Video Coding Engine
Video Coding Engine[1] (VCE, sometimes incorrectly referred to as Video Codec Engine[2]) is AMD's video encoding ASIC implementing the video codec H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. Since 2012 it is integrated into all of their GPUs and APUs except Oland.
Video Coding Engine was introduced with the Radeon HD 7900 on 22 December 2011.[3][4][5] VCE occupies a considerable amount of the die surface and is not to be confused with AMD's Unified Video Decoder (UVD).
Overview
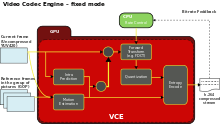
The handling of video data involves computation of data compression algorithms and possibly of video processing algorithms. As the template Compression methods shows, lossy video compression algorithms involve the steps: Motion estimation (ME), Discrete cosine transform (DCT), and entropy encoding (EC).
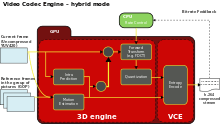
AMD Video Coding Engine (VCE) is a full hardware implementation of the video codec H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. The ASIC is capable of delivering 1080p at 60 frames/sec. Because its entropy encoding block is also a separately accessible Video Codec Engine, it can be operated in two modes: full-fixed mode and hybrid mode.[2][6]
By employing AMD APP SDK, available for Linux and Microsoft Windows, developers can create hybrid encoders that pair custom motion estimation, inverse discrete cosine transform and motion compensation with the hardware entropy encoding to achieve faster than real-time encoding. In hybrid mode, only the entropy encoding block of the VCE unit is used, while the remaining computation is offloaded to the 3D engine (GCN) of the GPU, so the computing scales with the number of available compute units (CUs).
VCE 1.0
As of April 2014, there are two versions of VCE.[1] Version 1.0 supports H.264 YUV420 (I & P frames), H.264 SVC Temporal Encode VCE, and Display Encode Mode (DEM).
It can be found on
- Piledriver-based
- Trinity APUs (Ax-5xxx, e.g. A10-5800K)
- Richland APUs (Ax-6xxx, e.g. A10-6800K)
- GPUs of the Southern Islands generation (GCN1: CAYMAN, ARUBA (Trinity/Richland), CAPE VERDE, PITCAIRN, TAHITI). These are
- Radeon HD 7700 series (except HD 7790 with VCE 2.0)
- Radeon HD 7800 series
- Radeon HD 7900 series
- Radeon HD 8570 to 8990 (except HD 8770 with VCE 2.0)
- Radeon R7 250E, 250X, 265 / R9 270, 270X, 280, 280X
- Radeon R7 360, 370, 455 / R9 370, 370X
- Mobile Radeon HD 77x0M to HD 7970M
- Mobile Radeon HD 8000-Series
- Mobile Radeon Rx M2xx Series (except R9 M280X with VCE 2.0 and R9 M295X with VCE 3.0)
- Mobile Radeon R5 M330 to R9 M390
- FirePro cards with 1st Generation GCN (GCN1)
VCE 2.0
Compared to the first version, VCE 2.0 adds H.264 YUV444 (I-Frames), B-frames for H.264 YUV420, and improvements to the DEM (Display Encode Mode), which results in a better encoding quality.
It can be found on
- Steamroller-based
- Kaveri APUs (Ax-7xxx, e.g. A10-7850K)
- Godavari APUs (Ax-7xxx, e.g. A10-7890K)
- Jaguar-based
- Kabini APUs (e.g. Athlon 5350, Sempron 2650)
- Temash APUs (e.g. A6-1450, A4-1200)
- Puma-based
- Beema and Mullins
- GPUs of the Sea Islands generation as well Bonaire or Hawaii GPUs (2nd Generation Graphics Core Next), such as
- Radeon HD 7790, 8770
- Radeon R7 260, 260X / R9 290, 290X, 295X2
- Radeon R7 360 / R9 390, 390X
- Mobile Radeon R9 M280X
- Mobile Radeon R9 M385, M385X
- Mobile Radeon R9 M470, M470X
- FirePro cards with 2nd Generation GCN (GCN2)
VCE 3.0
Video Coding Engine 3.0 (VCE 3.0) technology features a new high-quality video scaling.,[7] and will also support for High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC, H.265,[8] but As of May 2015, there are no announcements about VP9 video codec support.[9][10][11]
It, together with UVD 6.0, can be found on 3rd generation of Graphics Core Next (GCN3) with "Tonga", "Fiji", "Iceland", and "Carrizo" (VCE 3.1) based graphics controller hardware, which is now used AMD Radeon Rx 300 Series (Pirate Islands GPU family) and VCE 3.4 by actual AMD Radeon Rx 400 Series and AMD Radeon 500 Series (both Polaris GPU family).
