taken prisoner.[51] Windows and doors were barricaded, food and supplies were secured, and first aid posts were set up. Barricades were erected on the streets to hinder British Army movement.[52]
A joint force of about 400 Volunteers and Citizen Army gathered at Liberty Hall under the command of Commandant James Connolly. This was the headquarters battalion, and it also included Commander-in-Chief Patrick Pearse, as well as Tom Clarke, Seán MacDermott and Joseph Plunkett.[53] They marched to the General Post Office (GPO) on O'Connell Street, Dublin's main thoroughfare, occupied the building and hoisted two republican flags. Pearse stood outside and read the Proclamation of the Irish Republic.[54] Copies of the Proclamation were also pasted on walls and handed out to bystanders by Volunteers and newsboys.[55] The GPO would be the rebels' headquarters for most of the Rising. Volunteers from the GPO also occupied other buildings on the street, including buildings overlooking O'Connell Bridge. They took over a wireless telegraph station and sent out a radio broadcast in Morse code, announcing that an Irish Republic had been declared. This was the first radio broadcast in Ireland.[56]
Elsewhere, some of the headquarters battalion under Michael Mallin occupied St Stephen's Green, where they dug trenches and barricaded the surrounding roads. The 1st battalion, under Edward 'Ned' Daly, occupied the Four Courts and surrounding buildings, while a company under Seán Heuston occupied the Mendicity Institution, across the River Liffey from the Four Courts. The 2nd battalion, under Thomas MacDonagh, occupied Jacob's biscuit factory. The 3rd battalion, under Éamon de Valera, occupied Boland's Mill and surrounding buildings. The 4th battalion, under Éamonn Ceannt, occupied the South Dublin Union and the distillery on Marrowbone Lane. From each of these 'garrisons', small units of rebels established outposts in the surrounding area.[57]
The rebels also attempted to cut transport and communication links. As well as erecting roadblocks, they took control of various bridges and cut telephone and telegraph wires. Westland Row and Harcourt Street railway stations were occupied, though the latter only briefly. The railway line was cut at Fairview and the line was damaged by bombs at Amiens Street, Broadstone, Kingsbridge and Lansdowne Road.[58]
Around midday, a small team of Volunteers and Fianna Éireann members swiftly captured the Magazine Fort in the Phoenix Park and disarmed the guards. The goal was to seize weapons and blow up the ammunition store to signal that the Rising had begun. They seized weapons and planted explosives, but the blast was not big enough to be heard across the city.[59] The 23-year-old son of the fort's commander was fatally shot when he ran to raise the alarm.[60]

A contingent under Seán Connolly occupied Dublin City Hall and adjacent buildings.[61] They attempted to seize neighbouring Dublin Castle, the heart of British rule in Ireland. As they approached the gate a lone police sentry, James O'Brien, attempted to stop them and was shot dead by Connolly. According to some accounts, he was the first casualty of the Rising. The rebels overpowered the soldiers in the guardroom, but failed to press further. The British Army's chief intelligence officer, Major Ivon Price, fired on the rebels while the Under-Secretary for Ireland, Sir Matthew Nathan, helped shut the castle gates. Unbeknownst to the rebels, the Castle was lightly guarded and could have been taken with ease.[62] The rebels instead laid siege to the Castle from City Hall. Fierce fighting erupted there after British reinforcements arrived. The rebels on the roof exchanged fire with soldiers on the street. Seán Connolly was shot dead by a sniper, becoming the first rebel casualty.[45] By the following morning, British forces had re-captured City Hall and taken the rebels prisoner.[45]
The rebels did not attempt to take some other key locations, notably Trinity College, in the heart of the city centre and defended by only a handful of armed unionist students.[63] The failure to occupy strategic locations was attributed to lack of manpower.[49] In at least two incidents, at Jacob's[64] and Stephen's Green,[65] the Volunteers and Citizen Army shot dead civilians trying to attack them or dismantle their barricades. Elsewhere, they hit civilians with their rifle butts to drive them off.[66]
The British military were caught totally unprepared by the rebellion and their response of the first day was generally un-coordinated. Two troops of British cavalry were sent to investigate what was happening. They took fire and casualties from rebel forces at the GPO and at the Four Courts.[67][68] As one troop passed Nelson's Pillar, the rebels opened fire from the GPO, killing three cavalrymen and two horses[68] and fatally wounding a fourth man. The cavalrymen retreated and were withdrawn to barracks. On Mount Street, a group of Volunteer Training Corps men stumbled upon the rebel position and four were killed before they reached Beggars Bush barracks.[69]
The only substantial combat of the first day of the Rising took place at the South Dublin Union where a piquet from the Royal Irish Regiment encountered an outpost of Éamonn Ceannt's force at the northwestern corner of the South Dublin Union. The British troops, after taking some casualties, managed to regroup and launch several assaults on the position before they forced their way inside and the small rebel force in the tin huts at the eastern end of the Union surrendered.[70] However, the Union complex as a whole remained in rebel hands. A nurse in uniform, Margaret Keogh, was shot dead by British soldiers at the Union. She is believed to have been the first civilian killed in the Rising.[71]
Three unarmed Dublin Metropolitan Police were shot dead on the first day of the Rising and their Commissioner pulled them off the streets. Partly as a result of the police withdrawal, a wave of looting broke out in the city centre, especially in the O'Connell Street area. A total of 425 people were arrested after the Rising for looting.[72]
Tuesday and Wednesday

Lord Wimborne, the Lord Lieutenant, declared martial law on Tuesday evening and handed over civil power to Brigadier-General William Lowe. British forces initially put their efforts into securing the approaches to Dublin Castle and isolating the rebel headquarters, which they believed was in Liberty Hall. The British commander, Lowe, worked slowly, unsure of the size of the force he was up against, and with only 1,269 troops in the city when he arrived from the Curragh Camp in the early hours of Tuesday 25 April. City Hall was taken from the rebel unit that had attacked Dublin Castle on Tuesday morning.[74][75]
In the early hours of Tuesday, 120 British soldiers, with machine-guns, occupied two buildings overlooking St Stephen's Green: the Shelbourne Hotel and United Services Club.[76] At dawn they opened fire on the Citizen Army occupying the green. The rebels returned fire, but were forced to retreat to the Royal College of Surgeons building. They remained there for the rest of the week, exchanging fire with British forces.[45]
Fighting erupted along the northern edge of the city centre on Tuesday afternoon. In the northeast, British troops left Amiens Street railway station in an armoured train, to secure and repair a section of damaged tracks. They were attacked by rebels who had taken up position at Annesley Bridge. After a two-hour battle, the British were forced to retreat and several soldiers were captured.[77] At Phibsborough, in the northwest, rebels had occupied buildings and erected barricades at junctions on the North Circular Road. The British summoned 18-pounder field artillery from Athlone and shelled the rebel positions, destroying the barricades. After a fierce firefight, the rebels withdrew.[77] They later made an unsuccessful attack on troops at Broadstone railway station.[45]
That afternoon, Pearse, walked out into O'Connell Street with a small escort and stood in front of Nelson's Pillar. As a large crowd gathered, he read out a 'manifesto to the citizens of Dublin', calling on them to support the Rising.[78]
The rebels had failed to take either of Dublin's two main railway stations or either of its ports, at Dublin Port and Kingstown. As a result, during the following week, the British were able to bring in thousands of reinforcements from Britain and from their garrisons at the Curragh and Belfast. By the end of the week, British strength stood at over 16,000 men.[75][79] Their firepower was provided by field artillery which they positioned on the northside of the city at Phibsborough and at Trinity College, and by the patrol vessel Helga, which sailed up the Liffey, having been summoned from the port at Kingstown. On Wednesday, 26 April, the guns at Trinity College and Helga shelled Liberty Hall, and the Trinity College guns then began firing at rebel positions, first at Boland's Mill and then in O'Connell Street.[75] Some rebel commanders, particularly James Connolly, did not believe that the British would shell the 'second city' of the British Empire.[80][81]

The principal rebel positions at the GPO, the Four Courts, Jacob's Factory and Boland's Mill saw little action. The British surrounded and bombarded them rather than assault them directly. One Volunteer in the GPO recalled, "we did practically no shooting as there was no target".[82] However, where the insurgents dominated the routes by which the British tried to funnel reinforcements into the city, there was fierce fighting.
