Duisburg
| Duisburg | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
| |||
 Duisburg | |||
Location of Duisburg within NRW  | |||
| Coordinates: 51°26′6.53″N 6°45′45.69″E / 51.4351472°N 6.7626917°ECoordinates: 51°26′6.53″N 6°45′45.69″E / 51.4351472°N 6.7626917°E | |||
| Country | Germany | ||
| State | North Rhine-Westphalia | ||
| Admin. region | Düsseldorf | ||
| District | Urban district | ||
| Government | |||
| • Lord Mayor | Sören Link (SPD) | ||
| • Governing parties | SPD / Greens / Left | ||
| Area | |||
| • City | 232.82 km2 (89.89 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 31 m (102 ft) | ||
| Population (2015-12-31)[1] | |||
| • City | 491,231 | ||
| • Density | 2,100/km2 (5,500/sq mi) | ||
| • Metro | 11,316,429 (Rhine-Ruhr) | ||
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) | ||
| Postal codes | 47001–47279 | ||
| Dialling codes | 0203 | ||
| Vehicle registration | DU | ||
| Website | www.duisburg.de | ||
Duisburg (German pronunciation: [ˈdyːsbʊɐ̯k]) is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. The world's biggest inland port,[2] it is also close to Düsseldorf Airport.
In the early Middle Ages it was a royal court of the Franks, first mentioned in writing in 883.
Duisburg is a result of numerous incorporations of surrounding towns and smaller cities. It is the fifteenth-largest city in Germany and the fifth-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia with 486,855 residents at the end of 2013. It is the central city of the Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan area. The city is renowned for its steel industry. All blast furnaces in the Ruhr are now located in Duisburg. In 2000, 49% of all hot metal and 34.4% of all pig iron in Germany was produced here. It also has a large brewery, König. The University of Duisburg-Essen, with 39,000 students, ranks among the ten largest German universities.
Geography
Duisburg is in the Lowland Rhine area at the confluence of the Rhine and Ruhr and near the outskirts of the Bergisches Land. The city spreads along both sides of these rivers.
Adjacent cities
The following cities border Duisburg (clockwise starting from north-east): Oberhausen, Mülheim an der Ruhr, Ratingen, Düsseldorf, Meerbusch, Krefeld, Moers, Rheinberg, and Dinslaken.
Districts
Since 1 January 1975, Duisburg has been divided into seven districts or boroughs (Stadtbezirk) from the north to the south:[3]
- Walsum (51,528)
- Hamborn (71,528)
- Meiderich/Beeck (73,881)
- Homberg/Ruhrort/Baerl (41,153)
- Duisburg-Mitte (center) (105,961)
- Rheinhausen (77,933)
- Duisburg-Süd (73,321)
- Neumühl (17,131)
Climate
Duisburg has an oceanic climate (Cfb).
| Climate data for Duisburg | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 4 (39) |
5 (41) |
8 (46) |
12 (54) |
17 (63) |
20 (68) |
22 (72) |
22 (72) |
18 (64) |
14 (57) |
8 (46) |
5 (41) |
12.9 (55.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2 (36) |
3 (37) |
5 (41) |
8 (46) |
13 (55) |
16 (61) |
17 (63) |
17 (63) |
14 (57) |
11 (52) |
6 (43) |
3 (37) |
9.6 (49.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0 (32) |
0 (32) |
2 (36) |
5 (41) |
9 (48) |
12 (54) |
13 (55) |
13 (55) |
11 (52) |
8 (46) |
3 (37) |
1 (34) |
6.4 (43.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 81.3 (3.201) |
55.9 (2.201) |
76.2 (3) |
68.6 (2.701) |
73.7 (2.902) |
96.5 (3.799) |
88.9 (3.5) |
76.2 (3) |
73.7 (2.902) |
71.1 (2.799) |
83.8 (3.299) |
88.9 (3.5) |
934.8 (36.804) |
| Source: weather.com[4] | |||||||||||||
History
The first syllable of the name of the city could go back to the Germanic word "dheus", which means something like "wet area" or "flood plain". Duisburg therefore could mean "fortified place in the floodplain". Another interpretation assumes that the name is derived from the Old German "duis" which means "hill". Duisburg could mean something like "castle on the hill". Thus, a place on a hill overlooking the Rhine, that could refer to the area of the present Town Hall. Duisburggau (Diuspurgau) was also the name of the medieval Gau (country subdivision) on the Lower Rhine.
