E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial (video game)
| E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial | |
|---|---|
|
Atari's silver label box art depicts E.T., the titular protagonist, and Elliot. | |
| Developer(s) | Atari, Inc. |
| Publisher(s) | Atari, Inc. |
| Designer(s) | Howard Scott Warshaw |
| Platform(s) | Atari 2600 |
| Release | |
| Genre(s) | Adventure |
| Mode(s) | Single player |
E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial (also referred to simply as E.T.) is a 1982 adventure video game developed and published by Atari, Inc. for the Atari 2600 video game console. It is based on the film of the same name, and was designed by Howard Scott Warshaw. The objective of the game is to guide the eponymous character through various screens in a cubic world[2] to collect three pieces of an interplanetary telephone that will allow him to contact his home planet.
Warshaw intended the game to be an innovative adaptation of the film, and Atari thought it would achieve high sales figures based on its connection with the film, which was extremely popular throughout the world. Negotiations to secure the rights to make the game ended in late July 1982, giving Warshaw only five and a half weeks[3] to develop the game in time for the 1982 Christmas season. The final release was critically panned, with nearly every aspect of the game facing heavy criticism. E.T. is often cited as one of the worst video games of all time and one of the biggest commercial failures in video game history. Despite this, it is considered to be one of the most significant titles in the history of video games, as it is cited as a major contributing factor to the video game industry crash of 1983, and has been frequently referenced and mocked in popular culture in the years since its release, often being used as a cautionary tale about the dangers of rushed game development and studio interference.
An urban legend stated that as a result of overproduction and returns, millions of unsold cartridges were buried in an Alamogordo, New Mexico landfill. In 2013, plans were revealed to conduct an excavation to determine the accuracy of reports about the burial,[4] and in April of the following year, the diggers confirmed that the Alamogordo burial did include E.T. cartridges among other titles.[5][6] James Heller, the former Atari manager who was in charge of the original burial, was also on hand at the excavation and revealed to the Associated Press that 728,000 cartridges of various titles were buried.[7]
Gameplay
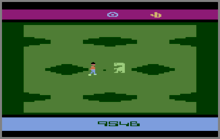
E.T. is an adventure game in which players control an alien (E.T.) from a top-down perspective. The objective of the game is to collect three pieces of an interplanetary telephone. The pieces are found scattered randomly throughout various pits (also referred to as wells). The player is provided with an on-screen energy bar, which decreases when E.T. performs any actions (including moving, teleporting, or falling into a pit, as well as levitating back to the top). To prevent this, E.T. can collect Reese's Pieces, which are used to restore his energy or, when nine are collected, E.T. can call Elliott to obtain a piece of the telephone, or the player can save the candy pieces for bonus points at the end. After the three phone pieces have been collected, the player must guide E.T. to an area where he can use the phone, which allows him to call his home planet. When the call is made, E.T. must reach the spaceship in a given time limit. Once E.T. gets to the forest where his ship abandoned him and stands and waits in the designated area for the ship to come, the ship will appear on screen and take him back to his home planet. Then the game starts over, with the same difficulty level, while changing the location of the telephone pieces. The score obtained during the round is carried over to the next iteration. The game ends when the energy bar depletes.[8] E.T. has three lives and if he dies within those three lives Elliot will come in and revive him. E.T. can get a fourth life if the player is lucky enough to find a geranium in one of the wells. It turns into a sprite from some games that Howard Scott Warshaw made, such as Raiders of the Lost Ark.
The game is divided into six environments, each representing a different setting from the film. To accomplish the objective of the game, the player must guide E.T. into the wells. Once all items found in a well are collected, the player must levitate E.T. out of them.[9] An icon at the top of each screen represents the current area, each area enabling the player to perform different actions. Antagonists include a scientist who takes E.T. for observation and an FBI agent who chases the alien to confiscate one of the collected telephone pieces, or candy.[8] The game offers diverse difficulty settings that affect the number and speed of humans present, and the conditions needed to accomplish the objective.
