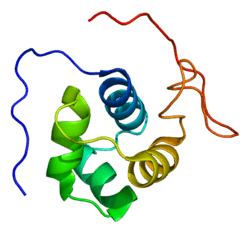
EDF1
Endothelial differentiation-related factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EDF1 gene.[3][4][5]
Function
This gene encodes a protein that may regulate endothelial cell differentiation. It has been postulated that the protein functions as a bridging molecule that interconnects regulatory proteins and the basal transcriptional machinery, thereby modulating the transcription of genes involved in endothelial differentiation. This protein has also been found to act as a transcriptional coactivator by interconnecting the general transcription factor TATA element-binding protein (TBP) and gene-specific activators. Two alternatively spliced transcripts which encode distinct proteins have been found for this gene.[5]
Interactions
EDF1 has been shown to interact with:
- Liver X receptor alpha,[6]
- Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma,[6] and
- TATA binding protein.[6][7][8]
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Dragoni I, Mariotti M, Consalez GG, Soria MR, Maier JA (December 1998). "EDF-1, a novel gene product down-regulated in human endothelial cell differentiation". J Biol Chem. 273 (47): 31119–24. PMID 9813014. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.47.31119.
- ↑ Ballabio E, Mariotti M, De Benedictis L, Maier JA (April 2004). "The dual role of endothelial differentiation-related factor-1 in the cytosol and nucleus: modulation by protein kinase A". Cell Mol Life Sci. 61 (9): 1069–74. PMID 15112053. doi:10.1007/s00018-004-4016-0.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: EDF1 endothelial differentiation-related factor 1".
- 1 2 3 Brendel C, Gelman L, Auwerx J (June 2002). "Multiprotein bridging factor-1 (MBF-1) is a cofactor for nuclear receptors that regulate lipid metabolism". Mol. Endocrinol. 16 (6): 1367–77. PMID 12040021. doi:10.1210/mend.16.6.0843.
- ↑ Mariotti M, De Benedictis L, Avon E, Maier JA (August 2000). "Interaction between endothelial differentiation-related factor-1 and calmodulin in vitro and in vivo". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (31): 24047–51. PMID 10816571. doi:10.1074/jbc.M001928200.
- ↑ Kabe Y, Goto M, Shima D, Imai T, Wada T, Morohashi Ki, Shirakawa M, Hirose S, Handa H (November 1999). "The role of human MBF1 as a transcriptional coactivator". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (48): 34196–202. PMID 10567391. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.48.34196.
Further reading
- Li FQ, Ueda H, Hirose S (1994). "Mediators of activation of fushi tarazu gene transcription by BmFTZ-F1". Mol. Cell. Biol. 14 (5): 3013–21. PMC 358669
 . PMID 8164657.
. PMID 8164657. - Ozaki J, Takemaru KI, Ikegami T, Mishima M, Ueda H, Hirose S, Kabe Y, Handa H, Shirakawa M (1999). "Identification of the core domain and the secondary structure of the transcriptional coactivator MBF1". Genes Cells. 4 (7): 415–24. PMID 10469174. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2443.1999.00267.x.
- Mariotti M, De Benedictis L, Avon E, Maier JA (2000). "Interaction between endothelial differentiation-related factor-1 and calmodulin in vitro and in vivo". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (31): 24047–51. PMID 10816571. doi:10.1074/jbc.M001928200.
- Brendel C, Gelman L, Auwerx J (2003). "Multiprotein bridging factor-1 (MBF-1) is a cofactor for nuclear receptors that regulate lipid metabolism". Mol. Endocrinol. 16 (6): 1367–77. PMID 12040021. doi:10.1210/mend.16.6.0843.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. PMID 16189514. doi:10.1038/nature04209.
- Bolognese F, Pitarque-Martì M, Lo Cicero V, Mantovani R, Maier JA (2006). "Characterization of the human EDF-1 minimal promoter: involvement of NFY and Sp1 in the regulation of basal transcription". Gene. 374: 87–95. PMID 16567061. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2006.01.030.