Early modern period
| Human history | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ↑ Prehistory | |||
| Recorded history | |||
| Ancient | |||
| Postclassical | |||
| Modern | |||
|
|||
| ↓ Future | |||
The early modern period of modern history follows the late Middle Ages of the post-classical era. Although the chronological limits of the period are open to debate, the timeframe spans the period after the late portion of the post-classical age (c. 1500), known as the Middle Ages, through the beginning of the Age of Revolutions (c. 1800) and is variously demarcated by historians as beginning with the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, with the Renaissance period, and with the Age of Discovery (especially with the voyages of Christopher Columbus beginning in 1492, but also with Vasco da Gama's discovery of the sea route to the East in 1498), and ending around the French Revolution in 1789.
Historians in recent decades have argued that from a worldwide standpoint, the most important feature of the early modern period was its globalizing character.[1] The period witnessed the exploration and colonization of the Americas and the rise of sustained contacts between previously isolated parts of the globe. The historical powers became involved in global trade, as the exchange of goods, plants, animals, and food crops extended to the Old World and the New World. The Columbian Exchange greatly affected the human environment.
New economies and institutions emerged, becoming more sophisticated and globally articulated over the course of the early modern period. This process began in the medieval North Italian city-states, particularly Genoa, Venice, and Milan. The early modern period also included the rise of the dominance of the economic theory of mercantilism. The European colonization of the Americas, Asia, and Africa occurred during the 15th to 19th centuries, and spread Christianity around the world.
The early modern trends in various regions of the world represented a shift away from medieval modes of organization, politically and economically. Feudalism declined in Europe, while the period also included the Protestant Reformation, the disastrous Thirty Years' War, the Commercial Revolution, the European colonization of the Americas, and the Golden Age of Piracy.
By the 16th century the economy under the Ming Dynasty was stimulated by trade with the Portuguese, the Spanish, and the Dutch, while Japan engaged in the Nanban trade after the arrival of the first European Portuguese during the Azuchi-Momoyama period.
Other notable trends of the early modern period include the development of experimental science, accelerated travel due to improvements in mapping and ship design, increasingly rapid technological progress, secularized civic politics, and the emergence of nation states. Historians typically date the end of the early modern period when the French Revolution of the 1790s began the "modern" period.[2]
Early modern timeline

- Dates are approximate. Consult particular article for details.
- Early modern themes Other
East Asia
Chinese dynasties
In 16th-century China, the Ming Dynasty's economy was stimulated by maritime trade with the Portuguese, Spanish and Dutch Empires. China became involved in a new global trade of goods, plants, animals and crops. Trade with Early Modern Europe and Japan brought in massive amounts of silver, which then replaced copper and paper banknotes as the common medium of exchange in China.
During the last decades of the Ming dynasty, the flow of silver into China was greatly diminished, undermining state revenues and the entire Chinese economy. The damage to the economy was compounded by the effects on agriculture of the incipient Little Ice Age, natural calamities, crop failure and sudden epidemics. The ensuing breakdown of authority and people's livelihoods allowed rebel leaders, such as Li Zicheng, to challenge Ming authority.
The Ming Dynasty fell around 1644 to the Qing Dynasty, the last ruling dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 (with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917). During its reign, the Qing Dynasty became highly integrated with Chinese culture.
Japanese shogunates
Following contact with the Portuguese on Tanegashima Isle in 1543, the Japanese adopted several of the technologies and cultural practices of their visitors, whether in the military area (the arquebus, European-style cuirasses, European ships), religion (Christianity), decorative art, language (integration to Japanese of a Western vocabulary) and culinary: the Portuguese introduced tempura and valuable refined sugar.
The Azuchi-Momoyama period saw the political unification that preceded the establishment of the Tokugawa shogunate. Although a start date of 1573 is often given, in more broad terms, the period begins with Oda Nobunaga's entry into Kyoto in 1568, when he led his army to the imperial capital in order to install Ashikaga Yoshiaki as the 15th, and ultimately final, shogun of the Ashikaga shogunate, and it lasts until the coming to power of Tokugawa Ieyasu after his victory over supporters of the Toyotomi clan at the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600.[3]
The Edo period from 1600 to 1868 characterized early modern Japan. The Tokugawa shogunate was a feudal regime of Japan established by Tokugawa Ieyasu and ruled by the shoguns of the Tokugawa family. The period gets its name from the capital city, Edo, now called Tokyo. The Tokugawa shogunate ruled from Edo Castle from 1603 until 1868, when it was abolished during the Meiji Restoration in the late Edo period (often called the Late Tokugawa shogunate).
Korean dynasty
In 1392, General Yi Seong-gye established the Joseon Dynasty (1392–1910) with a largely bloodless coup. Joseon experienced advances in science and culture. King Sejong the Great (1418–1450) promulgated hangul, the Korean alphabet. The period saw various other cultural and technological advances as well as the dominance of neo-Confucianism over the entirety of Korea.
During the late 16th and early 17th centuries, invasions by the neighboring Japanese and northern Manchus nearly overran the Korean peninsula.
After invasions from Manchuria, Joseon experienced nearly 200 years of peace. However, whatever power the kingdom recovered during its isolation further waned as the 18th century came to a close, and Korea was faced with internal strife, power struggles, international pressure and rebellions at home. The Joseon Dynasty declined rapidly in the late 19th century.
Indian Empires

On the Indian subcontinent, the Lodhi Dynasty ruled over the Delhi Sultanate during its last phase. The dynasty founded by Bhalul Lodhi ruled from 1451 to 1526. The dynasty's last ruler, Ibrahim Lodhi, was defeated and killed by Babur in the first Battle of Panipat.
The Vijayanagara Empire was based in the Deccan Plateau, but its power was diminished after a major military defeat in 1565 by the Deccan sultanates. The empire is named after its capital city of Vijayanagara.
The rise of the Great Mughal Empire is usually dated from 1526, around the end of the Middle Ages. It was an Islamic Persianate[4] imperial power that ruled most of the area as Hindustan by the late 17th and the early 18th centuries.[5] The empire dominated South and Southwestern Asia.
Southeast Asia
At the start of the modern era, the Spice Route between India and China crossed Majapahit,[6] an archipelagic empire based on the island of Java. It was the last of the major Hindu empires of Maritime Southeast Asia and is considered one of the greatest states in Indonesian history.[6] Its influence extended to states in Sumatra, the Malay Peninsula, Borneo and eastern Indonesia, but the effectiveness of the influence is the subject of debate.[7] Majapahit found itself unable to control the rising power of the Sultanate of Malacca, which grew to stretch from Muslim Malay settlements of Bukit (Phuket), Setol (Satun), Pantai ni (Pattani) bordering Ayutthaya Kingdom of Siam (Thailand) in the north to Sumatra in the southwest. The Portuguese invaded its capital in 1511 and in 1528 the Sultanate of Johor was established by a Malaccan prince to succeed Malacca.