A legend recorded by Johannes Aventinus (fl. 1525) holds that Duisburg, (along with Deutz, Cologne, Duisdorf in Bonn, and Doesburg in the Netherlands, all on the Rhine's right bank) was built by the namesake Tuisto, mythical progenitor of Germans, ca. 2395 BC. There is nothing to establish any historical basis for such an early founding of Duisburg, which would have made it among the earliest cities in Europe.
Roman period
Latest archaeological studies show that the present-day market-place was already in use in the first century. It has been the major central trading place of the city since the 5th century. The city itself was located at the "Hellweg", an important medieval trade route, and at a ford across the River Rhine. The Romans already guarded the ford.
- 420: The Franks usurp the Roman settlement and recolonize the old part of the town.
- 883: The Normans conquer Duisburg and stay for the winter. First historic document mentioning Duisburg.
Middle Ages
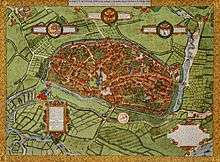

Due to the town's favorable geographic position a palatinate was built and the town was soon granted the royal charter of a free city. Duisburg became a member of the Hanseatic League. Around 1000 the river Rhine moved westward from the city. This put an end to the city's development as a trading town and it soon grew into a quiet rural city. The productions of cartographer Gerardus Mercator and the foundation of a university in 1655 established the city's renown as "Educated Duisburg" ("Duisburgum Doctum").
- 1120: construction of the city wall
- 1279: "city charter" granted by King Lothar III
- 1290 Duisburg becomes part of the County (after 1417 Duchy) of Cleves
- 1445 attack by Archbishop-Elector Dietrich II von Moers (de) of Cologne was thwarted
- 1566 Johannes Corputius completes his city map of Duisburg.
- 1666 Duisburg within the Duchy of Cleves becomes a part of Brandenburg-Prussia
Industrial revolution

The rise of tobacco and textile industries in the 18th century made Duisburg an industrial center. Big industrial companies such as iron and steel producing firms (Thyssen and Krupp) influenced the development of the city within the Prussian Rhine Province. Large housing areas near production sites were being built as workers and their families moved in.
- 1823 a district ("Landkreis") Duisburg is established including the cities of Essen and Mülheim an der Ruhr.
- 1824 construction of the sulfuric acid factory Fr. W. Curtius; beginning of the industry age in Duisburg.
- 1828 Franz Haniel builds a dockyard for steamships
- 1846 railway line to Düsseldorf
- 1847 railway line via Dortmund to Minden
- 1873 Duisburg becomes an independent city borough.
- 1904 Birth of the 100,000th resident (Ernst R. Straube)
- 1921 French Infantry occupy the city on 8 March to secure war reparation payments incurred during World War I.
- 1929 The city of Hamborn and Duisburg are joined together. The new city is given the name of Duisburg-Hamborn.
- 1935 Duisburg-Hamborn is renamed Duisburg.
- 1938 (November) The Nazis destroy the city's synagogue.
World War II
A major logistical center in the Ruhr and location of chemical, steel and iron industries, Duisburg was a primary target of Allied bombers. As such, it is considered by some historians to be the single most heavily bombed German city by the Allies during World War II, with industrial areas and residential blocks targeted by Allied incendiary bombs.
On the night of 12–13 June 1941, British bombers dropped a total of 445 tons of bombs in and around Duisburg. As part of the Battle of the Ruhr, another British raid of 577 bombers destroyed the old city between 12–13 May 1943 with 1,599 tons of bombs. During the bombing raids, 96,000 people were made homeless with countless lives lost.
In 1944 the city was again badly damaged as a total of 2,000 tons of bombs were dropped on 22 May. On 14 October, the tonnage was repeated with 2,018 tons when Halifax, Lancaster, and Mosquito bombers appeared over Duisburg as part of Operation Hurricane. This daylight raid was followed by a night attack; over 24 hours about 9,000 tons of HE and incendiaries had been dropped on Duisburg. Numerous similar attacks followed until the end of 1944.
The Allied ground advance into Germany reached Duisburg in April 1945. The US 17th Airborne Division, acting as regular infantry and not in a parachute role, met only scattered resistance in the vicinity and captured the city on 12 April 1945.[5]
On 8 May 1945 the ADSEC Engineer Group A, led by Col. Helmer Swenholt, commanding officer of the 332nd Engineer General Service Regiment, constructed a railway bridge between Duisburg and Rheinhausen across the Rhine. It was 860 meters long, and constructed in six days, fifteen hours and twenty minutes, a record time. It was named the "Victory Bridge".[6]
Post-World War II period
A total of 299 bombing raids had almost completely destroyed the historic cityscape. 80% of all residential buildings had been destroyed or partly damaged. Almost the whole of the city had to be rebuilt, and most historic landmarks had been lost.