At 5:25PM volunteers Eamon Martin, Garry Holohan, Robert Beggs, Sean Cody, Dinny O'Callaghan, Charles Shelley, Peadar Breslin and five others attempted to occupy Broadstone railway station on Church Street, the attack was unsuccessful and Martin was injured.[83][84][85][86]
On Wednesday morning, hundreds of British troops encircled the Mendicity Institute, which was occupied by 26 Volunteers under Seán Heuston. British troops advanced on the building, supported by snipers and machine gun fire, but the Volunteers put up stiff resistance. Eventually, the troops got close enough to hurl grenades into the building, some of which the rebels threw back. Exhausted and almost out of ammunition, Heuston's men became the first rebel position to surrender. Heuston had been ordered to hold his position for a few hours, to delay the British, but had held on for three days.[87]
Reinforcements were sent to Dublin from Britain, and disembarked at Kingstown on the morning of Wednesday 26 April. Heavy fighting occurred at the rebel-held positions around the Grand Canal as these troops advanced towards Dublin. More than 1,000 Sherwood Foresters were repeatedly caught in a cross-fire trying to cross the canal at Mount Street Bridge. Seventeen Volunteers were able to severely disrupt the British advance, killing or wounding 240 men.[88] Despite there being alternative routes across the canal nearby, General Lowe ordered repeated frontal assaults on the Mount Street position.[89] The British eventually took the position, which had not been reinforced by the nearby rebel garrison at Boland's Mills, on Thursday,[90] but the fighting there inflicted up to two thirds of their casualties for the entire week for a cost of just four dead Volunteers.[91] It had taken nearly nine hours for the British to advance 300 yd (270 m).[45]
On Wednesday Linenhall barracks on Constitution Hill was burnt down under the orders of Commandant Edward Daly to prevent its reoccupation by the British army.[92]
Thursday to Saturday
The rebel position at the South Dublin Union (site of the present day St. James's Hospital) and Marrowbone Lane, further west along the canal, also inflicted heavy losses on British troops. The South Dublin Union was a large complex of buildings and there was vicious fighting around and inside the buildings. Cathal Brugha, a rebel officer, distinguished himself in this action and was badly wounded. By the end of the week, the British had taken some of the buildings in the Union, but others remained in rebel hands.[93] British troops also took casualties in unsuccessful frontal assaults on the Marrowbone Lane Distillery.[94]

The third major scene of fighting during the week was in the area of North King Street, north of the Four Courts. The rebels had established strong outposts in the area, occupying numerous small buildings and barricading the streets. From Thursday to Saturday, the British made repeated attempts to take the area, in what was some of the fiercest fighting of the Rising. As the troops moved in, the rebels continually opened fire from windows and behind chimneys and barricades. At one point, a platoon led by Major Sheppard made a bayonet charge on one of the barricades, but was cut down by rebel fire. The British employed machine guns and attempted to avoid direct fire by using makeshift armoured trucks, and by mouse-holing through the inside walls of terraced houses to get near the rebel positions.[95] By the time of the rebel headquarters' surrender on Saturday, the South Staffordshire Regiment under Colonel Taylor had advanced only 150 yd (140 m) down the street at a cost of 11 dead and 28 wounded.[96] The enraged troops broke into the houses along the street and shot or bayoneted 15 unarmed male civilians whom they accused of being rebel fighters.[97]
Elsewhere, at Portobello Barracks, an officer named Bowen Colthurst summarily executed six civilians, including the pacifist nationalist activist, Francis Sheehy-Skeffington.[98] These instances of British troops killing Irish civilians would later be highly controversial in Ireland.
Surrender

The headquarters garrison at the GPO, after days of shelling, was forced to abandon their headquarters when fire caused by the shells spread to the GPO. Connolly had been incapacitated by a bullet wound to the ankle and had passed command on to Pearse. The O'Rahilly was killed in a sortie from the GPO. They tunnelled through the walls of the neighbouring buildings in order to evacuate the Post Office without coming under fire and took up a new position in 16 Moore Street. The young Seán McLoughlin was given military command and planned a break out, but Pearse realised this plan would lead to further loss of civilian life.[99]
On Saturday 29 April, from this new headquarters, Pearse issued an order for all companies to surrender.[100] Pearse surrendered unconditionally to Brigadier-General Lowe. The surrender document read:
In order to prevent the further slaughter of Dublin citizens, and in the hope of saving the lives of our followers now surrounded and hopelessly outnumbered, the members of the Provisional Government present at headquarters have agreed to an unconditional surrender, and the commandants of the various districts in the City and County will order their commands to lay down arms.[101]
The other posts surrendered only after Pearse's surrender order, carried by nurse Elizabeth O'Farrell, reached them.[102] Sporadic fighting therefore continued until Sunday, when word of the surrender was got to the other rebel garrisons.[103] Command of British forces had passed from Lowe to General John Maxwell, who arrived in Dublin just in time to take the surrender. Maxwell was made temporary military governor of Ireland.[104]
The Rising outside Dublin
Irish Volunteer units mobilised on Easter Sunday in several places outside of Dublin, but because of Eoin MacNeill's countermanding order, most of them returned home without fighting. In addition, because of the interception of the German arms aboard the Aud, the provincial Volunteer units were very poorly armed.