Development
Following the commercial success of the film in June 1982, Steve Ross, chief executive officer (CEO) of Atari's parent company Warner Communications, started negotiations with Steven Spielberg and Universal Pictures to acquire the license to produce a video game based on the film. In late June, Warner announced its exclusive worldwide rights to market coin-operated and console games based on the movie.[10] Although the exact details of the transaction were not disclosed in the announcement, it was later reported that Atari had paid US$20–25 million for the rights, a high figure for video game licensing at the time.[11] [12][13][14] When asked by Ross what he thought about making an E.T.-based video game, Atari CEO Ray Kassar replied, "I think it's a dumb idea. We've never really made an action game out of a movie."[13] An arcade game based on the E.T. property had also been planned, but this was deemed to be impossible given the short deadline.[15]
After negotiations completed, Kassar called Howard Scott Warshaw on July 27, 1982 to commission him as developer of the video game.[16][17] Kassar informed him that Spielberg asked for Warshaw specifically and that development needed to be completed by September 1 to meet a production schedule for the Christmas holiday. Though Warshaw had spent over a year working on consecutive development schedules for games (seven months working on Yars' Revenge and then six months on Raiders of the Lost Ark), he accepted the offer based on the challenge of completing a game in a short time frame and at Spielberg's request.[15][17] Warshaw considered it an opportunity to develop an innovative Atari 2600 game based on a movie he enjoyed, "provided we reach the right arrangement".[17][18]:9:34 Kassar reportedly offered Warshaw US$200,000 and an all-expenses-paid vacation to Hawaii in compensation.[15] Kassar then told him to arrive at the San Jose Airport a few days later to have a meeting with Spielberg.[17]
Warshaw used those days to design the structure of the game and segmented the concept into four ideas: world, objective, path to achieve the objective, and obstacles. He envisioned a three-dimensional cube world as the setting and adapted part of the film's plot, E.T. phoning home, as the goal. Warshaw then conceived that E.T. would need to assemble a special phone to call his ship and arrive at a special landing site to achieve this goal. He considered obstacles as an element that would determine the success of a game, and experienced difficulties when taking into account the time constraints and technical limitations of the console. Inspired by the movie, adults were implemented as antagonists that would chase the alien. Feeling more adversity was needed, Warshaw included a time limit for players to accomplish the goal. Pits were devised as an element to hide the pieces of the phone as well as expand the game's world.[17]
Warshaw and other Atari executives presented this design to Spielberg, who did not express enthusiasm.[16] Spielberg instead asked him to create a game similar to Namco's Pac-Man.[17] Believing the concept too derivative of a common game design, Warshaw proceeded with his concept, which he felt would capture the sentimentality he saw in the original film.[12][16] (In retrospect, however, Warshaw stated that Spielberg's idea might have had merit.[16][17]) He spent the remaining time programming the game. Atari anticipated enormous sales based on the popularity of the film, as well as the stability the video game industry was experiencing in 1982. Due to time limitations, Atari decided to skip audience testing for the game.[19] Emanual Gerard, co-chief operating officer of Warner at the time, later suggested that the company had fallen into a false sense of security by the success of its previous releases, particularly its console version of Pac-Man, which was commercially successful despite poor critical reaction.[20][21]
Reception

Anticipation for E.T. was high in 1982, and it was a sought-after Christmas gift.[17] In early December 1982, The New York Times reported that video games based on successful movies, specifically E.T., would become "an increasingly profitable source" for video game development.[22] At first, retailers ordered more supplies than what was expected to be sold, but Atari received an increasing number of order cancellations as new competitors entered the market, an event the company had not anticipated.[20][23][24] John Hubner and William Kistner of InfoWorld attribute the cancellations to changes Atari initiated in its relationship to distributors. On November 1, 1982, Atari informed them that their contracts were canceled and that exclusive deals would be established with select distributors. Hubner and Kistner believed the action prompted retailers to cancel orders, which Atari had not properly tracked.[25]