Beginning in the mid-1960s, the decline of Duisburg's steel and mining industry caused a significant loss of residents. While in 1975 approximately 590,000 people were living in Duisburg, the number has shrunk to 518,000 in 1985.
Duisburg celebrated its 1100th anniversary in 1983. The city's population recovered a little in the following years, up to 537,000 in 1992. It declined to 488,000 in 2011. On 19 July 2004, it was hit by a tornado. The municipal theater and parts of the city center were damaged. The city hosted the 7th World Games in 2005. In 2010, 21 people died because of a mass panic at the Love Parade; over 500 people were injured.
Links to the September 11 attacks
In 2007, evidence surfaced that linked a mosque in the city with the Hamburg cell, and also with ringleader Mohammed Atta. Also, the police uncovered calendars owned by people who attended the mosque, with the dates April 15, 2001 (the date when many hijackers slipped into the US to finalize preparations for the September 11 attacks) inscribed with 'The program begins' and September 11, 2001 inscribed with 'The program ends' in Arabic. Further investigation revealed that Guantanamo Bay inmate Mohamed Ould Slahi was a frequent visitor to the mosque, and had helped Atta recruit conspirators for the attacks. It was also believed that Ould Slahi was present in the city on September 10 discussing the attacks with other unidentified extremists.[7] This evidence arose at around the same time as news broke of German Islamists being trained in Pakistani terrorist camps.[8]
Demographics
In 2010, the city had a population of 489,600. Hence, Duisburg has seen a slight decrease in its population since 2006.
Population structure[9]
| Rank | Nationality | Population (2016)[10] |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 34,682 | |
| 2 | 8,816 | |
| 3 | 8,463 | |
| 4 | 7,185 | |
| 5 | 5,558 | |
| 6 | 3,594 | |
| 7 | 2,541 | |
| 8 | 2,311 | |
| 9 | 1,894 | |
| 10 | 1,750 | |
Turks in Duisburg
Duisburg is home to 85,000 people of Turkish origin.[11] Other estimates suggest that the Turkish population is as many as 100,000[12][13][14] The new Merkez Mosque, one of the largest Muslim place of worship in Western Europe, was built with help by the way of contribution of 3.2 million euro from the EU and the state of North Rhine-Westphalia.[15] Asiye Nur Fettahoğlu, a Turkish-German actress was born in Duisburg on November 12, 1980.
Transport
Duisburg Port
"Duisport"[16] is the largest inland port in the world.[17] It is officially regarded as a "seaport" because seagoing river vessels go to ports in Europe, Africa and the Middle East. Numerous docks are mostly located at the mouth of Ruhr river where it joins the Rhine river.
Each year more than 40 million tonnes of various goods are handled with more than 20,000 ships calling at the port. The public harbor facilities stretch across an area of 7.4 square kilometres (2.9 sq mi). There are 21 docks covering an area of 1.8 km2 (0.7 sq mi) and 40 kilometres (25 miles) of wharf. The area of the Logport Logistic Center Duisburg stretches across an area of 2.65 km2 (1.02 sq mi). With 2.5 million TEU it is also the largest inland container port based on 2011 figures.[18] A number of companies run their own private docks and 114 million tonnes of goods yearly (2010) are handled in Duisburg in total.
Roads
Duisburg is served by several Autobahns, with 3 East-West routes and 2 North-South routes. A3 forms a bypass east of the city and mostly serves through traffic. A59 runs parallel to A3 and serves the city from North to South with 14 interchanges, much more than most other cities in the Ruhr area. The A40 and A42 are two East-West routes that serve central and Northern Duisburg. Autobahn A40 also serves major through traffic from the Netherlands to Berlin and points East. A short spur, A524 serves southern Duisburg. Most Autobahns have six lanes or are upgraded to six lanes (A59).
Apart from the Autobahns, no Bundesstraßen serve the city directly. B8 runs through the city, but uses A59's alignment. B288 runs in the extreme South of the city, and serves traffic to and from Krefeld. Several bridges span the Rhine, most prominently the A40 and A42 bridges, but also the L287 suspension bridge and the L237 arch bridge, a three-lane bridge with 2 lanes per peak direction with dynamic lane usage.