In the south, around 1,200 Volunteers mustered in Cork, under Tomás Mac Curtain, on the Sunday, but they dispersed on Wednesday after receiving nine contradictory orders by dispatch from the Volunteer leadership in Dublin. At their Sheares Street headquarters, some of the Volunteers engaged in a standoff with British forces. Much to the anger of many Volunteers, MacCurtain, under pressure from Catholic clergy, agreed to surrender his men's arms to the British.[105] The only violence in Cork occurred when the RIC attempted to raid the home of the Kent family. The Kent brothers, who were Volunteers, engaged in a three-hour firefight with the RIC. An RIC officer and one of the brothers were killed, while another brother was later executed.[106]
In the north, Volunteer companies were mobilised in County Tyrone at Coalisland (including 132 men from Belfast led by IRB President Dennis McCullough) and Carrickmore, under the leadership of Patrick McCartan. They also mobilised at Creeslough, County Donegal under Daniel Kelly and James McNulty.[107] However, in part because of the confusion caused by the countermanding order, the Volunteers in these locations dispersed without fighting.[108]
Fingal
In Fingal (or north County Dublin), about 60 Volunteers mobilised near Swords. They belonged to the 5th Battalion of the Dublin Brigade (also known as the Fingal Battalion), and were led by Thomas Ashe and his second in command, Richard Mulcahy. Unlike the rebels elsewhere, the Fingal Battalion successfully employed guerrilla tactics. They set up camp and Ashe split the battalion into four sections: three would undertake operations while the fourth was kept in reserve, guarding camp and foraging for food.[109] The Volunteers moved against the RIC barracks in Swords, Donabate and Garristown, forcing the RIC to surrender and seizing all the weapons.[109] They also damaged railway lines and cut telegraph wires. The railway line at Blanchardstown was bombed to prevent a troop train reaching Dublin.[109] This derailed a cattle train, which had been sent ahead of the troop train.[110]
The only large-scale engagement of the Rising, outside Dublin city, was at Ashbourne.[111][112] On Friday, about 35 Fingal Volunteers surrounded the Ashbourne RIC barracks and called on it to surrender, but the RIC responded with a volley of gunfire.[109] A firefight followed, and the RIC surrendered after the Volunteers attacked the building with a homemade grenade.[109] Before the surrender could be taken, up to sixty RIC men arrived in a convoy, sparking a five-hour gun battle, in which eight RIC men were killed and 18 wounded.[109] Two Volunteers were also killed and five wounded,[113] and a civilian was fatally shot.[114] The RIC surrendered and were disarmed. Ashe let them go after warning them not to fight against the Irish Republic again.[109] Ashe's men camped at Kilsalaghan near Dublin until they received orders to surrender on Saturday.[115] The Fingal Battalion's tactics during the Rising foreshadowed those of the IRA during the War of Independence that followed.[109]
Volunteer contingents also mobilised nearby in counties Meath and Louth, but proved unable to link up with the North Dublin unit until after it had surrendered. In County Louth, Volunteers shot dead an RIC man near the village of Castlebellingham on 24 April, in an incident in which 15 RIC men were also taken prisoner.[111][116]
Enniscorthy
.jpg)
In County Wexford, 100–200 Volunteers—led by Robert Brennan, Séamus Doyle and Seán Etchingham—took over the town of Enniscorthy on Thursday 27 April until Sunday.[111] Volunteer officer Paul Galligan had cycled 200 km from rebel headquarters in Dublin with orders to mobilise.[117] They blocked all roads into the town and made a brief attack on the RIC barracks, but chose to blockade it rather than attempt to capture it. They flew the tricolour over the Athenaeum building, which they had made their headquarters, and paraded uniformed in the streets.[118] They also occupied Vinegar Hill, where the United Irishmen had made a last stand in the 1798 rebellion.[117] The public largely supported the rebels and many local men offered to join them.[117]
By Saturday, up to 1,000 rebels had been mobilised, and a detachment was sent to occupy the nearby village of Ferns.[117] In Wexford, the British assembled a column of 1,000 soldiers (including the Connaught Rangers[111]), two field guns and a 4.7 inch naval gun on a makeshift armoured train.[117] On Sunday, the British sent messengers to Enniscorthy, informing the rebels of Pearse's surrender order. However, the Volunteer officers were skeptical.[117] Two of them were escorted by the British to Arbour Hill Prison, where Pearse confirmed the surrender order.[119]
Galway
In County Galway, 600–700 Volunteers mobilised on Tuesday under Liam Mellows. His plan was to "bottle up the British garrison and divert the British from concentrating on Dublin".[120] However, his men were poorly armed, with only 25 rifles, 60 revolvers, 300 shotguns and some homemade grenades – many of them only had pikes.[121] Most of the action took place in a rural area to the east of Galway city. They made unsuccessful attacks on the RIC barracks at Clarinbridge and Oranmore, captured several officers, and bombed a bridge and railway line, before taking up position near Athenry.[121] There was also a skirmish between rebels and an RIC mobile patrol at Carnmore crossroads. A constable, Patrick Whelan, was shot dead after he had called to the rebels: "Surrender, boys, I know ye all".[120]
On Wednesday, HMS Laburnum arrived in Galway Bay and shelled the countryside on the northeastern edge of Galway.[121] The rebels retreated southeast to Moyode, an abandoned country house and estate. From here they set up lookout posts and sent out scouting parties.[121] On Friday, HMS Gloucester landed 200 Royal Marines and began shelling the countryside near the rebel position.[120][122] The rebels retreated further south to Limepark, another abandoned country house. Deeming the situation to be hopeless, they dispersed on Saturday morning. Many went home and were arrested following the rising, while others, including Mellows, went "on the run". By the time British reinforcements arrived in the west, the rising there had already disintegrated.[123]
Casualties
The Easter Rising resulted in at least 485 deaths, according to the Glasnevin Trust.[1] Of those killed:
- 260 (about 54%) were civilians
- 126 (about 26%) were British forces (120 British soldiers, 5 Volunteer Training Corps members and one Canadian soldier)
- 82 (about 16%) were Irish rebel forces (64 Irish Volunteers, 15 Irish Citizen Army and 3 Fianna Éireann)
- 17 (about 4%) were police (14 Royal Irish Constabulary and 3 Dublin Metropolitan Police)[1]
More than 2,600 were wounded; including at least 2,200 civilians and rebels, at least 370 British soldiers and 29 policemen.[124] All 16 police fatalities and 22 of the British soldiers killed were Irishmen.[125] About 40 of those killed were children (i.e. under 17 years old),[126] four of whom were members of the rebel forces.[127]
The number of casualties each day steadily rose, with 55 killed on Monday and 78 killed on Saturday.[1] The British Army suffered their biggest losses in the Battle of Mount Street Bridge on Wednesday, when at least 30 soldiers were killed. The rebels also suffered their biggest losses on that day. The RIC suffered most of their casualties in the Battle of Ashbourne on Friday.[1]
The majority of the casualties, both killed and wounded, were civilians. Most of the civilian casualties, and most of the casualties overall, were caused by the British Army.[128] This was due to the British using artillery, incendiary shells and heavy machine guns in built-up areas, as well as their "inability to discern rebels from civilians".[128] One Royal Irish Regiment officer recalled, "they regarded, not unreasonably, everyone they saw as an enemy, and fired at anything that moved".[128] Many other civilians were killed when caught in the crossfire. Both sides, British and rebel, also shot civilians deliberately on occasion; for not obeying orders (such as to stop at checkpoints), for assaulting or attempting to hinder them, and for looting.[128] There were also instances of British troops killing unarmed civilians out of revenge or frustration: notably in the North King Street Massacre, where fifteen were killed, and at Portobello Barracks, where six were shot.[129] Furthermore, there were incidents of friendly fire. On 29 April, the Royal Dublin Fusiliers under Company Quartermaster Sergeant Robert Flood shot dead two British officers and two Irish civilian employees of the Guinness brewery after he decided they were rebels. Flood was court-martialled for murder but acquitted.[130]
According to historian Fearghal McGarry, the rebels attempted to avoid needless bloodshed. Desmond Ryan stated that Volunteers were told "no firing was to take place except under orders or to repel attack".[131] Aside from the engagement at Ashbourne, policemen and unarmed soldiers were not systematically targeted, and a large group of policemen were allowed to stand at Nelson's Pillar throughout Monday.[131] McGarry writes that the Irish Citizen Army "were more ruthless than Volunteers when it came to shooting policemen" and attributes this to the "acrimonious legacy" of the Dublin Lock-out.[131]
The vast majority of the Irish casualties were buried in Glasnevin Cemetery in the aftermath of the fighting.[1] British families came to Dublin Castle in May 1916 to reclaim the bodies of British soldiers, and funerals were arranged. Soldiers whose bodies were not claimed were given military funerals in Grangegorman Military Cemetery.
Aftermath
.jpg)

.jpg)




Arrests and executions
General Maxwell quickly signalled his intention "to arrest all dangerous Sinn Feiners", including "those who have taken an active part in the movement although not in the present rebellion",[132] reflecting the popular belief that Sinn Féin, a separatist organisation that was neither militant nor republican, was behind the Rising.
A total of 3,430 men and 79 women were arrested, although most were subsequently released.[133] When the RIC attempted to arrest members of the Kent family in County Cork on 2 May, a Head Constable and one of the Kent brothers were killed in the ensuing gun battle. The other brothers were arrested. Most of those arrested were held at Richmond Barracks, Dublin.