Africa and the Near East
The Ottoman Empire

During the early modern era, the Ottoman state enjoyed an expansion and consolidation of power, leading to a Pax Ottomana. This was perhaps the golden age of the Ottoman Empire. The Ottomans expanded southwest into North Africa while battling with the re-emergent Persian Shi'a Safavid Empire to the east.
North and Northeast Africa
In the Saracen sphere, the Ottomans seized Egypt in 1517 and established the regencies of Algeria, Tunisia, and Tripoli (between 1519 and 1551), Morocco remaining an independent Arabized Berber state under the Sharifan dynasty.
In the Ethiopian Highlands, the Solomonic dynasty established itself in the 13th century. Claiming direct descent from the old Axumite royal house, the Solomonic ruled the region well into modern history. In the 16th century, Shewa and the rest of Abyssinia were conquered by the forces of Ahmed Gurey of the Adal Sultanate to the northwest. The conquest of the area by the Oromo ended in the contraction of both Adal and Abyssinia, changing regional dynamics for centuries to come.
The Ajuran Empire, which was one of the largest and strongest empires in the Horn of Africa, began to decline in the 17th century, and several powerful successor states came to prominence. The Geledi Sultanate, established by Ibrahim Adeer, was a notable successor of the Ajuran Sultanate. The Sultanate reached its apex under the successive reigns of Sultan Yusuf Mahamud Ibrahim (reigned 1798 to 1848), who successfully consolidated Geledi power during the Bardera wars, and Sultan Ahmed Yusuf, who forced regional powers such as the Omani Empire to pay tribute. The Majeerteen Sultanate was a Somali Sultanate in the Horn of Africa. Ruled by King Osman Mahamuud during its golden age, it controlled much of northern and central Somalia in the 19th and early 20th centuries. The polity had all of the organs of an integrated modern state and maintained a robust trading network. Along with the Sultanate of Hobyo ruled by Sultan Yusuf Ali Kenadid, the Majeerteen Sultanate was eventually annexed into Italian Somaliland in the early 20th century, following the military Campaign of the Sultanates.
Sub-Saharan Africa
The Songhai Empire took control of the trans-Saharan trade at the beginning of the modern era. It seized Timbuktu in 1468 and Jenne in 1473, building the regime on trade revenues and the cooperation of Muslim merchants. The empire eventually made Islam the official religion, built mosques, and brought Muslim scholars to Gao.[8]
Around the beginning of the modern era, the Benin Empire was an independent trading power in West Africa, blocking the access of other inland nations to the coastal ports. Benin may have housed 100,000 inhabitants at its height, spreading over twenty-five square kilometres, enclosed by three concentric rings of earthworks. By the late 15th century Benin was in contact with Portugal. At its apogee in the 16th and 17th centuries, Benin encompassed parts of southeastern Yorubaland and the western Igbo.
Safavids
The Safavid Empire was a great Shia Persianate empire after the Islamic conquest of Persia and established of Islam, marking an important point in the history of Islam in the east. The Safavid dynasty was founded about 1501. From their base in Ardabil, the Safavids established control over all of Persia and reasserted the Iranian identity of the region, thus becoming the first native dynasty since the Sassanids to establish a unified Iranian state. Problematic for the Safavids was the powerful Ottoman Empire. The Ottomans, a Sunni dynasty, fought several campaigns against the Safavids.
What fueled the growth of Safavid economy was its position between the burgeoning civilizations of Europe to its west and Islamic Central Asia to its east and north. The Silk Road, which led from Europe to East Asia, revived in the 16th century. Leaders also supported direct sea trade with Europe, particularly England and The Netherlands, which sought Persian carpet, silk, and textiles. Other exports were horses, goat hair, pearls, and an inedible bitter almond hadam-talka used as a spice in India. The main imports were spice, textiles (woolens from Europe, cotton from Gujarat), metals, coffee, and sugar. Despite their demise in 1722, the Safavids left their mark by establishing and spreading Shi'a Islam in major parts of the Caucasus and West Asia.
Uzbeks and Afghan Pashtuns
In the 16th to early 18th centuries, Central Asia was under the rule of Uzbeks, and the far eastern portions were ruled by the local Pashtuns. Between the 15th and 16th centuries, various nomadic tribes arrived from the steppes, including the Kipchaks, Naymans, Kanglis, Kungrats, and Manġits. These groups were led by Muhammad Shaybani, who was the Khan of the Uzbeks.
The lineage of the Afghan Pashtuns stretches back to the Hotaki dynasty.[9] Following Muslim Arab and Turkic conquests, Pashtun ghazis (warriors for the faith) invaded and conquered much of northern India during the Lodhi dynasty and Suri dynasty. Pashtun forces also invaded Persia, and the opposing forces were defeated in the Battle of Gulnabad. The Pashtuns later formed the Durrani Empire.
Europe
European events and dates
The beginning of the early modern period is not clear-cut, but is generally accepted as in the late 15th century or early 16th century. Significant dates in this transitional phase from medieval to early modern Europe can be noted:
|
This era in Western Europe is referred to as the early modern European period and includes the Protestant Reformation, the European wars of religion, the Age of Discovery and the beginning of European colonialism, the rise of strong centralized governments, the beginnings of recognizable nation-states that are the direct antecedents of today's states, the Age of Enlightenment, and from the associated scientific advances the first phase of the Industrial Revolution. The emergence of cultural and political dominance of the Western world during this period is known as the Great Divergence.
The early modern period is taken to end with the French Revolution, the Napoleonic Wars, and the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire at the Congress of Vienna. At the end of the early modern period, the British and Russian empires had emerged as world powers from the multipolar contest of colonial empires, while the three great Asian empires of the early modern period, Ottoman Turkey, Mughal India and Qing China, all entered a period of stagnation or decline.