Public transport
Duisburg Hbf is served by the InterCityExpress and InterCity long-distance network of the Deutsche Bahn, in addition lines S 1 and S 2 of the S-Bahn line connect Duisburg with other cities of the Rhine-Ruhr area.
A Stadtbahn light rail line, the Duisburg tramway network, and a bus system, all operated by the Duisburger Verkehrsgesellschaft provide local services. Stadtbahn line U79, the so-called D-Bahn, is a connection to the neighbouring city of Düsseldorf and is operated jointly with the Rheinbahn of Düsseldorf. All S-Bahn, Stadtbahn and bus lines operate under the umbrella of the Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Ruhr
Media
There are several newspapers reporting on local events and politics, including the "Westdeutsche Allgemeine" (WAZ), the "Neue Ruhr Zeitung" (NRZ) and the "Rheinische Post" (RP). The local radio station "Radio Duisburg" was the first local radio broadcaster in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It started broadcasting in 1990. There is a local television station ("STUDIO 47"), which was the first local station to broadcast in North Rhine-Westphalia. It started broadcasting in 2006. In its Duisburg studios the WDR produces a local programme for the city of Duisburg and the Lower Rhine region north of Düsseldorf. WDR is part of the German television and radio network ARD.
Culture
Duisburg hosts a comprehensive range of cultural facilities and events. A highlight is the annual "Duisburger Akzente",[19] a festival focusing on modern social, political and cultural topics.

Besides Düsseldorf Duisburg is a residence of the Deutsche Oper am Rhein, one of the major opera houses in Germany. The Duisburg Philharmonic Orchestra is one of Germany's orchestras with an international reputation.
Thanks to its history as a harbor city and a trade and industrial center Duisburg offers a variety of architectural places of interest, such as the German Inland Waterways Museum. The spectrum goes from old churches such as "St Johann Baptist" in Duisburg-Hamborn, which was built in 900, to modern age buildings like Micro-Electronic-Centrum in Duisburg-Neudorf, built in 1995. Another subject of interest is the Landschaftspark Duisburg-Nord[20] an abandoned industrial complex open to the public and an Anchor Point of ERIH, The European Route of Industrial Heritage. The city center locates the Wilhelm Lehmbruck Museum,[21] the municipal theatre[22] and the shopping street known as "fountain mile".
The city also contains two botanical gardens, the Botanischer Garten Duisburg-Hamborn and the Botanischer Garten Kaiserberg, as well as a number of municipal parks.
On 24 July 2010, 21 people were killed and hundreds injured in the city during the Love Parade, an electronic music procession and party.[23]
Sport
| Club | Sport | League | Venue |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSV Duisburg | Football | 3. Liga | MSV Arena |
| EV Duisburg | Ice hockey | Regionalliga West (4th District League) | Scania Arena |
| MSV-Duisburg | Women's football | Bundesliga 2nd German League | PCC-Stadion |
| Duisburg Dockers | Baseball, American football | Landesliga II (2nd District League) | Schwelgernstadion |
| Amateur SC Duisburg | Water polo | Deutsche Wasserball-Liga (1st Water Polo League) | Schwimmstadion and club pool |
| Club Raffelberg | Hockey | Regionalliga West (3rd Hockey League) | Kalkweg |
Duisburg is involved in many kinds of sports. Nevertheless, most important for its inhabitants is the local football club MSV Duisburg. Recently, with the new MSV Arena the city received a brand new sports stadium for various kinds of sports such as football and American football. During the summer months of 2005 the World Games took place in Duisburg. During the 2006 FIFA World Cup, Duisburg was the stage for preparation of the Portuguese team and the residence of the Italian football team, who won the cup in the final match against France. Duisburg is also known for its Rhein-Ruhr-Marathon, its rowing and canoeing regattas and the world championships that take place there regularly. Other popular sports are icehockey, baseball, American football, water polo and hockey.
Notable people
- Gerardus Mercator (1512-1594), Flemish cartographer who created a world map based on a new projection
- Ludwig Susen (1807-1863), German elementary teacher
- Wilhelm Lehmbruck (1881-1919), German sculpturor
- August Thyssen (1842-1926), German industrialist
- Paul Bäumer (1896-1927), German pilot World War I ace
- Daisy Door (born 1944), Slagermusic singer
- Hans-Werner Gessmann (born 1950), founder of Humanistic Psychodrama, one of the 30 most influential psychologists working today
- Jacob Goll (born 1992), German professional ice hockey goaltender
- Ramin Djawadi (born 1974), German-Iranian composer of orchestral music for film and television (e.g., Game of Thrones and Iron Man)
International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
Duisburg is twinned with:[24][25]
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Duisburg. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Duisburg. |
- ↑ "Amtliche Bevölkerungszahlen". Landesbetrieb Information und Technik NRW (in German). 18 July 2016.