A series of courts-martial began on 2 May, in which 187 people were tried, most of them at Richmond Barracks. The president of the courts-martial was Charles Blackader. Controversially, Maxwell decided that the courts-martial would be held in secret and without a defence, which Crown law officers later ruled to have been illegal.[133] Some of those who conducted the trials had commanded British troops involved in suppressing the Rising, a conflict of interest that the Military Manual prohibited.[133] Only one of those tried by courts-martial was a woman, Constance Markievicz.[133] Ninety were sentenced to death. Fifteen of those (including all seven signatories of the Proclamation) had their sentences confirmed by Maxwell and were executed by firing squad at Kilmainham Gaol between 3 and 12 May. Among them was the seriously wounded Connolly, who was shot while tied to a chair because of his shattered ankle. Maxwell stated that only the "ringleaders" and those proven to have committed "coldblooded murder" would be executed. However, the evidence presented was weak, and some of those executed were not leaders and did not kill anyone: Willie Pearse described himself as "a personal attaché to my brother, Patrick Pearse"; John MacBride had not even been aware of the Rising until it began, but had fought against the British in the Boer War fifteen years before; Thomas Kent did not come out at all—he was executed for the killing of a police officer during the raid on his house the week after the Rising. The most prominent leader to escape execution was Éamon de Valera, Commandant of the 3rd Battalion, who did so partly because of his American birth.[134]
Most of the executions took place over a ten-day period:
- 3 May: Patrick Pearse, Thomas MacDonagh and Thomas Clarke
- 4 May: Joseph Plunkett, William Pearse, Edward Daly and Michael O'Hanrahan
- 5 May: John MacBride
- 8 May: Éamonn Ceannt, Michael Mallin, Seán Heuston and Con Colbert
- 12 May: James Connolly and Sean MacDiarmada
As the executions went on, the Irish public grew increasingly hostile towards the British and sympathetic to the rebels. After the first three executions, John Redmond, leader of the moderate Irish Parliamentary Party, said in the British Parliament that the rising "happily, seems to be over. It has been dealt with with firmness, which was not only right, but it was the duty of the Government to so deal with it".[135] However, he urged the Government "not to show undue hardship or severity to the great masses of those who are implicated".[135] As the executions continued, Redmond pleaded with Prime Minister H. H. Asquith to stop them, warning that "if more executions take place in Ireland, the position will become impossible for any constitutional party".[136] Ulster Unionist Party leader Edward Carson expressed similar views.[135][137] Redmond's deputy, John Dillon, made an impassioned speech in parliament, saying "thousands of people […] who ten days ago were bitterly opposed to the whole of the Sinn Fein movement and to the rebellion, are now becoming infuriated against the Government on account of these executions". He said "it is not murderers who are being executed; it is insurgents who have fought a clean fight, a brave fight, however misguided". Dillon was heckled by English MPs.[138] The British Government itself had also become concerned at the reaction to the executions, and at the way the courts-martial were being carried out. Asquith had warned Maxwell that "a large number of executions would […] sow the seeds of lasting trouble in Ireland".[139] After Connolly's execution, Maxwell bowed to pressure and had the other death sentences commuted to penal servitude.[140]
Under Regulation 14B of the Defence of the Realm Act 1914 1,836 men were interned at internment camps and prisons in England and Wales.[133] Many of them, like Arthur Griffith, had little or nothing to do with the Rising. Camps such as Frongoch internment camp became "Universities of Revolution" where future leaders including Michael Collins, Terence McSwiney and J. J. O'Connell began to plan the coming struggle for independence.[141]
Sir Roger Casement was tried in London for high treason and hanged at Pentonville Prison on 3 August.
British atrocities
After the Rising, claims of atrocities carried out by British troops began to emerge. Although they did not receive as much attention as the executions, they sparked outrage among the Irish public and were raised by Irish MPs in Parliament.
One incident was the 'Portobello killings'. On Tuesday 25 April, Dubliner Francis Sheehy-Skeffington, a pacifist nationalist activist, had been arrested by British soldiers. Captain John Bowen-Colthurst then took him with a British raiding party as a hostage and human shield. On Rathmines Road he stopped a boy named James Coade, whom he shot dead. His troops then destroyed a tobacconist's shop with grenades and seized journalists Thomas Dickson and Patrick MacIntyre. The next morning, Colthurst had Skeffington and the two journalists shot by firing squad in Portobello Barracks.[142] The bodies were then buried there. Later that day he shot a Labour Party councillor, Richard O'Carroll. When Major Sir Francis Vane learned of the killings he telephoned his superiors in Dublin Castle, but no action was taken. Vane informed Herbert Kitchener, who told General Maxwell to arrest Colthurst, but Maxwell refused. Colthurst was eventually arrested and court-martialled in June. He was found guilty of murder but insane, and detained for twenty months at Broadmoor. Public and political pressure led to a public inquiry, which reached similar conclusions. Major Vane was discharged "owing to his action in the Skeffington murder case".[143][144][145][146][147]
The other incident was the 'North King Street massacre'. On the night of 28–29 April, British soldiers of the South Staffordshire Regiment, under Colonel Henry Taylor, had burst into houses on North King Street and killed 15 male civilians whom they accused of being rebels. The soldiers shot or bayoneted the victims, then secretly buried some of them in cellars or back yards after robbing them. The area saw some of the fiercest fighting of the Rising and the British had taken heavy casualties for little gain. General Maxwell attempted to excuse the killings and argued that the rebels were ultimately responsible. He claimed that "the rebels wore no uniform" and that the people of North King Street were rebel sympathisers. Maxwell concluded that such incidents "are absolutely unavoidable in such a business as this" and that "Under the circumstance the troops [...] behaved with the greatest restraint". A private brief, prepared for the Prime Minister, said the soldiers "had orders not to take any prisoners" but took it to mean they were to shoot any suspected rebel. The City Coroner's inquest found that soldiers had killed "unarmed and unoffending" residents. The military court of inquiry ruled that no specific soldiers could be held responsible, and no action was taken.[148][149][150][151][152]
These killings, and the British response to them, helped sway Irish public opinion against the British.[153]
Inquiry
A Royal Commission was set up to enquire into the causes of the Rising. It began hearings on 18 May under the chairmanship of Lord Hardinge of Penshurst. The Commission heard evidence from Sir Matthew Nathan, Augustine Birrell, Lord Wimborne, Sir Neville Chamberlain (Inspector-General of the Royal Irish Constabulary), General Lovick Friend, Major Ivor Price of Military Intelligence and others.[154] The report, published on 26 June, was critical of the Dublin administration, saying that "Ireland for several years had been administered on the principle that it was safer and more expedient to leave the law in abeyance if collision with any faction of the Irish people could thereby be avoided."[155] Birrell and Nathan had resigned immediately after the Rising. Wimborne had also reluctantly resigned, recalled to London by Lloyd George, but was re-appointed in late 1917. Chamberlain resigned soon after.[156]
Reaction of the Dublin public
At first, many Dubliners were bewildered by the outbreak of the Rising.[157] James Stephens, who was in Dublin during the week, thought, "None of these people were prepared for Insurrection. The thing had been sprung on them so suddenly they were unable to take sides."[158]
There was great hostility towards the Volunteers in some parts of the city. Historian Keith Jeffery noted that most of the opposition came from people whose relatives were in the British Army and who depended on their Army allowances.[159] Those most openly hostile to the Volunteers were the "separation women" (so-called because they were paid "separation money" by the British government), whose husbands and sons were fighting in the British Army in the First World War. There was also hostility from unionists.[160] Supporters of the Irish Parliamentary Party also felt the rebellion was a betrayal of their party.[161] When occupying positions in the South Dublin Union and Jacob's factory, the rebels got involved in physical confrontations with civilians who tried to tear down the rebel barricades and prevent them taking over buildings. The Volunteers shot and clubbed a number of civilians who assaulted them or tried to dismantle their barricades.[162]