Renaissance and "early modern"
The expression "early modern" is at times incorrectly used as a substitute for the term Renaissance. However, "Renaissance" is properly used in relation to a diverse series of cultural developments that occurred over several hundred years in many different parts of Europe — especially central and northern Italy — and it spans the transition from late medieval civilization to the opening of the early modern period. In the visual arts and architecture, the term 'early modern' is not a common designation as the Renaissance period is clearly distinct from what came later. Only in the study of literature is the early modern period a standard designation. European music of the period is generally divided between Renaissance and Baroque. Similarly, philosophy is divided between Renaissance philosophy and the Enlightenment. In other fields, there is far more continuity through the period such as warfare and science.
European kingdoms and movements
In the early modern period, the Holy Roman Empire was a union of territories in Central Europe under a Holy Roman Emperor. The first emperor of the Holy Roman Empire was Otto I. The last was Francis II, who abdicated and dissolved the Empire in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. Despite its name, for much of its history the Empire did not include Rome within its borders.
The Renaissance[10] was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historic era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not uniform across Europe, this is a general use of the term. As a cultural movement, it encompassed a rebellion of learning based on classical sources, the development of linear perspective in painting, and gradual but widespread educational reform.
Notable individuals

Johannes Gutenberg is credited as the first European to use movable type printing, around 1439, and as the global inventor of the mechanical printing press. Nicolaus Copernicus formulated a comprehensive heliocentric cosmology (1543), which displaced the Earth from the center of the universe.[11] His book, De revolutionibus orbium coelestium (On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres) began modern astronomy and sparked the Scientific Revolution. Another notable individual was Machiavelli, an Italian political philosopher, considered a founder of modern political science. Machiavelli is most famous for a short political treatise, The Prince, a work of realist political theory.
Among the notable royalty of the time, Charles the Bold, known as Charles the Bold (or Rash) to his enemies,[12] he was the last Valois Duke of Burgundy, and his early death was a pivotal, if under-recognized, moment in European history. Charles has often been regarded as the last representative of the feudal spirit — a man who possessed no other quality than a blind bravery. Upon his death, Charles left an unmarried nineteen-year-old daughter, Mary of Burgundy, as his heir. Her marriage would have enormous implications for the political balance of Europe. The Habsburg Emperor secured the match for his son, the future Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, with the aid of Mary's stepmother, Margaret. In 1477, the territory of the Duchy of Burgundy was annexed by France. In the same year, Mary married Maximilian, Archduke of Austria, giving the Habsburgs control of the remainder of the Burgundian Inheritance.

Claude de Lorraine was the first Duke of Guise, from 1528 to his death. Claude distinguished himself at the battle of Marignano (1515), and was long in recovering from the twenty-two wounds he received in the battle. In 1521, he fought at Fuenterrabia, and Louise of Savoy ascribed the capture of the place to his efforts. In 1523 he became governor of Champagne and Burgundy, after defeating at Neufchâteau the imperial troops who had invaded this province. In 1525 he destroyed the Anabaptist peasant army, which was overrunning Lorraine, at Lupstein, near Saverne (Zabern). On the return of Francis I from captivity in 1528, Claude was made Duke of Guise in the peerage of France, though up to this time only princes of the royal house had held the title of duke and peer of France. The Guises, as cadets of the sovereign house of Lorraine and descendants of the house of Anjou, claimed precedence of the Bourbon princes of Condé and Conti.
The 3rd Duke of Alba was a nobleman of importance in the early modern period, nicknamed the "Iron Duke" by the Protestants of the Low Countries because of his harsh rule and cruelty. Tales of atrocities committed during his military operations in Flanders became part of Dutch and English folklore, forming a central component of the Black Legend.
In England, Henry VIII was the King of England and a significant figure in the history of the English monarchy. Although in the greater part of his reign he brutally suppressed the influence of the Protestant Reformation in England,[13] a movement having some roots with John Wycliffe in the 14th century, he is more popularly known for his political struggles with Rome. These struggles ultimately led to the separation of the Church of England from papal authority, the Dissolution of the Monasteries, and establishing himself as the Supreme Head of the Church of England. Though Henry reportedly became a Protestant on his death-bed, he advocated Catholic ceremony and doctrine throughout his life. Royal support for the English Reformation began with his heirs, the devout Edward VI and the renowned Elizabeth I, whilst daughter Mary I temporarily reinstated papal authority over England. Henry also oversaw the legal union of England and Wales with the Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542. He is also noted for his six wives, two of whom were beheaded.
Christians and Christendom
Christianity was challenged at the beginning of the modern period with the fall of Constantinople in 1453 and later by various movements to reform the church (including Lutheran, Zwinglian, and Calvinist), followed by the Counter Reformation.
End of the Crusades and Unity
The Hussite Crusades involved the military actions against and amongst the followers of Jan Hus in Bohemia ending ultimately with the Battle of Grotniki. Also known as the Hussite Wars, they were arguably the first European war in which hand-held gunpowder weapons such as muskets made a decisive contribution. The Taborite faction of the Hussite warriors were basically infantry, and their many defeats of larger armies with heavily armored knights helped effect the infantry revolution. In totality, the Hussite Crusades were inconclusive.
The last crusade, the Crusade of 1456, was organized to counter the expanding Ottoman Empire and lift the Siege of Belgrade, and was led by John Hunyadi and Giovanni da Capistrano. The siege eventually escalated into a major battle, during which Hunyadi led a sudden counterattack that overran the Turkish camp, ultimately compelling the wounded Sultan Mehmet II to lift the siege and retreat. The siege of Belgrade has been characterized as having "decided the fate of Christendom".[14] The noon bell ordered by Pope Callixtus III commemorates the victory throughout the Christian world to this day.
Nearly a hundred years later, the Peace of Augsburg officially ended the idea that all Christians could be united under one church. The principle of cuius regio, eius religio ("whose the region is, [it shall have] his religion") established the religious, political and geographic divisions of Christianity, and this was established in international law with the Treaty of Westphalia in 1648, which legally ended the concept of a single Christian hegemony, i.e. the "One, Holy, Catholic, and Apostolic Church" of the Nicene Creed. Each government determined the religion of their own state. Christians living in states where their denomination was not the established church were guaranteed the right to practice their faith in public during allotted hours and in private at their will. With the Treaty of Westphalia, the Wars of Religion came to an end, and in the Treaty of Utrecht of 1713 the concept of the sovereign national state was born. The Corpus Christianum has since existed with the modern idea of a tolerant and diverse society consisting of many different communities.