E.T. met with initial commercial success. It was among the top four on Billboard magazine's "Top 15 Video Games" sales list in December 1982 and January 1983.[26] The game eventually sold 1.5 million units, becoming one of the best-selling Atari 2600 titles.[21][27] However, between 2.5 and 3.5 million cartridges went unsold,[9][27][28] and one retailer said that "mostly grandmothers" bought the game, not children, an example of word of mouth affecting sales.[11]
Hubner and Kistner commented that the large number of produced cartridges may have resulted in excess inventory regardless of E.T.'s success.[25] Even though the game was a best seller during the holiday season, retailers still stated that its sales figures did not meet expectations. Warner Communications also expressed disappointment at the number of sales.[14] Lower-than-expected sales figures combined with excess inventory, which produced a negative supply and demand event, prompted retailers to repeatedly discount price. According to Ray Kassar, about 3.5 million of the 4 million produced were sent back to the company as unsold inventory or customer returns.[29] Despite sales figures, the quantity of unsold merchandise, coupled with the expensive movie license and the large number of returns, made E.T. a major financial failure for Atari.[28] By 2004, the cartridges were still very common and offered at very low prices.[30]
Critical response
While reviews of the movie version of E.T. were highly positive, the game was negatively received by critics, with common complaints focused on the plot, gameplay, and visuals. New York magazine's Nicholas Pileggi described it as a loser when compared to other games Atari could have released like Donkey Kong and Frogger.[24] Video Games called the game "really for kids (the littler ones)."[31] Kevin Bowen of GameSpy's Classic Gaming called the gameplay "convoluted and inane", also criticizing its story for departing from the serious tone of the film.[8] Author Steven Kent described the game as "infamous" within the industry, citing "primitive" graphics, "dull" gameplay, and a "disappointing story".[13] In 1984 Softline readers named the game the second-worst Atari program of 1983, after Congo Bongo.[32]
Nevertheless, the game also received some more positive reviews. An editor for The Miami Herald described it as a difficult game to learn to play, but felt it was worth dedicating the time.[33] Vidiot's Kevin Christopher criticized the protagonist's repeated falling down back into holes, but considered it "about the only flaw with an otherwise A-1 game."[34] Arcade Express scored it 6 out of 10 in December 1982.[35]
—Howard Scott Warshaw on E.T.'s reception[17]
Critics bemoaned the gameplay's repetitive use of falling down holes.[13][36] Emru Townsend of PC World discussed the game with a group, and found a universal dislike for the pits that E.T. falls into, describing it as "monotonous".[36] Writer Sean "Seanbaby" Reiley also criticized the pits, claiming that they are "time-consuming" and "difficult to leave without falling back in".[37] Trent Ward, a former Next Generation Magazine reviewer, commented that this element prompted him to immediately return the game for a refund after purchasing it in his youth,[38] and the children who found games in the New Mexico landfill gave the E.T. cartridges away because, as one later said, the "game sucked ... you couldn't finish it".[39][40] Classic Gaming argued that despite the negative reception, the game can be enjoyable after the player has learned to navigate the pits.[41]
In published materials written over a decade after its initial release, E.T. has been universally panned by critics and is frequently listed as the worst video game ever.[17] Reiley ranked it number one in a list of the 20 worst games of all time in Electronic Gaming Monthly's 150th issue.[37] Michael Dolan, deputy editor of FHM magazine, has also listed the game as his pick for the worst video game of all time.[42] Townsend placed E.T. at the top of his list of worst video games, noting that, "about a third of the people I quizzed came up with this title almost instantly, and it's not hard to see why."[36] GameTrailers ranked the game the second worst on their "Top Ten Best and Worst Games of All Time" list.[43]