That the Rising resulted in a great deal of death and destruction, as well as disrupting food supplies, also contributed to the antagonism toward the rebels. After the surrender, the Volunteers were hissed at, pelted with refuse, and denounced as "murderers" and "starvers of the people".[163] Volunteer Robert Holland for example remembered being "subjected to very ugly remarks and cat-calls from the poorer classes" as they marched to surrender. He also reported being abused by people he knew as he was marched through the Kilmainham area into captivity and said the British troops saved them from being manhandled by the crowd.[164][165]
.jpg)
However, some Dubliners expressed support for the rebels.[166] Canadian journalist and writer Frederick Arthur McKenzie wrote that in poorer areas, "there was a vast amount of sympathy with the rebels, particularly after the rebels were defeated".[167] He wrote of crowds cheering a column of rebel prisoners as it passed, with one woman remarking "Shure, we cheer them. Why shouldn't we? Aren't they our own flesh and blood?".[168] At Boland's Mill, the defeated rebels were met with a large crowd, "many weeping and expressing sympathy and sorrow, all of them friendly and kind".[166] Other onlookers were sympathetic but watched in silence.[166] Christopher M. Kennedy notes that "those who sympathised with the rebels would, out of fear for their own safety, keep their opinions to themselves".[168] Áine Ceannt witnessed British soldiers arresting a woman who cheered the captured rebels.[166] An RIC District Inspector's report stated: "Martial law, of course, prevents any expression of it; but a strong undercurrent of disloyalty exists".[168] Thomas Johnson, the Labour leader, thought there was, "no sign of sympathy for the rebels, but general admiration for their courage and strategy".[169]
The aftermath of the Rising, and in particular the British reaction to it, helped sway a large section of Irish nationalist opinion away from hostility or ambivalence and towards support for the rebels of Easter 1916. Dublin businessman and Quaker James G. Douglas, for example, hitherto a Home Ruler, wrote that his political outlook changed radically during the course of the Rising because of the British military occupation of the city and that he became convinced that parliamentary methods would not be enough to remove the British presence.[170]
Rise of Sinn Féin
A meeting called by Count Plunkett on 19 April 1917 led to the formation of a broad political movement under the banner of Sinn Féin[171] which was formalised at the Sinn Féin Ard Fheis of 25 October 1917. The Conscription Crisis of 1918 further intensified public support for Sinn Féin before the general elections to the British Parliament on 14 December 1918, which resulted in a landslide victory for Sinn Féin, winning 73 seats out of 105, whose MPs gathered in Dublin on 21 January 1919 to form Dáil Éireann and adopt the Declaration of Independence.[172]
Legacy
Shortly after the Easter Rising, poet Francis Ledwidge wrote "O’Connell Street" and "Lament for the Poets of 1916", which both describe his sense of loss and an expression of holding the same "dreams",[173] as the Easter Rising's Irish Republicans. He would also go on to write lament for Thomas MacDonagh for his fallen friend and fellow Irish Volunteer.
A few months after the Easter Rising, W. B. Yeats commemorated some of the fallen figures of the Irish Republican movement, as well as his torn emotions regarding these events, in the poem Easter, 1916.
Some of the survivors of the Rising went on to become leaders of the independent Irish state. Those who were executed were venerated by many as martyrs; their graves in Dublin's former military prison of Arbour Hill became a national monument and the Proclamation text was taught in schools. An annual commemorative military parade was held each year on Easter Sunday. In 1935, Éamonn de Valera unveiled a statue of the mythical Irish hero Cú Chulainn, sculpted by Oliver Sheppard, at the General Post Office as part of the Rising commemorations that year - it is often seen to be an important symbol of martyrdom in remembrance of the 1916 rebels. Memorials to the heroes of the Rising are to be found in other Irish cities, such as Limerick.
The parades culminated in a huge national celebration on the 50th anniversary of the Rising in 1966.[174] Medals were issued by the government to survivors who took part in the rising at the event. RTÉ, the Irish national broadcaster, as one of its first major undertakings made a series of commemorative programmes for the 1966 anniversary of the Rising. Roibéárd Ó Faracháin, head of programming said, "While still seeking historical truth, the emphasis will be on homage, on salutation."[175] At the same time, CIÉ, the Republic of Ireland's railway operator, named several of its major stations after republicans who played key roles in the Easter Rising.[176]
Ireland's first commemorative coin was also issued in 1966 to pay tribute to the Easter Rising. It was valued at 10 shillings, therefore having the highest denomination of any pre-decimal coin issued by the country. The coin featured a bust of Patrick Pearse on the obverse and an image of the statue of Cú Chulainn in the GPO on the reverse. Its edge inscription reads, "Éirí Amach na Cásca 1916", which translates to, "1916 Easter Rising". Due to their 83.5% silver content, many of the coins were melted down shortly after issue.[177] A €2 coin was also issued by Ireland in 2016, featuring the statue of Hibernia above the GPO, to commemorate the Rising's centenary.[178]
With the outbreak of the Troubles in Northern Ireland, government, academics and the media began to revise the country's militant past, and particularly the Easter Rising. The coalition government of 1973–77, in particular the Minister for Posts and Telegraphs, Conor Cruise O'Brien, began to promote the view that the violence of 1916 was essentially no different from the violence then taking place in the streets of Belfast and Derry.
O'Brien and others asserted that the Rising was doomed to military defeat from the outset, and that it failed to account for the determination of Ulster Unionists to remain in the United Kingdom.[179]
Irish republicans continue to venerate the Rising and its leaders with murals in republican areas of Belfast and other towns celebrating the actions of Pearse and his comrades, and annual parades in remembrance of the Rising. The Irish government, however, discontinued its annual parade in Dublin in the early 1970s, and in 1976 it took the unprecedented step of proscribing (under the Offences against the State Act) a 1916 commemoration ceremony at the GPO organised by Sinn Féin and the Republican commemoration Committee.[180] A Labour Party TD, David Thornley, embarrassed the government (of which Labour was a member) by appearing on the platform at the ceremony, along with Máire Comerford, who had fought in the Rising, and Fiona Plunkett, sister of Joseph Plunkett.[181]
With the advent of a Provisional IRA ceasefire and the beginning of what became known as the Peace Process during the 1990s, the official view of the Rising grew more positive and in 1996 an 80th anniversary commemoration at the Garden of Remembrance in Dublin was attended by the Taoiseach and leader of Fine Gael, John Bruton.[182] In 2005, the Taoiseach, Bertie Ahern, announced the government's intention to resume the military parade past the GPO from Easter 2006, and to form a committee to plan centenary celebrations in 2016.[183] The 90th anniversary was celebrated with a military parade in Dublin on Easter Sunday, 2006, attended by the President of Ireland, the Taoiseach and the Lord Mayor of Dublin.[184] There is now an annual ceremony at Easter attended by relatives of those who fought, by the President, the Taoiseach, ministers, senators and TDs, and by usually large and respectful crowds.
In December 2014 Dublin City Council approved a proposal to create a historical path commemorating the Rising, similar to the Freedom Trail in Boston. Lord Mayor of Dublin Christy Burke announced that the council had committed to building the trail, marking it with a green line or bricks, with brass plates marking the related historic sites such as the Rotunda and the General Post Office.[185]
A pedestrian staircase that runs along 53rd Avenue, from 65th Place to 64th Street in west Queens, New York City was named 'Easter Rising Way' in 2016. Sinn Féin leader, Gerry Adams spoke at the naming ceremony.[186]
 Plaque commemorating the Easter Rising at the General Post Office, Dublin, with the Irish text in Gaelic script, and the English text in regular Latin script
Plaque commemorating the Easter Rising at the General Post Office, Dublin, with the Irish text in Gaelic script, and the English text in regular Latin script This bronze statue of the dying Cú Chulainn was unveiled in the General Post Office, Dublin, in 1935 in memory of the Easter Rising
This bronze statue of the dying Cú Chulainn was unveiled in the General Post Office, Dublin, in 1935 in memory of the Easter Rising Memorial in Cobh, County Cork, to the 1916 volunteers from that town.