Inquisitions and Reformations
The modern Inquisition refers to any one of several institutions charged with trying and convicting heretics (or other offenders against canon law) within the Catholic Church. In the modern era, the first manifestation was the Spanish Inquisition of 1478 to 1834.[15] The Inquisition prosecuted individuals accused of a wide array of crimes related to heresy, including sorcery,[16] blasphemy, Judaizing and witchcraft, as well for censorship of printed literature. Because of its objective — combating heresy — the Inquisition had jurisdiction only over baptized members of the Church (which, however, encompassed the vast majority of the population in Catholic countries). Secular courts could still try non-Christians for blasphemy (most of the witch trials went through secular courts).
The Protestant Reformation and rise of modernity in the early 16th century entailed the start of a series of changes in the Corpus Christianum. Martin Luther challenged the Catholic Church with his Ninety-Five Theses, generally accepted as the beginning of the Reformation, a Christian reform movement in Europe, though precursors such as Jan Hus predate him. The Protestant movement of the 16th century occurred under the protection of the Electorate of Saxony, an independent hereditary electorate of the Holy Roman Empire. The Elector Frederick III established a university at Wittenberg in 1502. The Augustinian monk Martin Luther became professor of philosophy there in 1508. At the same time, he became one of the preachers at the castle church of Wittenberg.
On 31 October 1517, Luther posted his Ninety-Five Theses on the door of the All Saints' Church, which served as a notice board for university-related announcements.[17] These were points for debate that criticized the Church and the Pope. The most controversial points centered on the practice of selling indulgences (especially by Johann Tetzel) and the Church's policy on purgatory. The reform movement soon split along certain doctrinal lines. Religious disagreements between various leading figures led to the emergence of rival Protestant churches. The most important denominations to emerge directly from the Reformation were the Lutherans, and the Reformed/Calvinists/Presbyterians. The process of reform had decidedly different causes and effects in other countries. In England, where it gave rise to Anglicanism, the period became known as the English Reformation. Subsequent Protestant denominations generally trace their roots back to the initial reforming movements.
The Diet of Worms in 1521, presided by Emperor Charles V, declared Martin Luther a heretic and an outlaw (although Charles V was more preoccupied with maintaining his vast empire than with arresting Luther). As a result of Charles V's distractions in East Europe and in Spain, he agreed through the Diet of Speyer in 1526 to allow German princes to effectively decide themselves whether to enforce the Edict of Worms or not, for the time being. After returning to the empire, Charles V attended the Diet of Augsburg in 1530 to order all Protestants in the empire to revert to Catholicism. In response, the Protestant territories in and around Germany formed the Schmalkaldic League to fight against the Catholic Holy Roman Empire. Charles V left again to handle the advance of the Ottoman Turks. He returned in 1547 to launch a military campaign against the Schmalkaldic League and to issue an imperial law requiring all Protestants to return to Catholic practices (with a few superficial concessions to Protestant practices). Warfare ended when Charles V relented in the Peace of Passau (1552) and in the Peace of Augsburg (1555), which formalized the law that the rulers of a land decide its religion.
Of the late Inquisitions in the modern era, there were two different manifestations:[15]
- the Portuguese Inquisition (1536–1821)
- the Roman Inquisition (1542 – c.1860)
This Portuguese inquisition was a local analogue of the more famous Spanish Inquisition. The Roman Inquisition covered most of the Italian peninsula as well as Malta and also existed in isolated pockets of papal jurisdiction in other parts of Europe, including Avignon.
The Catholic Reformation began in 1545 when the Council of Trent was called in reaction to the Protestant Rebellion. The idea was to reform the state of worldliness and disarray that had befallen some of the clergy of the Church, while reaffirming the spiritual authority of the Catholic Church and its position as the sole true Church of Christ on Earth. The effort sought to prevent further damage to the Church and her faithful at the hands of the newly formed Protestant denominations.
Tsardom of Russia
In development of the Third Rome ideas, the Grand Duke Ivan IV (the "Awesome"[18] or "the Terrible") was officially crowned the first Tsar ("Caesar") of Russia in 1547. The Tsar promulgated a new code of laws (Sudebnik of 1550), established the first Russian feudal representative body (Zemsky Sobor) and introduced local self-management into the rural regions.[19][20] During his long reign, Ivan IV nearly doubled the already large Russian territory by annexing the three Tatar khanates (parts of disintegrated Golden Horde): Kazan and Astrakhan along the Volga River, and Sibirean Khanate in South Western Siberia. Thus by the end of the 16th century Russia was transformed into a multiethnic, multiconfessional and transcontinental state.
Discovery and trade

The Age of Discovery was a period from the early 15th century and continuing into the early 17th century, during which European ships traveled around the world to search for new trading routes and partners to feed burgeoning capitalism in Europe. They also were in search of trading goods such as gold, silver and spices. In the process, Europeans encountered peoples and mapped lands previously unknown to them. This factor in the early European modern period was a globalizing character; the 'discovery' of the Americas and the rise of sustained contacts between previously isolated parts of the globe was an important historical event.
The search for new routes was based on the fact that the Silk Road was controlled by the Ottoman Empire, which was an impediment to European commercial interests, and other Eastern trade routes were not available to the Europeans due to Muslim control. The ability to outflank the Muslim states of North Africa was seen as crucial to European survival. At the same time, the Iberians learnt much from their Arab neighbors. The northwestern region of Eurasia has a very long coastline, and has arguably been more influenced by its maritime history than any other continent. Europe is uniquely situated between several navigable seas, and intersected by navigable rivers running into them in a way that greatly facilitated the influence of maritime traffic and commerce. In the maritime history of Europe, the carrack and caravel both incorporated the lateen sail that made ships far more maneuverable. By translating the Arab versions of lost ancient Greek geographical works into Latin, European navigators acquired a deeper knowledge of the shape of Africa and Asia.
Mercantile capitalism
Mercantilism was the dominant school of economic thought throughout the early modern period (from the 16th to the 18th century). This led to some of the first instances of significant government intervention and control over the economy, and it was during this period that much of the modern capitalist system was established. Internationally, mercantilism encouraged the many European wars of the period and fueled European imperialism. Belief in mercantilism began to fade in the late 18th century, as the arguments of Adam Smith and the other classical economists won out.
The Commercial Revolution was a period of economic expansion, colonialism, and mercantilism that lasted from approximately the 16th century until the early 18th century. Beginning with the Crusades, Europeans rediscovered spices, silks, and other commodities rare in Europe. This development created a new desire for trade, which expanded in the second half of the Middle Ages. European nations, through voyages of discovery, were looking for new trade routes in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries, which allowed the European powers to build vast, new international trade networks. Nations also sought new sources of wealth. To deal with this new-found wealth, new economic theories and practices were created. Because of competing national interest, nations had the desire for increased world power through their colonial empires. The Commercial Revolution is marked by an increase in general commerce, and in the growth of non-manufacturing pursuits, such as banking, insurance, and investing.