Critics often attribute the poor quality to the short development time.[44][45] Townsend commented that the rushed development was very apparent after playing the game.[36] Warshaw's contributions to the game have been met with mixed responses. Classic Gaming called the game poorly designed, while IGN's Levi Buchanan stated the "impossibly tight schedule" given to Warshaw absolves him of blame.[21] Warshaw does not express regret for his part in E.T., and feels he created a good game given the time available to him.[12][17]
Impact and legacy
E.T. is one of the earliest video games based on a movie.[46] GamePro, GameTrailers, and Bowen cite the game as the first poor quality-film–video-game tie-in.[8][43][47] Patrick O'Luanaigh of SCi Games called it the most famous disaster story among film-inspired video games as well as within the industry.[48] Describing it as one of the "games that changed the world", GamePro stated that E.T. established a standard of subpar quality video games based on movies. They further commented that other publishers adopted similar marketing and production practices with licensed movie properties.[49] The publication listed the game as the second "worst movie game ever", citing it as an example of how poor gameplay can bring negative reception to strong licenses.[47] Surviving copies of the game are commonly found on eBay selling for low prices – the appeal for collectors comes from the often-designated title of "the worst video game of all time".[50]
Effect on the industry
E.T. is often cited as one of the most important titles in the industry's history.[51][52][53] As early as January 1983, after Atari admitted that the game had sold poorly, an industry executive said that "the lesson of E.T. has not been lost on the industry".[11] Infamously, the game is also cited to be one of the main causes of the video game industry crisis of 1983.[54][55][56] Billboard magazine's Earl Paige reported that the large number of unsold E.T. games along with an increase in competition prompted retailers to demand official return programs from video game manufacturers.[57] By the end of 1982, Atari had begun to lose dominance as more competitors entered the market.[14][11] Poor critical reception and lack of a profitable marketing strategy made this game one of many cited decisions that led Atari to report a $536 million loss in 1983 and led to the company being divided and sold in 1984.[28] GameSpy's Classic Gaming called E.T. Atari's biggest mistake, as well as the largest financial failure in the industry.[41][58] Reiley commented that the game's poor quality was responsible for ending the product life of the Atari 2600.[37] Occurring soon after Pac-Man's negative critical response on the Atari 2600, E.T.'s poor reception was attributed by Kent to a negative impact on Atari's reputation and profitability.[13] Authors Nick Montfort and Ian Bogost echoed similar comments about Pac-Man and E.T.'s combined effect on the company's reputation and the industry's reaction.[59] Buchanan also cited the game as a factor to Atari and the industry's crash. He stated that the large amount of unsold merchandise was a financial burden to Atari, which pushed the company into debt.[21]
On December 7, 1982, Kassar announced that Atari's revenue forecasts for 1982 were cut from a 50 percent increase over 1981 to a 15 percent increase.[60] Immediately following the announcement, Warner Communications' stock value dropped by around 35 percent—from US$54 to US$35—resulting in the company losing US$1.3 billion in market valuation.[61] Kassar sold five thousand of his Warner shares a half-hour before the announcement.[60] This prompted an investigation for insider trading against him by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission.[60] Atari attempted to regain their market share by licensing popular arcade games for the Atari consoles. The games, however, did not reverse Atari's decline and they went further into debt. In 1983, the company had decreased its workforce by 30 percent and lost US$356 million. Other companies—Activision, Bally Manufacturing, and Mattel—experienced similar results as the industry declined.[13]
Atari video game burial
.jpg)