Memorial in Cobh, County Cork, to the 1916 volunteers from that town. Mural in Belfast depicting the Easter Rising of 1916
Mural in Belfast depicting the Easter Rising of 1916
Date of commemoration
The Easter Rising lasted from Easter Monday 24 April 1916 to Easter Saturday 29 April 1916. Annual commemorations, rather than taking place on 24–29 April, are typically based on the date of Easter, which is a moveable feast. For example, the annual military parade is on Easter Sunday; the date of coming into force of the Republic of Ireland Act 1948 was symbolically chosen as Easter Monday (18 April) 1949.[187] The official programme of centenary events in 2016 climaxed from 25 March (Good Friday) to 2 April (Easter Saturday) with other events earlier and later in the year taking place on the calendrical anniversaries.[188]
In popular culture
- "The Foggy Dew" is a song by Canon Charles O'Neill, composed sometime after 1919, that eulogises the rebels of the Easter Rising.
- The Plough and the Stars is a 1926 play by Seán O'Casey that takes place during the Easter Rising.
- Insurrection is a 1950 novel by Liam O'Flaherty.
- The Red and the Green is a 1965 novel by Iris Murdoch that covers the events leading up to and during the Easter Rising.
- Insurrection is an eight-part 1966 docudrama made by Telefís Éireann for the 50th anniversary of the Rising. It was rebroadcast during the centenary celebrations in 2016.[189]
- 1916, A Novel of the Irish Rebellion is a 1998 historical novel by Morgan Llywelyn.
- A Star Called Henry is a 1999 novel by Roddy Doyle that partly recounts the Easter Rising through the involvement of the novel's protagonist Henry Smart.
- At Swim, Two Boys is a 2001 novel by Irish writer Jamie O'Neill, set in Dublin before and during the 1916 Easter Rising.
- Blood Upon the Rose is a 2009 graphic novel by Gerry Hunt depicting the events of the Easter Rising.[190][191]
- Rebellion is a 2016 mini-series about the Easter Rising.
- 1916 is a 2016 three part documentary mini-series about the Easter Rising narrated by Liam Neeson.[192]
See also
- Easter, 1916, a poem by W. B. Yeats
- List of Irish uprisings
Notes
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 1916 Necrology. Glasnevin Trust.
- ↑ "Department of the Taoiseach – Easter Rising". Taoiseach.gov.ie. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- ↑ Leaders and Men of the Easter Rising: Dublin 1916 Francis X. Martin 1967 p105
- ↑ MacDonagh, pp. 14–17
- ↑ Behrendt, Stephen C. (2010). British Women Poets and the Romantic Writing Community. JHU Press. pp. 244–5. ISBN 0801895081. Retrieved 23 August 2016.
- ↑ Mansergh, Nicholas, The Irish Question 1840–1921, George Allen & Unwin, 1978, ISBN 0-04-901022-0 p. 244
- ↑ MacDonagh, Oliver, pp. 72–74
- ↑ Feeney, p. 22
- ↑ Feeney, p. 37
- ↑ "Those who set the stage" (PDF). The 1916 Rising: Personalities and Perspectives. National Library of Ireland. Retrieved 7 December 2009.
- ↑ Foy and Barton, pp. 7–8
- ↑ Macardle, pp. 90–92
- ↑ Townshend, p. 49
- ↑ Collins, M.E.. Sovereignty and partition, 1912–1949. Edco Publishing, 2004. pp.32–33
- ↑ Townshend, pp. 59–60
- ↑ Caulfield, Max, p. 18
- ↑ Foy and Barton, p. 16
- ↑ Foy and Barton, p. 13
- ↑ Sean Farrell Moran, Patrick Pearse and the Politics of Redemption: The Mind of the Easter Rising, (1994), Ruth Dudley Edwards, Patrick Pearse and the Triumph of Failure, (1977), Joost Augustin, Patrick Pearse', (2009)
- ↑ Townshend, p. 92
- ↑ Foy and Barton, pp. 16, 19
- ↑ McGarry, p.116
- ↑ Townshend, p. 94
- ↑ Macardle, p. 119
- ↑ Foy and Barton, p.25
- ↑ Townshend, p. 104
- ↑ Foy and Barton, p. 105
- ↑ McNally and Dennis, p. 30
- ↑ Foy and Barton, pp.25-28
- ↑ Eoin Neeson, Myths from Easter 1916, p. ?
- ↑ Kennedy, pp.199–200
- ↑ Foy and Barton, p.56
- ↑ Townshend, pp. 131–132
- ↑ Foy and Barton, p.47
- ↑ McGarry, p.117
- ↑ Foy and Barton, p.48
- ↑ Foy and Barton, p.52
- ↑ Michael Tierney, Eoin MacNeill, pp. 199, 214
- ↑ Foy and Barton, pp.57-58
- ↑ Ó Broin, p. 138
- ↑ Ó Broin, p. 79
- ↑ Ó Broin, pp. 81–87
- ↑ Ó Broin, p. 88
- ↑ Foy and Barton, p.66
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Chronology of the Easter Rising. Century Ireland – RTÉ.
- ↑ Ward, Alan. The Easter Rising: Revolution and Irish Nationalism. Wiley, 2003. p.5
- ↑ Cottrel, Peter. The War for Ireland: 1913-1923. Osprey, 2009. p.41
- ↑ Dorney, John. The Weapons of 1916. Irish Independent. 3 March 2016.
- 1 2 McGarry, p.129
- ↑ Dorney, John. The Story of the Easter Rising, 1916. Green Lamp, 2010. p.33
- ↑ McGarry, p.133
- ↑ McGarry, p.135
- ↑ McNally and Dennis, p. 41
- ↑ Foy and Barton, pp. 192, 195
- ↑ McGarry, p.134
- ↑ McGee, John. "Time to celebrate a centenary of Irish broadcast heroes". Irish Independent, 6 March 2016.
- ↑ McNally and Dennis, pp. 39-40
- ↑ McKenna, Joseph. Guerrilla Warfare in the Irish War of Independence. McFarland, 2011. p.19
- ↑ Caulfield, Max, pp. 48–50
- ↑ "Children of the Revolution". History Ireland. Volume 1, issue 23 (May/June 2013).
- ↑ Foy and Barton, pp. 87–90
- ↑ Foy and Barton, pp. 84–85
- ↑ Townshend, pp.163-164
- ↑ McGarry p.142
- ↑ Stephens p. 18
- ↑ McGarry, pp.142-143; Townshend, p.174
- ↑ Caulfield, Max, pp. 54–55
- 1 2 Coffey, Thomas M. Agony at Easter: The 1916 Irish Uprising, pp.38, 44, 155
- ↑ O'Brien, Blood on the Streets, the Battle for Mount Street, pp.22-23
- ↑ Caulfield, Max, pp. 76–80
- ↑ "Nurse Margaret Keogh, the first civilian fatality of the Rising". Irish Independent. 4 March 2016.
- ↑ Townshend, pp.263-264
- ↑ "Statement by Joseph Sweeney Curious Journey: An Oral History of Ireland’s Unfinished Revolution". BBC. Retrieved 18 October 2009.
- ↑ Coogan 2001, p.107
- 1 2 3 Townshend, p.191
- ↑ Caulfield, p.122
- 1 2 Caulfield, pp.145-146
- ↑ Foy and Barton, p.180
- ↑ McGarry, pp.167-169
- ↑ McGarry, p.192
- ↑ Foy and Barton, p.181
- ↑ McGarry, p.175
- ↑ Witness Statement by Eamon Martin to Bureau of Military History, 1951
- ↑ Witness Statement of Sean Cody to Bureau of Military History, 1954
- ↑ Witness Statement of Nicholas Kaftan to Bureau of Military History
- ↑ Witness Statement of Charles Shelley to Bureau of Military History, 1953
- ↑ O'Brien, Paul. Heuston's Fort – The Battle for the Mendicity Institute, 1916. The Irish Story. 15 August 2012.
