E and M signaling
E and M signaling is a type of supervisory line signaling that uses DC signals on separate leads, called the "E" lead and "M" lead, traditionally used in the telecommunications industry between telephone switches. Various mnemonic names have been used to memorize these letters, such as Ear and Mouth, the most common variation.
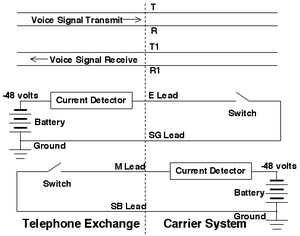
E&M was originally developed to allow PABXs in different geographic locations to communicate over an analog private circuit. Some digital interfaces such as Channel Associated Signaling also use versions of E&M signaling. E&M is considered an obsolete technology for new installations, which generally use Basic Rate (BRI) or Primary Rate (PRI) digital interfaces.
Signaling units and trunk circuits
The E&M standards were initially developed by Bell Labs and extended by national PTT administrations. The standard defines two sides to the interface:
- Trunk circuit – this is normally the PABX
- Signaling unit – this used to refer to the special modem that converted the DC signaling systems into tones that could be transmitted over a 4-wire link back to the PTT exchange.
The signaling unit and trunk circuit communicate their status over the E and M leads, using a combination of Battery and Earth (also known as Ground). The Battery signal used in the standard is nominally −48VDC. All E&M installations require that the +ve terminal of the Battery is connected to a shared reliable Earth.
The maximum distance between the Signaling Unit and the Trunk interface is determined by the resistance of the wire, but will normally be less than 100m for adequate noise immunity.
Variants
The group of E&M signaling includes the following variations:
- Type I is the most common standard in North America and Japan, and signals an outgoing call to the signaling unit with Battery on the M ("Mouth") lead. Incoming calls are signaled by an Earth (ground) signal on the E ("Ear") lead. The interface is vulnerable to poor earthing at either end, and interference from external electrical noise
- Types II to IV are variants which attempt to overcome the main limitation of Type I, which is the reference to Earth at each end of the circuit. Types II-IV use the Signal Battery (SB) and Signal Ground (SG) lead in conjunction with the E&M wires. This improves noise immunity as the Signal Ground does not carry the same heavy currents as normal Ground connections and provides a low resistance return path for signaling. However, if the main Ground connection fails all Earth current may flow via the interface, causing signaling failure, hum and in extreme cases destruction of equipment.
- Type V is the most common variant in use outside United States. In contrast to Type I, both ends of the connection indicate a call by grounding the relevant lead. This means that it is easy to interconnect two PABXs "back-to-back" by crossing over the E&M leads and transmit and receive pairs.
- SSDC5 is commonly used in the United Kingdom and unlike Type V the on- and off-hook state, are backwards to allow for fail-safe operation. If line breaks interface defaults to busy.
Number of wires
E&M defines eight wires:
- E: It is often called ear or earth
- M: It is often called mouth or magneto
- SG and SB: signal ground and signal battery
- T and R: Tip and Ring – the ground and battery of the receiver voice pair
- T1 and R1: the ground and battery of the transmitter voice pair
4-wire E&M uses a 4-wire (2-pair) transmission path for the voice signal. 2-wire E&M uses a single pair for both transmit and receive voice signal. This is much inferior to 4-wire E&M as the 2-wire interface uses hybrid transformers which reduce signal quality and can introduce echo.
Address signaling
The mechanisms described so far only allow circuit seizure – on-hook and off-hook – to be signaled. In order to allow dialing over the interface, "start" signaling mechanisms are defined. This allows the other end to know when to send the dialed digits, which are transmitted by pulse (loop disconnect) or multi-frequency tones. E&M defines three methods of "start" signaling:
- Wink Start – when the originator goes off hook, the other end transmits a short (140-290ms) off-hook signal and returns to on-hook. The originator detects the wink and then sends the dialed digits. The other end goes permanently off-hook (seized) when the call is answered.
- Delay Start – the originator goes off hook, waits a pre-defined delay, and then checks for on-hook from the other end before sending the digits.
- Immediate Start – The originator goes off hook, waits 150ms and then sends the dialed digits.
Origin of "E&M"
The choice of letters for the E and M leads was fortuitous, unrelated to any names or meanings.[1] However, various names have been associated with the letters E and M:
- E for ear, i.e., when the near-end E lead was grounded, the far end was calling and wanted your ear. Whereas M is commonly called mouth, because when the near-end wanted to call (i.e., speak to) the far end, −48 vdc was applied to that lead.
- E for earth and magneto for M, from the very earliest days of telephony. An actual magneto was used to apply −48 volts to the M lead through mechanical relay switches, while the E lead is normally held to ground (earth) unless acknowledging the signaling from the M lead.
- In another story, the proposed labels were R and T for reception and transmission of signaling. However R and T were already used as labels for the tip and ring wire pair carrying voice signals. Thus a letter within each of the word recEive and transMit was chosen.
- Yet another explanation is that these were sequential designations on the wiring list of the original design.
See also
References
- ↑ Bell Telephone Laboratories, G.E. Schindler (ed.), A History of Engineering and Science in the Bell System—Switching Technology (1925-1975), 1982, p.52