Trade and the New Economy
In the Old World, the most desired trading goods were gold, silver, and spices. Western Europeans used the compass, new sailing ship technologies, new maps, and advances in astronomy to seek a viable trade route to Asia for valuable spices that Mediterranean powers could not contest.
|
|
In terms of shipping advances, the most important developments were the creation of the carrack and caravel designs in Portugal. These vessels evolved from medieval European designs from the North Sea and both the Christian and Islamic Mediterranean. They were the first ships that could leave the relatively placid and calm Mediterranean, Baltic or North Sea and sail safely on the open Atlantic.
When the carrack and then the caravel were developed in Iberia, European thoughts returned to the fabled East. These explorations have a number of causes. Monetarists believe the main reason the Age of Exploration began was because of a severe shortage of bullion in Europe. The European economy was dependent on gold and silver currency, but low domestic supplies had plunged much of Europe into a recession. Another factor was the centuries-long conflict between the Iberians and the Muslims to the south.
Piracy's Golden Age
The Golden Age of Piracy is a designation given to one or more outbursts of piracy in the early modern period, spanning from the mid-17th century to the mid-18th century. The buccaneering period covers approximately the late 17th century. The period is characterized by Anglo-French seamen based on Jamaica and Tortuga attacking Spanish colonies and shipping in the Caribbean and eastern Pacific. A sailing route known as the Pirate Round was followed by certain Anglo-American pirates at the turn of the 18th century, associated with long-distance voyages from Bermuda and the Americas to rob Muslim and East India Company targets in the Indian Ocean and Red Sea. The post-Spanish Succession period extending into the early 18th century, when Anglo-American sailors and privateers left unemployed by the end of the War of the Spanish Succession turned en masse to piracy in the Caribbean, the American eastern seaboard, the West African coast, and the Indian Ocean.
European states and politics
The 15th to 18th century period is marked by the first European colonies, the rise of strong centralized governments, and the beginnings of recognizable European nation states that are the direct antecedents of today's states. Although the Renaissance saw revolutions in many intellectual pursuits, as well as social and political upheaval, it is perhaps best known for European artistic developments and the contributions of such polymaths as Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo, who inspired the term "Renaissance man".[21][22]
The Baroque period brought the Thirty Years' War in Central Europe, which decimated the population by up to 20%. The treaties in 1648 ended several wars in Europe and established the beginning of sovereign states. The Peace of Westphalia refers to the two peace treaties of Osnabrück and Münster, signed on May 15 and October 24, 1648, respectively, and written in French, that ended both the Thirty Years' War in the Holy Roman Empire (today mostly Germany) and the Eighty Years' War between Spain and the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. The treaties involved the Holy Roman Emperor, Ferdinand III (Habsburg), the Kingdoms of Spain, France and Sweden, the Netherlands and their respective allies among the princes and the Republican Imperial States of the Holy Roman Empire.
The Peace of Westphalia resulted from the first modern diplomatic congress. Until 1806, the regulations became part of the constitutional laws of the Holy Roman Empire. The Treaty of the Pyrenees, signed in 1659, ended the war between France and Spain and is often considered part of the overall accord.
Absolutism
The Age of Absolutism describes the monarchical power that was unrestrained by any other institutions, such as churches, legislatures, or social elites of the European monarchs during the transition from feudalism to capitalism. Monarchs described as absolute can especially be found in the 17th century through the 19th century. Nations that adopted Absolutism include France, Prussia, and Russia. Nobles tended to trade privileges for allegiance throughout the eighteenth century, so that the interests of the nobility aligned with that of the crown. Absolutism is characterized by the ending of feudal partitioning, consolidation of power with the monarch, rise of state power, unification of the state laws, drastic increase in tax revenue collected by the monarch, and a decrease in the influence of nobility.
French power
For much of the reign of Louis XIV, who was known as the Sun King (French: le Roi Soleil), France stood as the leading power in Europe, engaging in three major wars—the Franco-Dutch War, the War of the League of Augsburg, and the War of the Spanish Succession—and two minor conflicts—the War of Devolution, and the War of the Reunions. Louis believed in the Divine Right of Kings, the theory that the King was crowned by God and accountable to him alone. Consequently, he has long been considered the archetypal absolute monarch. Louis XIV continued the work of his predecessor to create a centralized state, governed from the capital to sweep away the remnants of feudalism that persisted in parts of France. He succeeded in breaking the power of the provincial nobility, much of which had risen in revolt during his minority called the Fronde, and forced many leading nobles to live with him in his lavish Palace of Versailles.
Men who featured prominently in the political and military life of France during this period include Mazarin, Jean-Baptiste Colbert, Turenne, Vauban. French culture likewise flourished during this era, producing a number of figures of great renown, including Molière, Racine, Boileau, La Fontaine, Lully, Le Brun, Rigaud, Louis Le Vau, Jules Hardouin Mansart, Claude Perrault and Le Nôtre.
Early English revolutions
Before the Age of Revolution, the English Civil War was a series of armed conflicts and political machinations between Parliamentarians and Royalists. The first and second civil wars pitted the supporters of King Charles I against the supporters of the Long Parliament, while the third war saw fighting between supporters of King Charles II and supporters of the Rump Parliament. The Civil War ended with the Parliamentary victory at the Battle of Worcester. The monopoly of the Church of England on Christian worship in England ended with the victors consolidating the established Protestant Ascendancy in Ireland. Constitutionally, the wars established the precedent that an English monarch cannot govern without Parliament's consent. The English Restoration, or simply put as the Restoration, began in 1660 when the English, Scottish and Irish monarchies were all restored under Charles II after the Commonwealth of England that followed the English Civil War. The Glorious Revolution of 1688 establishes modern parliamentary democracy in England.
International balance of power
The War of the Spanish Succession was a war fought between 1701 and 1714, in which several European powers combined to stop a possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under a single Bourbon monarch, upsetting the European balance of power. It was fought mostly in Europe, but it included Queen Anne's War in North America. The war was marked by the military leadership of notable generals like the duc de Villars, the Jacobite Duke of Berwick, the Duke of Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy.
The Peace of Utrecht established after a series of individual peace treaties signed in the Dutch city of Utrecht concluded between various European states helped end the War of the Spanish Succession. The representatives who met were Louis XIV of France and Philip V of Spain on the one hand, and representatives of Queen Anne of Great Britain, the Duke of Savoy, and the United Provinces on the other. The treaty enregistred the defeat of French ambitions expressed in the wars of Louis XIV and preserved the European system based on the balance of power.[23] The Treaty of Utrecht marked the change from Spanish to British naval supremacy.