In September 1983, the Alamogordo Daily News of Alamogordo, New Mexico, reported in a series of articles that between ten and twenty[62] semi-trailer truckloads of Atari boxes, cartridges, and systems from an Atari storehouse in El Paso, Texas, were crushed and buried at the landfill within the city. It was Atari's first dealings with the landfill, which was chosen because no scavenging was allowed and its garbage was crushed and buried nightly. Atari officials and others gave differing reports of what was buried,[63][64][65] but it has been speculated that most unsold copies of E.T. are buried in this landfill, crushed and encased in cement.[66] The story of the buried cartridges was erroneously regarded by some as an urban legend, with skeptics—including Warshaw—disregarding the official accounts.[12][45][48]
On May 28, 2013, the Alamogordo City Commission approved Fuel Industries, an Ottawa-based entertainment company, for six months of landfill access both to create a documentary about the legend and to excavate the burial site.[67] On April 26, 2014, remnants of E.T. and other Atari games were discovered in the early hours of the excavation.[6][68]
A fictional account of the game's disposal is the main basis for James Rolfe's 2014 independent film Angry Video Game Nerd: The Movie.[69] A documentary called Atari: Game Over in which several of the buried games were unearthed was released in 2014.[70]
In December 2014, The Smithsonian Institution added an excavated cartridge of E.T. to their collection.[71] In 2015, The Henry Ford museum added several excavated cartridges and a video touchpad, a sample of landfill dirt taken from the site of the burial, and items of clothing worn by the excavation team to their collection. A selection of these items are on permanent display.[72][73]
Attempts at fixing the game
In 2006 the game was decompiled by Dennis Debro and a source code variant reconstructed.[74][75]
In February 2013, several unofficial fixes for the game were released by Neocomputer.org, a small personal website unrelated to Atari.[76] The website details and provides commentary on the game's shortcomings, including instruction on fixing it. According to Neocomputer, the infamous "bug" of E.T. falling into the pits was simply due to pixel-perfect collision detection; if any portion of E.T.'s sprite overlapped a pit, E.T. would then fall into the pit. The website also details certain other problems that were resolved.[76]
In December 2016, a homebrew remake was released that, for the most part, kept the original game the same. However, the mechanic of E.T. falling into the pit was amended so that a keypress was required before the player fell into the pit. The holes were also visually removed and were discovered with an indicator at the bottom left of the screen.[77][78]
Re-release
In October 2013 the Internet Archive provided a browser-playable version via MESS.[79]
In Q4 2014, KHAN Games ported the original Atari game to the Nintendo Entertainment System (NES). Some changes were made, including providing some more detailed instructions on how to play, as the original Atari version was often cited as having very little instruction on gameplay.[80] Later the game went "out of stock" on the store.[81]
See also
- E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial in video games
- List of commercial failures in video gaming
- List of video games notable for negative reception
References
- ↑ "E.T.™ NEEDS YOUR HELP!". AtariAge. Atari Age. Retrieved March 2, 2014.
- ↑ "The Cube World of E.T. The Extra-Terrestrial for the Atari 2600". Youtube. Replayability. Retrieved July 4, 2017.
- ↑ "DP Interviews". Digitpress.com. Retrieved March 6, 2014.
- ↑ "Alamogordo approves Atari excavation". ALAMOGORDO, N.M. (KRQE). Retrieved June 2, 2013.
- ↑ Schreier, Jason. "E.T. Found In New Mexico Landfill". Kotaku. Retrieved February 4, 2015.
- 1 2 Llorca, Juan Carlos (September 28, 1983). "Diggers Find Atari's E.T. Games in Landfill". ABC News. Retrieved April 26, 2014.
- ↑ "Diggers Find Atari's E.T. Games In Landfill". NPR. Associated Press. April 26, 2014. Retrieved April 26, 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 Bowen, Kevin. "Game of the Week: E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial". Classic Gaming. Archived from the original on January 9, 2014. Retrieved August 18, 2014.
- 1 2 "Good Game Stories - Game Review: E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial". ABC Television (AU). Retrieved September 21, 2009.
- ↑ New York Times Staff, "Atari Gets 'E.T.' Rights"
- 1 2 3 4 Harmetz, Aljean (January 15, 1983). "New Faces, More Profits For Video Games". Times-Union. p. 18. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 Keith, Phipps (February 2, 2005). "Howard Scott Warshaw". A.V. Club. Retrieved September 24, 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Kent, The Ultimate History of Video Games, pp. 237–239.