- ↑ Coogan , p.122
- ↑ Caulfield, p. 196
- ↑ O'Brien, p.69
- ↑ McGarry, p.173
- ↑ http://www.easter1916.ie/index.php/places/a-z/linenhall-barracks/
- ↑ Caulfield, pp.225–228
- ↑ Ryan, pp.128-133
- ↑ Dorney, John. "The North King Street Massacre, Dublin 1916". The Irish Story. 13 April 2012.
- ↑ Coogan pp.152-155
- ↑ Coogan , p.155, McGarry p.187
- ↑ Caulfield pp. 154, 166–167, 186–187
- ↑ Charlie McGuire, "Seán McLoughlin – the boy commandant of 1916", History Ireland, Vol.14, No.2
- ↑ Townshend, pp.243-246
- ↑ "Dublin may seek surrender letter". BBC News. 2006-01-09. Retrieved 2011-11-13.
- ↑ Townshend, pp.246-247
- ↑ Townshend, pp.246-250
- ↑ McGarry, pp.203-204
- ↑ Townshend, p.235
- ↑ Townshend, p.238
- ↑ O'Duibhir, Liam (2009). The Donegal Awakening. Mercier Press. pp. 39, 45, 76, 104, 255, 289, 292.
- ↑ Townshend, p.226
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Maguire, Paul. The Fingal Battalion: A Blueprint for the Future? Archived 6 May 2016 at the Wayback Machine.. The Irish Sword. Military History Society of Ireland, 2011. pp.9-13
- ↑ The 1916 Rebellion Handbook p.27
- 1 2 3 4 Boyle, John F. The Irish Rebellion of 1916: a brief history of the revolt and its suppression (Chapter IV: Outbreaks in the Country). BiblioBazaar, 2009. pp.127–152
- ↑ Townshend, pp.215-216
- ↑ Townshend, pp.218-221
- ↑ McGarry, pp.235-237
- ↑ Townshend, p.221
- ↑ Townshend, p.224
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dorney, John. The Easter Rising in County Wexford. The Irish Story. 10 April 2012.
- ↑ Townshend, p.241
- ↑ Townshend, pp.241-242
- 1 2 3 Dorney, John. The Easter Rising in Galway, 1916. The Irish Story. 4 March 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Mark McCarthy & Shirley Wrynn. County Galway's 1916 Rising: A Short History. Galway County Council.
- ↑ Townshend, pp.227-230
- ↑ McGarry, p.233
- ↑ Foy and Barton, page 325
- ↑ 1916 Rebellion Handbook, pp.50-55
- ↑ "40 children were killed in the 1916 Rising but they are barely mentioned in our history". TheJournal.ie. 29 November 2015.
- ↑ Joe Duffy's list of Children Killed in 1916 Rising.
- 1 2 3 4 McGarry, pp.184-185
- ↑ McGarry, p.186-187
- ↑ Royal Dublin Fusiliers website - 5th Battalion RDF during the Easter Rising Retrieved March 21, 2016
- 1 2 3 McGarry, pp.176-177
- ↑ Townshend, p.273
- 1 2 3 4 5 Foy and Barton, pp.294-295
- ↑ S. J. Connolly (2004). Oxford Companion to Irish History. Oxford University Press. p. 607. ISBN 978-0-19-923483-7.
- 1 2 3 House of Commons debate, 3 May 1916: Resignation of Mr Birrell. Hansard.
- ↑ Finnan, Joseph. John Redmond and Irish Unity: 1912 – 1918. Syracuse University Press, 2004. p.196
- ↑ Lewis, Geoffrey. Carson: The Man Who Divided Ireland. Bloomsbury Publishing, 2006. p.185
- ↑ House of Commons debate, 11 May 1916: Continuance of martial law. Hansard.
- ↑ "Easter Rising 1916 – the aftermath: arrests and executions". The Irish Times, 24 March 2016.
- ↑ Foy and Barton, p.325
- ↑ "''The Green Dragon'' No 4, Autumn 1997". Ballinagree.freeservers.com. 31 March 2005. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- ↑ Bacon, Bryan (2015). A Terrible Duty: the Madness of Captain Bowen-Colthurst. Thena Press.
- ↑ McGarry, p.186
- ↑ Townshend, p.193
- ↑ Caulfield, Max, p. 187
- ↑ Yeates, Pádraig. A City in Wartime – Dublin 1914–1918: The Easter Rising 1916. Gill & Macmillan, 2011, p. ?.
- ↑ Redmond, Dara. "Officer who exposed pacifist's murder". The Irish Times. 26 August 2006.
- ↑ McGarry, p.187
- ↑ Caulfield, pp.338-340
- ↑ Coogan , pp.152-155
- ↑ Townshend, pp. 293-294
- ↑ Dorney, John. "The North King Street Massacre, Dublin 1916". The Irish Story. 13 April 2012.
- ↑ What was the Easter Rising?. Century Ireland - RTÉ.
- ↑ Ó Broin, Leon, Dublin Castle & the 1916 Rising pp. 153–159
- ↑ Townshend p. 297
- ↑ John Kendle, "Walter Long, Ireland, 1911-1924" (London 1992)
- ↑ "In many areas the reaction of civilians was puzzlement, they simply had no idea what was going on." Townshend
- ↑ Stephens p. 57
- ↑ Kennedy, p.286
- ↑ Foy and Barton, pp. 203-209
- ↑ "The loyalists spoke with an air of contempt, 'the troops will settle the matter in an hour or two, these pro-Germans will run away...' The Redmondites were more bitter, 'I hope they’ll all be hanged' ... 'Shooting’s too good for them. Trying to stir up trouble for us all.'" Ernie O’Malley, On Another Man's Wound, p. 60.
- ↑ Fearghal McGarry, The Rising: Ireland Easter 1916, p. 143
- ↑ McGarry, p. 252
- ↑ Ryan, p. 135
- ↑ "Witness statement of Robert Holland" (PDF). Bureau of Military History. Retrieved 14 May 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 McGarry, pp. 252-256
- ↑ Ellis, pp. 196-197
- 1 2 3 Kennedy, p.288
- ↑ Townshend, pp. 265-268
- ↑ J. Anthony Gaughan, ed. (1998). Memoirs of Senator James G. Douglas; concerned citizen. University College Dublin Press. pp. 52, 53. ISBN 978-1-900621-19-9. Retrieved 30 May 2010.
- ↑ Bell, p. 27
- ↑ Robert Kee The Green Flag: Ourselves Alone
- ↑ "Ledwidge, Francis, Life works Criticism Commentary Quotations References Notes".
- ↑ "News Items Relating to the 1916 Easter Rising Commemorations". IE: RTÉ. 1966
- ↑ Brennan, Cathal. "A TV pageant, the Golden Jubille Commemorations of the 1916 Rising"
- ↑ "Irish Station Names - Heroes of the Easter Uprising". www.sinfin.net. Retrieved 2016-07-23.
- ↑ "O’Brien Coin Guide: Irish Pre-Decimal Ten Shillings". The Old Currency Exchange is a specialist dealer and valuer of coins, tokens and banknotes. 2016-03-27. Retrieved 2016-07-23.
- ↑ "Commemorative €2 coin released to mark 1916 centenary". Retrieved 2016-10-05.
- ↑ O’Brien, Conor Cruise (1972). States of Ireland. Hutchinson. pp. 88, 99. ISBN 0-09-113100-6.