New World and Americas
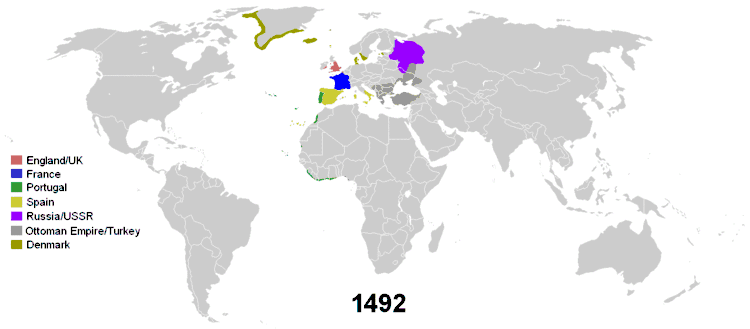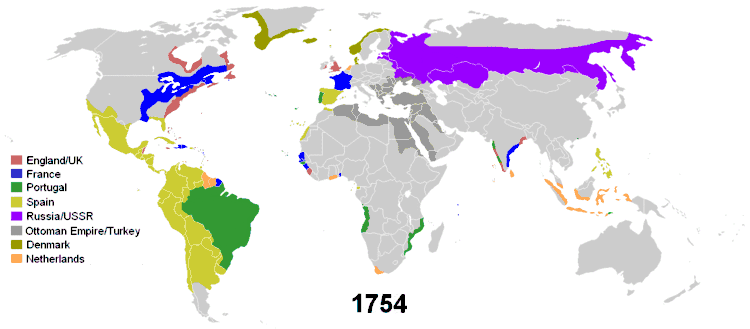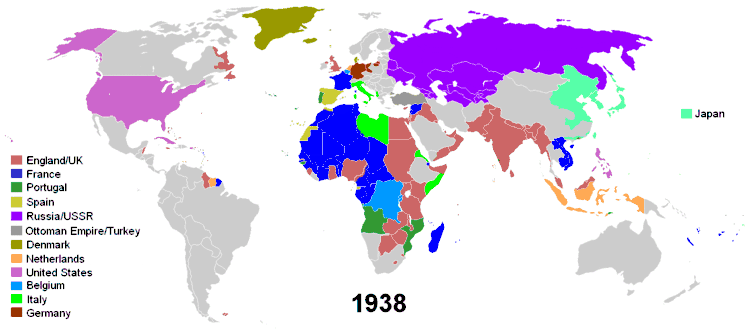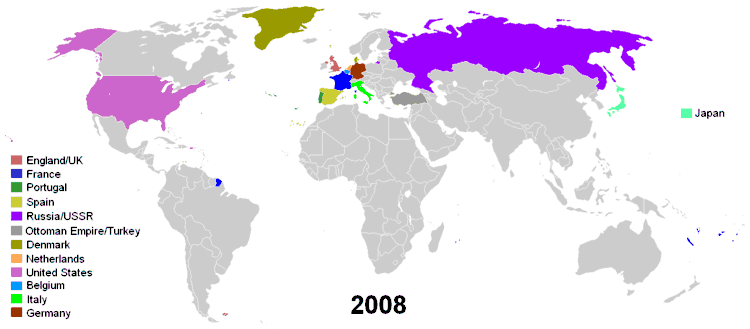
The historical phenomenon of colonization in the modern era centres on the British Empire, but the term colonialism is normally used with reference to discontiguous overseas empires rather than contiguous land-based empires, European or otherwise. European colonisation during the 15th to 19th centuries resulted in the spread of Christianity to Sub-Saharan Africa, the Americas, Australia and the Philippines.
Conquest and Americas exploration
Christopher Columbus discovered the Americas in 1492. Subsequently, the major sea powers in Europe sent expeditions to the New World to build trade networks and colonies and to convert the native peoples to Christianity. Pope Alexander VI divided newly discovered lands outside Europe between Spain and Portugal along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde islands (off the west coast of Africa). The division was never accepted by the rulers of England or France. (See also the Treaty of Tordesillas, which followed the papal decree.)
Colonial Latin America
What is now called Latin America, a designation first used in the late 19th century,[24] was claimed by Spain and Portugal. The Western Hemisphere, the New World,[25] was divided between the two Iberian powers by the Treaty of Tordesillas in what until the late 16th-century, was an area that could be called "Ibero-America." Spain called its overseas empire there "The Indies," with Portugal calling its territory in South America Brazil, after the dyewood found there. Spain concentrated building its empire where there were large indigenous populations, "Indians," who could be compelled to work and large deposits of precious metals, mainly silver. Both New Spain (colonial Mexico) and Peru fit those criteria and the Spanish crown established viceroyalties to rule those two large areas. As Spanish settlements and the economy grew in size and complexity, the Spanish established viceroyalties in the eighteenth century during administrative reforms Rio de la Plata (southeastern South America) and New Granada (northern South America).
Initially, Portuguese settlements (Brazil) in the coastal northeast were of lesser importance in the larger Portuguese overseas empire, where lucrative commerce and small settlements devoted to trade were established in coastal Africa, India and China. With sparse indigenous populations that could not be coerced to work and no known deposits of precious metals, Portugal sought a high-value, low-bulk export product and found it in sugarcane. Black African slave labour from Portugal's West African possessions was imported to do the grueling agricultural work. As the wealth of the Ibero-America increased, some Western European powers (Dutch, French, British, Danish) sought to duplicate the model in areas that the Iberians had not settled in numbers. They seized Caribbean islands from the Spanish and transferred the model of sugar production on plantations with slave labour and settled in northern areas of North America in what are now the Eastern Seaboard of the United States and Canada.[26]
Colonial North America
North America outside the zone of Spanish settlement was a contested area in the 17th century. Spain had founded small settlements in Florida and Georgia but nowhere near the size of those in New Spain or the Caribbean islands. France, The Netherlands, and Great Britain held several colonies in North America and the West Indies from the 17th century, 100 years after the Spanish and Portuguese established permanent colonies. The British colonies in North America were founded between 1607 (Virginia) and 1733 (Georgia). The Dutch explored the east coast of North America and began founding settlements in what they called New Netherland (now New York State.). France colonized what is now Eastern Canada, founding Quebec City in 1608. France's loss in the Seven Years' War resulted in the transfer of New France to Great Britain. The Thirteen Colonies, in lower British North America, rebelled against British rule in 1775, largely by the taxation that Great Britain was imposing on the colonies. The British colonies in Canada remained loyal to the crown, and a provisional government formed by the Thirteen Colonies proclaimed their independence on July 4, 1776 and subsequently became the original 13 United States of America. With the 1783 Treaty of Paris ending the American Revolutionary War, Britain recognised the former Thirteen Colonies' independence.