- 1 2 3 New York Times Staff, "E.T. Starring in Sales of Toys"
- 1 2 3 Los Angeles Times Staff, "Many Video Games Designers Travel Rags-to-Riches-to-Rags Journey"
- 1 2 3 4 Bowen, Kevin. "ClassicGaming Expo 2000: Atari 2600 Keynote". GameSpy. Archived from the original on January 9, 2014. Retrieved September 28, 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Warshaw, "Core Memory"
- ↑ "The Crash". G4 Icons. Season 2. Episode 14. G4techTV. Retrieved August 18, 2014.
- ↑ Cummings, "How I Got Here"
- 1 2 Pollack, "The Game Turns Serious at Atari"
- 1 2 3 4 Buchanan, Levi (August 26, 2008). "IGN: Top 10 Best-Selling Atari 2600 Games". IGN. Retrieved September 21, 2009.
- ↑ New York Times Staff, "A Squeeze in Video Games"
- ↑ Cohen, Zap! The Rise and Fall of Atari
- 1 2 Pileggi, Nicholas, "The Warner Case: Curiouser and Curioser"
- 1 2 Hubner and Kistner, "What went wrong at Atari"
- ↑ Billboard Staff, "Top 15 Video Games", Billboard Volume 95 Issue 1, p. 36
- 1 2 Glenday, Guinness World Records 2009 Gamer's Edition, "History of Gaming: 1980–1993", p. 20
- 1 2 3 "Five Million E.T. Pieces". Snopes. Retrieved July 1, 2006.
- ↑ Bruck, Master of the Game: Steve Ross and the Creation of Time Warner, pp 179-180
- ↑ Ellis, Official Price Guide to Classic Video Games, "The Atari VCS (2000)" p. 85.
- ↑ Wiswell, Phil (March 1983). "New Games From Well-Known Names". Video Games. p. 69. Retrieved May 26, 2014.
- ↑ "The Best and the Rest". St.Game. Mar–Apr 1984. p. 49. Retrieved July 28, 2014.
- ↑ The Miami Herald Staff, "E.T. Game is Extra-Tough But Worth The Effort"
- ↑ Christopher, Kevin (February–March 1983). "ET Phones Home for the Holidays". Vidiot (2): 41–43.
- ↑ http://www.digitpress.com/library/newsletters/arcadeexpress/arcade_express_v1n10.pdf#page=7
- 1 2 3 4 Townsend, Emru (October 23, 2006). "The 10 Worst Games of All Time". PC World. Retrieved January 24, 2007.
- 1 2 3 Reiley, Sean. "Seanbaby's EGM's Crapstravaganza: The 20 Worst Video Games of All Time. - #1: ET, The Extra Terrestrial (2600)". Electronic Gaming Monthly. Retrieved March 4, 2017.
- ↑ Next Generation Staff (April 1998). "What the hell happened?". Next Generation. Imagine Media: 47.
- ↑ Terdiman, Daniel (April 26, 2014). "Success! Atari E.T. games found in New Mexico dump". CNET. Retrieved April 27, 2014.
- ↑ Llorca, Juan Carlos (April 26, 2014). "Diggers begin quest to unearth Atari's E.T. games". The State Journal. Associated Press. Archived from the original on April 27, 2014. Retrieved April 27, 2014.
- 1 2 "ClassicGaming.com's Museum: Five Must-See 2600 Games". GameSpy. Archived from the original on October 5, 2008. Retrieved September 25, 2009.
- ↑ "History of Gaming: The Best and Worst Video Games of All Time". Public Broadcasting Service. Retrieved September 25, 2009.
- 1 2 "GT Countdown: Top Ten Best and Worst Games of All Time". GameTrailers. November 17, 2006. Retrieved September 25, 2009.
- ↑ Elektro, Dan (August 8, 2003). "Secrets & Lies". GamePro. Archived from the original on June 7, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- 1 2 Montfort and Bogost, Racing the Beam: The Atari Video Computer System, p. 127
- ↑ Glenday, Guinness World Records 2009 Gamer's Edition, "Movies & Games Round-Up", p. 184
- 1 2 Smithee, Alan (July 1, 2004). "10 to 1: The Worst Movie Games Ever". GamePro. Archived from the original on May 25, 2010. Retrieved September 28, 2009.