- ↑ Cioc, Mark (17 November 2009). "The Rhine: An Eco-Biography, 18152000". University of Washington Press. Retrieved 11 December 2016 – via Google Books.
- ↑ "Population statistics". Statistisches Landesamt NRW. Archived from the original on 2008-02-09.
- ↑ "Weather Information for Duisburg".
- ↑ Stanton, Shelby, World War II Order of Battle: An Encyclopedic Reference to U.S. Army Ground Forces from Battalion through Division, 1939-1946 (revised ed., 2006), Stackpole Books, p. 97.
- ↑ Peacock, Jim; Peacock, Tom. "Duisberg". Geocities. Yahoo. Archived from the original on 2009-10-23. Retrieved 2009-05-05.
- ↑ "Alleged Duisburg Link Stirs Debate on 9/11 Anniversary". Deutsche Welle. Germany. 11 September 2007. Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- ↑ "Germany Worried About Increased Terrorism Threat". Deutsche Welle. Germany. 23 July 2007. Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- ↑ "Ausländer_2006-2007_Kreise.xls" (PDF). Retrieved 2013-03-26.
- ↑ https://www.duisburg.de/vv/I-03/medien/Quartalszahlen_2014_2016.pdf
- ↑ "50 Jahre Deutsch-Türkisches Anwerbeabkommen | 50 jähriges Jubiläum zum Anwerbeabkommen der Türkei und der BRD" (in German). 50jahre.wir-sind-du.de. Retrieved 2013-03-12.
- ↑ DÜNYA. "TGRT Haber » Haberler » Dünya » Almanya'nın en büyük camisine yoğun ilgi". Tgrthaber.com. Retrieved 2013-03-12.
- ↑ ""Das ist Volkesstimme" – Thilo Sarrazin in Duisburg » xtranews - das Newsportal aus Duisburg » antonia-colloni, Duisburg, feindbild-islamkritik, hartmut-krauss-feindbild-islamkritik, Heinz Pletziger, heinz-gess, Horst Wackerbarth, Integration, islam-kritik-besprechungen, islamkritik-feindbild, Karl Janssen, kritiknetz-suddeutsche-hartmut-krauss, Lehmbruck Museum, Migration, raimund-stecker, sarrazin-duisburg, sarrazin-juden, sarrazin-zitate, Thilo Sarrazin". Xtranews.de. Retrieved 2013-03-12.
- ↑ "Türk Edebiyatı Avrupa’da". On5yirmi5.com. Retrieved 2013-03-12.
- ↑ Quantara.de retrieved July 25, 2008
- ↑ sprengerbleilevens. "Führende Logistikdrehscheibe in Zentraleuropa - Duisburger Hafen AG". Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- ↑ "Port of Duisburg". Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- ↑ Top 100 Container Ports 2012
- ↑ GmbH, Duisburg Marketing. "38. Duisburger Akzente 2017 - Theater, Bildende Kunst & Literatur". Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- ↑ "Duisburg-Nord Landscape Park". Landschaftspark.de. 2009-04-23. Retrieved 2009-05-05.
- ↑ Cynapsis Kommunikationsagentur GmbH in Münster. "Cynapsis - Die Kommunikations-Agentur in Münster". Lehmbruck.cynapsis.com. Retrieved 2009-05-05.
- ↑ "Theater Duisburg - Startseite". Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- ↑ Connolly, Kate (25 July 2010). "Love Parade stampede in Germany kills at least 18 - latimes.com". latimes.com. Retrieved 25 July 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Cities Twinned with Duisburg". www.duisburg.de. Retrieved 2009-05-07.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "List of Twin Towns in the Ruhr District" (PDF). © 2009 Twins2010.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 28, 2009. Retrieved 2009-10-28. External link in
|publisher=(help) - ↑ Portsmouth City Council. Twinning. Retrieved 22 August 2007.
- ↑ Brian Daugherty. "Portsmouth Duisburg Anglo-German Friends". Portsmouth-duisburg.tripod.com. Retrieved 2011-04-07.
- ↑ "Duisburger Portsmouthfreunde". Portsmouthfreunde.de. Retrieved 2011-04-07.
Bibliography
- See also: Bibliography of the history of Duisburg
External links
- Official website of the City (in English)