Atlantic World
A recent development in early modern history is the creation of Atlantic World as a category. The term generally encompasses western Europe, West Africa, North and South and America and the Caribbean islands. It seeks to show both local and regional development and the connections between the various geographical regions.
Religious trends and philosophy
Eastern philosophies
Concerning the development of Eastern philosophies, much of Eastern philosophy had been in an advanced state of development from study in the previous centuries. The various philosophies include Indian philosophy,[27] Chinese philosophy, Iranian philosophy, Japanese philosophy, and Korean philosophy.
Muslim world
The Islamic Golden Age reached its peak in the High Middle Ages, stopped short by the Mongol invasions of the 13th century. The re-establishment of three major Muslim empires by the 16th century (the aforementioned Ottoman Safavid and Mughal Empires) gave rise to a Muslim cultural revival. The Safavids established Twelver Shi'a Islam as Iran's official religion, thus giving Iran a separate identity from its Sunni neighbors.
Protestant Reformation
The early modern period was initiated by the Protestant Reformation and the collapse of the unity of the medieval Western Church. The theology of Calvinism in particular has been argued as instrumental to the rise of capitalism (The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism).
Counter-Reformation and Jesuits
The Counter-Reformation was a period of Catholic revival in response to the Protestant Reformation during the mid-16th to mid-17th centuries. The Counter-Reformation was a comprehensive effort, involving ecclesiastical or structural reforms as well as a political dimension and spiritual movements.
Such reforms included the foundation of seminaries for the proper training of priests in the spiritual life and the theological traditions of the Church, the reform of religious life by returning orders to their spiritual foundations and new spiritual movements focusing on the devotional life and a personal relationship with Christ, including the Spanish mystics and the French school of spirituality. It also involved political activities that included the Roman Inquisition.
New religious orders were a fundamental part of this trend. Orders such as the Capuchins, Ursulines, Theatines, Discalced Carmelites, the Barnabites, and especially the Jesuits strengthened rural parishes, improved popular piety, helped to curb corruption within the church and set examples that would be a strong impetus for Catholic renewal.
Humanism
With the adoption of large-scale printing after 1500, Italian Renaissance Humanism spread northward to France, Germany, Holland and England, where it became associated with the Protestant Reformation. In France, pre-eminent Humanist Guillaume Budé (1467–1540) applied the philological methods of Italian Humanism to the study of antique coinage and to legal history, composing a detailed commentary on Justinian's Code. Although a royal absolutist (and not a republican like the early Italian umanisti), Budé was active in civic life, serving as a diplomat for Francis I and helping to found the Collège des Lecteurs Royaux (later the Collège de France). Meanwhile, Marguerite de Navarre, the sister of Francis I, herself a poet, novelist and religious mystic,[28] gathered around her and protected a circle of vernacular poets and writers, including Clément Marot, Pierre de Ronsard and François Rabelais.
17th-century philosophy
The philosophy of 17th-century Europe marks the departure from medieval scholasticism and the often occultist approach of Renaissance philosophy. The period was typified in Europe by the great system-builders, philosophers who presented unified systems of epistemology, metaphysics, logic, and ethics and often politics and the physical sciences as well.
Immanuel Kant classified his predecessors into two schools: the rationalists and the empiricists,[29] The three main rationalists are normally taken to have been René Descartes, Baruch Spinoza, and Gottfried Leibniz.
The mid-17th century saw the first great advances towards modern science, most notably the theory of gravity by Isaac Newton (1643–1727).
He and Baruch Spinoza (1632–1677), John Locke (1632–1704) and Pierre Bayle (1647–1706) were philosophers sparking the Age of Enlightenment in the following century.
Age of Reason and the scientific revolution
The Great Divergence is epitomized by the Age of Enlightenment (or Age of Reason). The Enlightenment, starting in the 1750s, flourished until about 1790–1800 after which the emphasis on reason gave way to Romanticism's emphasis on emotion and a Counter-Enlightenment gained force.
The centre of the Enlightenment was France, where it was based in the salons and culminated in the great Encyclopédie (1751–1772), edited by Denis Diderot (1713–1784) with contributions by hundreds of leading philosophes (intellectuals) such as Voltaire (1694–1778) and Montesquieu (1689–1755). The French Enlightenment was received in Germany, notably fostered by Frederick the Great, the king of Prussia, and gave rise to a flowering of German philosophy, represented foremost by Immanuel Kant.
The French and German developments were further influential in Scottish, Russian, Spanish and Polish philosophy.
End of early period

In modern history, the end of the early period falls in the late 18th century, as an Age of Revolutions dawns, beginning with those in North America and France. Subsequent important political changes occurred throughout Europe, including upheavals following the Napoleonic Wars, the redrawing of the map of Europe through the Second Treaty of Paris, the rise of new concepts of nationalism and the reorganization in military forces. The end of the early modern period is usually also associated with the Industrial Revolution, which began in Britain in the mid-18th century.
See also
- Economic concepts
- Price revolution, Proto-globalization
- General concepts
- Renaissance, Early Modern English, Early Modern warfare, Periodization, Atlantic history, Timeline of early modern history
- Political powers
- Habsburg Spain, Habsburg Monarchy, Portuguese Empire, Dutch Republic, Early Modern Britain, Early Modern France, Early Modern Italy, Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, Ottoman Empire, Mughal Empire, Safavid Empire
References
- ↑ Jan De Vries, "The limits of globalization in the early modern world." Economic History Review (2010) 63#3 pp: 710–733.
- ↑ Christopher Alan Bayly, The birth of the modern world, 1780–1914: global connections and comparisons (2004).
- ↑ Kodansha Encyclopedia of Japan (First edition, 1983), section "Azuchi-Momoyama History (1568–1600)" by George Elison, in the entry for "history of Japan."
- ↑ L. Canfield, Robert; Jonathan Haas (2002). Turko-Persia in Historical Perspective. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-52291-5.; p. 20;
- ↑ "Manas: History and Politics, Mughals".