- 1 2 Morris, The Art of Game Worlds, p. 126
- ↑ "20 Games that Changed the World". GamePro. April 4, 2006. Archived from the original on January 11, 2010. Retrieved September 28, 2009.
- ↑ Guins, Raifrod (2009). "Concrete and Clay: The Life and Afterlife of E.T. The Extra-Terrestrial for the Atari 2600". Design and Culture. 1 (3).
- ↑ Montfort and Bogost, Racing the Beam: The Atari Video Computer System, p. 94
- ↑ "The 52 Most Important Video Games of All Time". GamePro. April 25, 2007. Archived from the original on September 12, 2008. Retrieved September 27, 2009.
- ↑ Parish, Jeremy. "The Most Important Games Ever Made: #13: E.T.". 1UP.com. Retrieved July 1, 2006.
- ↑ Dvorak, John C (August 12, 1985). "Is the PCJr Doomed To Be Landfill?". InfoWorld. 7 (32): 64. Retrieved September 10, 2011.
- ↑ Jary, Simon (August 19, 2011). "HP TouchPads to be dumped in landfill?". PC Advisor. Retrieved September 10, 2011.
- ↑ Kennedy, James (August 20, 2011). "Book Review: Super Mario". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved September 10, 2011.
- ↑ Earl Paige, "Video Game Firms Ready Formal Returns Policies", Billboard Volume 95 Issue 1, pp. 1 & 21
- ↑ "ClassicGaming.com's Museum: Atari 2600 - 1977-1984". GameSpy. Archived from the original on June 11, 2009. Retrieved September 25, 2009.
- ↑ Montfort and Bogost, Racing the Beam: The Atari Video Computer System, p. 76
- 1 2 3 Game Informer Staff, "This Month in Gaming History"
- ↑ Taylor, Thompson and Washburn, "Pac-Man Finally Meets His Match"
- ↑ Quote: "The number of actual trucks which have dumped locally was not known. Local BFI officials put it at 10. However, corporate spokesmen in Houston say it was closer to 20; and city officials say it is actually 14."
McQuiddy, "City cementing ban on dumping." - ↑ McQuiddy, "Dump here utilized."
- ↑ McQuiddy, "City cementing ban on dumping."
- ↑ McQuiddy, "City to Atari."
- ↑ Smith, "Raising Alamogordo's legendary Atari 'Titanic'"
- ↑ Goldsmith, Alex (May 30, 2013). "Alamogordo approves Atari excavation". KRQE. Archived from the original on June 1, 2013. Retrieved May 31, 2013.
- ↑ Hilliard, Kyle (April 26, 2014). "E.T. Atari Cartridge Landfill Excavation Uncovers Fabled Cache". Game Informer. Retrieved April 26, 2014.
- ↑ Santos, Fernanda (June 18, 2013). "Hunting for an E.T. Castoff in a Most Terrestrial Place". The New York Times. Retrieved June 18, 2013.
- ↑ Graser, Marc. "Xbox Documentary on Atari’s Lost ‘E.T.’ Games Debuts for Free". (November 20, 2014) Variety. Accessed 20 May 2016.
- ↑ Robarge, Drew (December 15, 2014). "From landfill to Smithsonian collections: "E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial" Atari 2600 game". Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved December 17, 2014.
- ↑ "Unearthing the Atari Tomb: How E.T. Found a Home at The Henry Ford". The Henry Ford Blog. Retrieved 2016-01-14.
- ↑ "Collection". collections.thehenryford.org. Retrieved 2016-01-14.
- ↑ Johnson, Phil (2014-05-06). "Digging up E.T.’s source code". ITworld.
The code, written in assembly language for the MOS Technology 6502 8-bit processor, has been around for a while, having been reconstructed by Dennis Debro in 2006.
- ↑ E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial(1982) Atari 2600 Source Code on pastebin.com
- 1 2 "Fixing E.T. The Extra-Terrestrial for the Atari 2600". Neocomputer. Retrieved April 6, 2013.