- ↑ Irish Times, 22 April 1976
- ↑ Irish Times, 26 April 1976
- ↑ Reconstructing the Easter Rising, Colin Murphy, The Village, 16 February 2006
- ↑ Irish Times, 22 October 2005
- ↑ "In pictures: Easter Rising commemorations". BBC News. 16 April 2006. Retrieved 29 March 2010.
- ↑ Hertz, Kayla (16 December 2014). "Dublin's 1916 Rising Freedom Trail will be based on Boston's". Irish Central. Retrieved 11 September 2016.
- ↑ New York’s newest street name? Easter Rising Way
- ↑ "S.I. No. 27/1949 - The Republic of Ireland Act, 1948 (Commencement) Order, 1949.". Irish Statute Book. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- ↑ "State Ceremonial". Ireland 2016. Government of Ireland. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- ↑ "RTÉ’s acclaimed Easter Rising drama from 1966 is coming back to TV screens". The Journal. 8 March 2016. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
- ↑ Edward Madigan, "Review of Gerry Hunt’s ‘Blood Upon the Rose’, part one", Pue's Occurrences, 2 November 2009
- ↑ Crosson, Seán and Werner Huber (eds.) (2015). "(Valérie Morisson) Rewriting Irish History (1916-1921) in popular Culture: Blood Upon the Rose and At War with the Empire by Gerry Hunt". Towards 2016: 1916 and Irish Literature, Culture & Society. Trier: Wissenschaftlicher Verlag Trier. pp. 113–132. ISBN 978-3-86821-622-6.
- ↑ https://1916.rte.ie/featuredhome/1916-2/
Bibliography
- Augusteijn, Joost (ed.)The Memoirs of John M. Regan, a Catholic Officer in the RIC and RUC, 1909–48, Witnessed Rising, ISBN 978-1-84682-069-4.
- Bell, J. Bowyer. The Secret Army: The IRA. ISBN 1-85371-813-0.
- Caulfield, Max, The Easter Rebellion, Dublin 1916 ISBN 1-57098-042-X
- Clayton, Xander (2007). Aud. Plymouth: GAC. ISBN 9780955562204.
- Coogan, Tim Pat, 1916: The Easter Rising (2001) ISBN 0-304-35902-5
- Coogan, Tim Pat, The IRA (2nd ed. 2000), ISBN 0-00-653155-5
- De Rosa, Peter. Rebels: The Irish Rising of 1916. Fawcett Columbine, New York. 1990. ISBN 0-449-90682-5
- Eberspächer, Cord/Wiechmann, Gerhard: "Erfolg Revolution kann Krieg entscheiden". Der Einsatz von S.M.H. LIBAU im irischen Osteraufstand 1916 ("Successful revolution may decide war". The use of S.M.H. LIBAU in the Irish Easter rising 1916), in: Schiff & Zeit, Nr. 67, Frühjahr 2008, S. 2–16.
- Ellis, Peter Berresford (2008). "1916: Insurrection or Rebellion? Making Judgements". In O'Donnell, Ruán. The Impact of the 1916 Rising: Among the Nations. Dublin: Irish Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-7165-2965-1.
- Feeney, Brian, Sinn Féin: A Hundred Turbulent Years, O'Brien Press, 2002, ISBN 0-86278-695-9
- Foster, R. F. Vivid Faces: The Revolutionary Generation in Ireland, 1890-1923 (2015) excerpt
- Foy, Michael and Barton, Brian, The Easter Rising ISBN 0-7509-2616-3
- Greaves, C. Desmond, The Life and Times of James Connolly
- The Irish Times (1998) [1917]. 1916 Rebellion Handbook. Introduction by Declan Kiberd (reprint ed.). Mourne River Press. ISBN 9781902090054.
- Kee, Robert, The Green Flag ISBN 0-14-029165-2
- Kennedy, Christopher M. (2010). Genesis of the Rising, 1912-1916: A Transformation of Nationalist Opinion. Peter Lang. ISBN 1433105004. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- Kostick, Conor & Collins, Lorcan, The Easter Rising, A Guide to Dublin in 1916 ISBN 0-86278-638-X
- Lyons, F.S.L., Ireland Since the Famine ISBN 0-00-633200-5
- Martin, F.X. (ed.), Leaders and Men of the Easter Rising, Dublin 1916
- Macardle, Dorothy, The Irish Republic (Dublin 1951)
- MacDonagh, Oliver, Ireland: The Union and its aftermath, George Allen & Unwin, 1977, ISBN 0-04-941004-0
- McKeown, Eitne, 'A Family in the Rising' Dublin Electricity Supply Board Journal 1966.
- McNally, Michael and Dennis, Peter, Easter Rising 1916: Birth of the Irish Republic (London 2007), Osprey Publishing, ISBN 978-1-84603-067-3
- Moran, Seán Farrell, Patrick Pearse and the Politics of Redemption, 1994, Catholic University of America Press, ISBN 978-0-81320-912-8
- "Patrick Pearse and the European Revolt Against Reason," in The Journal of the History of Ideas, 4, 1989.
- "Patrick Pearse and Patriotic Soteriology," in Yonah Alexander and Alan O'Day, eds, The Irish Terrorism Experience, 1991
- Murphy, John A., Ireland In the Twentieth Century
- Ó Broin, Leon, Dublin Castle & the 1916 Rising, Sidgwick & Jackson, 1970
- O'Farrell, Elizabeth, 'Events of Easter Week' The Catholic Bulletin (Dublin 1917).
- Purdon, Edward, The 1916 Rising
- Royal Commission on the Rebellion in Ireland (1916). Report. Command papers. Cd.8279. London: HMSO. Retrieved 11 September 2016.
- Royal Commission on the Rebellion in Ireland (1916). Minutes of Evidence and Appendix of Documents. Command papers. Cd.8311. London: HMSO. Retrieved 11 September 2016.
- Ryan, Annie, Witnesses: Inside the Easter Rising
- Shaw, Francis, S.J., "The Canon of Irish History: A Challenge", in Studies: An Irish Quarterly Review, LXI, 242, 1972, pp.113-52
- Stephens, James, The Insurrection in Dublin
- Townshend, Charles, Easter 1916: The Irish Rebellion (London 2006)
Historiography
- McCarthy, Mark. Ireland's 1916 Rising: Explorations of History-Making, Commemoration & Heritage in Modern Times (2013), historiography excerpt
- Neeson, Eoin, Myths from Easter 1916, Aubane Historical Society (Cork, 2007), ISBN 978-1-903497-34-0
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Easter Rising. |
- Easter 1916 - Digital Heritage Website
- The 1916 Rising – an Online Exhibition. National Library of Ireland
- The Letters of 1916 – Crowdsourcing Project Trinity College Dublin
- 1916 Rising Postcards, part of the Curran Collection. A UCD Digital Library Collection.
- Towards 2016: a selection of materials related to the 1916 rising held in UCD archives and collections. A UCD Digital Library Collection.
- Essay on the Rising, by Garret FitzGerald
- Lillian Stokes (1878–1955): account of the 1916 Easter Rising
- Special 90th Anniversary supplement from The Irish Times
- Easter Rising 50th Anniversary audio & video footage from RTÉ (Irish public television)
- Primary and secondary sources relating to the Easter Rising (Sources database, National Library of Ireland)
- Easter Rising site and walking tour of 1916 Dublin
- News articles and letters to the editor in The Age, 27 April 1916
- Podcast about the 1916 Easter Rising
- Press comments 1916–1996
- The 1916 Rising by Norman Teeling a 10-painting suite acquired by An Post for permanent display at the General Post Office (Dublin)
- The Easter Rising—BBC History
- The Irish Story archive on the Rising
- Easter Rising website
- Lenin's Essay on the Uprising
- Bureau of Military History - Witness Statements Online (PDF files)