- 1 2 M.C. Ricklefs, A History of Modern Indonesia Since c. 1300, 2nd ed. Stanford: Stanford University Press, 1991. page 19
- ↑ Prapantja, Rakawi, translated by Theodore Gauthier Pigeaud, Java in the 14th Century, A Study in Cultural History: The Negara-Kertagama by Pakawi Parakanca of Majapahit, 1365 AD (The Hague, Martinus Nijhoff, 1962), vol. 4, p. 29. 34; G.J. Resink, Indonesia's History Between the Myths: Essays in Legal History and Historical Theory (The Hague: W. van Hoeve, 1968), p. 21.
- ↑ Ira M. Lapidus, A History of Islamic Societies, Cambridge 1988
- ↑ Afghanistan: History, U.S. Department of State (retrieved 10 October 2006).
- ↑ "Online Etymology Dictionary".
- ↑ A Greek mathematician, Aristarchus of Samos, had already discussed heliocentric hypotheses as early as the third century BCE. However, there is little evidence that he ever developed his ideas beyond a very basic outline (Dreyer, 1953, pp.135–48; Linton, 2004, p. 39).
- ↑ The title was derived from his savage behavior against his enemies, and particularly from a war with France in late 1471: frustrated by the refusal of the French to engage in open battle, and angered by French attacks on his unprotected borders in Hainault and Flanders, Charles marched his army back from the Ile-de-France to Burgundian territory, burning over two thousand towns, villages and castles on his way—Taylor, Aline S. Isabel of Burgundy. Lanham, Md: Madison Books, c2001, pp. 212–213
- ↑ See Martyrdom of William Tyndale.
- ↑ Pope Calixtus III account from 1456 to the Burgundian bishop talking about the savior of Christianity at Belgrade
- 1 2 Medieval Sourcebook: Inquisition – Introduction
- ↑ this also includes black magic (Maleficium).
- ↑ Simon, Edith (1966). Great Ages of Man: The Reformation. Time-Life Books. pp. 120–121. ISBN 0-662-27820-8.
- ↑ Frank D. McConnell. Storytelling and Mythmaking: Images from Film and Literature. Oxford University Press, 1979. ISBN 0-19-502572-5; Quote from page 78: "But Ivan IV, Ivan the Terrible, or as the Russian has it, Ivan Groznyi, "Ivan the Magnificent" or "Ivan the Awesome," is precisely a man who has become a legend"
- ↑ Solovyov, S. (2001). History of Russia from the Earliest Times. 6. AST. pp. 562–604. ISBN 5-17-002142-9.
- ↑ Skrynnikov, R. (1981). Ivan the Terrible. Academic Intl Pr. p. 219. ISBN 0-87569-039-4.
- ↑ BBC Science & Nature, Leonardo da Vinci (Retrieved on May 12, 2007)
- ↑ BBC History, Michelangelo (Retrieved on May 12, 2007)
- ↑ R.R. Palmer, A History of the Modern World 2nd ed. 1961, p. 234.
- ↑ José C. Moya, ed. The Oxford Handbook of Latin America. New York: Oxford University Press 2011
- ↑ There is no known human evolution in the Western Hemisphere so all humans came on foot or boat to the vast new area.
- ↑ James Lockhart and Stuart B. Schwartz, Early Latin America. New York: Cambridge University Press 1983.
- ↑ Of note in modern Indian philosophy are the philosophers who gave contemporary meaning to traditional philosophy, such as Swami Vivekananda.
- ↑ She was the author of Miroir de l'ame pecheresse (The Mirror of a Sinful Soul), published after her death, among other devotional poetry. See also "Marguerite de Navarre: Religious Reformist" in Jonathan A. Reid, King's sister—queen of dissent: Marguerite of Navarre (1492–1549) and her evangelical network (Studies in medieval and Reformation traditions, 1573–4188; v. 139). Leiden; Boston: Brill, 2009. (2 v.: (xxii, 795 p.) ISBN 978-90-04-17760-4 (v. 1), 9789004177611 (v. 2)
- ↑ "Kant, Immanuel: Metaphysics – Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy".
Further reading
- Cavallo, Sandra, and Silvia Evangelisti, eds. A Cultural History of Childhood and Family in the Early Modern Age (2014)
- De Vries, Jan. "The limits of globalization in the early modern world." Economic History Review (2010) 63#3 pp: 710–733. online
- Duara, Prasenjit et al. eds. A Companion to Global Historical Thought (Wiley Blackwell 2014)
- Goldstone, Jack A. "Early Modern World." in Sociological Worlds: Comparative and Historical Readings on Society (2013) pp: 249+
- Goldstone, Jack A. Revolution and Rebellion in the Early Modern World (1993)
- Goldstone, Jack A. "The Rise of the West–or not? A revision to socio-economic history," Sociological Theory (2000). 18#2 pp 173–194
- Knoll, Martin, and Reinhold Reith, eds. An Environmental History of the Early Modern Period (2014)
- Kümin, Beat A. A cultural history of food in the early modern age (1600–1800) (Berg, 2011)
- Parker, Charles H. Global Interactions in the Early Modern Age, 1400–1800 (2010)
- Pomeranz, Kenneth. The great divergence: China, Europe, and the making of the modern world economy (Princeton University Press, 2000), a highly influential statement
- Wong, R. Bin. China Transformed; Historical Change and the Limits of European Experience (Cornell U.P., 1997)
External links
- Internet Modern History Sourcebook, fordham.edu
- Websites
- Discussion of the medieval/modern transition from the introduction to the pioneering Cambridge Modern History (1902–1912)
- Society for Renaissance Studies
- Early Modern Culture
- Early Modern Resources
- Video
- Int'l Commerce, Snorkeling Camels, and The Indian Ocean Trade on YouTube: Crash Course World History #18 – YouTube
- Venice and the Ottoman Empire on YouTube: Crash Course World History #19 – YouTube
- Columbus, de Gama, and Zheng He! 15th Century Mariners on YouTube. Crash Course : World History #21 – YouTube
- The Columbian Exchange on YouTube: Crash Course World History #23 – YouTube
- The Atlantic Slave Trade on YouTube: Crash Course World History #24 – YouTube
- The Spanish Empire, Silver, & Runaway Inflation on YouTube: Crash Course World History #25 – YouTube
- The Seven Years War on YouTube: Crash Course World History #26 – YouTube
- Tea, Taxes, and The American Revolution on YouTube: Crash Course World History #28 – YouTube
| Preceded by Postclassical Era |
History by period 1450 CE – 1750 CE |
Succeeded by Modern history |