- ↑ "E.T. Homebrew Remake". Stupendous Stuff.
- ↑ "E.T. Remake on Mobygames". Mobygames.
- ↑ Robertson, Adi (October 25, 2013). "The Internet Archive puts Atari games and obsolete software directly in your browser". The Verge. Retrieved October 29, 2013.
- ↑ "E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial". khangames.com.
- ↑ E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial
Bibliography
- Books
- Bruck, Connie (1995). Master of the Game: Steve Ross and the Creation of Time Warner. Penguin Books. ISBN 0-14-024454-9.
- Cohen, Scott (1984). Zap! The Rise and Fall of Atari. McGraw Hill Book Company. ISBN 0-07-011543-5.
- Ellis, David (2004). Official Price Guide to Classic Video Games. Random House. ISBN 0-375-72038-3.
- Glenday, Craig, ed. (2009). Guinness World Records 2009 Gamer's Edition. Guinness World Records. ISBN 978-1-904994-45-9.
- Kent, Steven L. (2001). The Ultimate History of Video Games. Roseville, California: Prima. ISBN 0-7615-3643-4.
- Montfort, Nick; Ian Bogost (2009). Racing the Beam: The Atari Video Computer System. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-01257-7.
- Morris, Dave (2004). The Art of Game Worlds. HarperCollins. ISBN 0-06-072430-7.
- Periodicals
- "E.T. Needs Your Help! (advertisement)". Atari Age. The Atari Club Inc. 1 (4): 3. November–December 1982. Retrieved January 31, 2010.
- Cummings, Betsy (December 2003). "How I got here". Sales and Marketing Management.
- "This Month in Gaming History". Game Informer. GameStop (140): 202. December 2004.
- Hubner, John; William F. Kistner Jr. (December 5, 1983). "What went wrong at Atari". InfoWorld. 5 (49): 145–155. ISSN 0199-6649.
- McQuiddy, Marian E. (September 25, 1983). "Tons of Atari Games Buried; Dump here utilized". Alamogordo Daily News. p. 1. Archived 2005-04-01.
- McQuiddy, Marian E. (September 27, 1983). "City to Atari: 'E.T.' trash go home". Alamogordo Daily News. Archived 2005-04-01.
- McQuiddy, Marian E. (September 28, 1983). "City cementing ban on dumping: Landfill won't house any more 'Atari rejects'". Alamogordo Daily News.
- "E.T. Game is Extra-Tough but Worth the Effort". The Miami Herald. March 5, 1983.
- "Atari Gets 'E.T.' Rights". The New York Times. August 19, 1982.
- "A Squeeze in Video Games". The New York Times. December 7, 1982.
- "E.T. Starring in Sales of Toys". The New York Times. December 13, 1982.
- "Atari Parts Are Dumped". The New York Times. September 28, 1983.
- Pileggi, Nicholas (January 24, 1983). "The Warner Case: Curiouser and Curioser". New York. New York Media, LLC. 16 (4): 26–32. ISSN 0028-7369.
- Pollack, Andrew (December 19, 1982). "The Game Turns Serious at Atari". The New York Times. Section 3, p. 1.
- Smith, Shelley (April 12, 2005). "Raising Alamogordo's legendary Atari 'Titanic'". Alamogordo Daily News.
- Taylor, Alexander L.; Thompson, Dick; Washburn, Susanne (December 20, 1982). "Pac-Man Finally Meets His Match". Time. Retrieved September 30, 2009.
- Paige, Earl (January 8, 1983). "Video Game Firms Ready Formal Return Policies". Billboard. Nielsen Business Media, Inc. 95 (1): 1, 21. ISSN 0006-2510.
- Warshaw, Howard Scott (November 2007). "Core Memory". GamesTM (63): 140–141. Retrieved September 26, 2009.
- From The Washington Post (January 14, 1986). "Many Video Games Designers Travel Rags-to-Riches-to-Rags Journey". Los Angeles Times.
External links