- Tonga: Radeon R9 285, 380, 380X; Mobile Radeon R9 M390X, M395, M395X, M485X
- Tonga XT: FirePro W7100, S7100X, S7150, S7150 X2
- Fiji: Radeon R9 Fury, Fury X, Nano; Radeon Pro Duo (2016); FirePro S9300, W7170M
- Polaris: RX 460, 470, 480; RX 550, 560, 570, 580; Radeon Pro Duo (2017)
VCE 4.0
The Video Coding Engine 4.0 encoder and UVD 7.0 decoder are reported to be included in the upcoming Vega based GPUs.[12]
Feature overview
APUs
| Brand | Llano | Trinity | Richland | Kaveri | Carrizo | Bristol Ridge | Raven Ridge | Desna, Ontario, Zacate | Kabini, Temash | Beema, Mullins | Carrizo-L | Stoney Ridge | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platform | Desktop, Mobile | Mobile | Desktop, Mobile | Ultra-mobile | |||||||||
| Released | Aug 2011 | Oct 2012 | Jun 2013 | Jan 2014 | Jun 2015 | Jun 2016 | TBA | Jan 2011 | May 2013 | Q2 2014 | May 2015 | June 2016 | |
| Fab. (nm) | GlobalFoundries 32 SOI | 28 | 14 | TSMC 40 | 28 | ||||||||
| Die size (mm2) | 228 | 246 | 245 | 244.62 | 250.04 | TBA | 75 (+ 28 FCH) | ~107 | TBA | 125 | |||
| Socket | FM1, FS1 | FM2, FS1+, FP2 | FM2+, FP3 | FM2+[lower-alpha 1], FP4 | AM4, FP4 | AM4, FP5 | FT1 | AM1, FT3 | FT3b | FP4 | FP4 | ||
| CPU architecture | AMD 10h | Piledriver | Steamroller | Excavator | Zen | Bobcat | Jaguar | Puma | Puma+[13] | Excavator | |||
| Memory support | DDR3-1866 DDR3-1600 DDR3-1333 | DDR3-2133 DDR3-1866 DDR3-1600 DDR3-1333 | DDR4-2400 DDR4-2133 DDR4-1866 DDR4-1600 | DDR3L-1333 DDR3L-1066 | DDR3L-1866 DDR3L-1600 DDR3L-1333 DDR3L-1066 | DDR3L-1866 DDR3L-1600 DDR3L-1333 | Up to DDR4-2133 | ||||||
| 3D engine[lower-alpha 2] | TeraScale (VLIW5) | TeraScale (VLIW4) | GCN 2nd Gen (Mantle, HSA) | GCN 3rd Gen (Mantle, HSA) | GCN 5th Gen[14] (Mantle, HSA) | TeraScale (VLIW5) | GCN 2nd Gen | GCN 3rd Gen[14] | |||||
| Up to 400:20:8 | Up to 384:24:6 | Up to 512:32:8 | TBA | 80:8:4 | 128:8:4 | Up to 192:?:? | |||||||
| IOMMUv1 | IOMMUv2 | IOMMUv1[15] | TBA | TBA | |||||||||
| Unified Video Decoder | UVD 3 | UVD 4.2 | UVD 6 | TBA | UVD 3 | UVD 4 | UVD 4.2 | UVD 6 | UVD 6.3 | ||||
| Video Coding Engine | N/A | VCE 1.0 | VCE 2.0 | VCE 3.1 | TBA | N/A | VCE 2.0 | VCE 3.1 | |||||
| GPU power saving | PowerPlay | PowerTune | N/A | PowerTune[16] | |||||||||
| Max. displays[lower-alpha 3] | 2–3 | 2–4 | 2–4 | 3 | 4 | TBA | 2 | TBA | TBA | ||||
| TrueAudio | N/A | N/A[15] | TBA | ||||||||||
| FreeSync | N/A | N/A | TBA | ||||||||||
/drm/radeon[19][20] |
N/A | N/A | |||||||||||
/drm/amdgpu[21] |
N/A | N/A | |||||||||||
- ↑ No APU models. Athlon X4 845 only.
- ↑ Unified shaders : texture mapping units : render output units
- ↑ To feed more than two displays, the additional panels must have native DisplayPort support.[17] Alternatively active DisplayPort-to-DVI/HDMI/VGA adapters can be employed.
GPUs
| R100 | R200 | R300 | R400 | R500 | R600 | RV670 | R700 | Evergreen | Northern Islands |
Southern Islands |
Sea Islands |
Volcanic Islands |
Arctic Islands |
Vega | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Released | Apr 2000 | Aug 2001 | Sep 2002 | May 2004 | Oct 2005 | May 2007 | Nov 2007 | Jun 2008 | Sep 2009 | Oct 2010 | Jan 2012 | Sep 2013 | Jun 2015 | Jun 2016 | Jun 2017 |
| Instruction set | not publicly known | TeraScale instruction set | GCN instruction set | ||||||||||||
| Microarchitecture | TeraScale 1 (VLIW5) | TeraScale 2 (VLIW5) | TeraScale 3 (VLIW4) | GCN 1st gen | GCN 2nd gen | GCN 3rd gen | GCN 4th gen | GCN 5th gen | |||||||
| Type | Fixed pipeline | Programmable pixel&vertex pipelines | Unified shader model | ||||||||||||
| Direct3D | 7.0 | 8.1 | 9.0 | 9.0b | 9.0c | 10.0 | 10.1 | 11.0 | 11.1 | 12.0 | |||||
| Shader Model | N/A | 1.4 | 2.0+ | 2.0b | 3.0 | 4.0 | 4.1 | 5.0 | 5.1 | 6.0 | |||||
| OpenGL | 1.3 | 2.0 | 3.3 | 4.4 | 4.5 | ||||||||||
| Vulkan | N/A | Linux experimental Windows 7+ full support for 1.0 |
1.0 | ||||||||||||
| OpenCL | N/A | Close to Metal | 1.1 | 1.2 | 2.0 | ||||||||||
| Power saving | Unknown | PowerPlay | PowerTune | PowerTune & ZeroCore Power | |||||||||||
| Unified Video Decoder | N/A | Avivo/UVD | UVD+ | UVD 2 | UVD 2.2 | UVD 3 | UVD 4 | UVD 4.2 | UVD 5.0 or 6.0 | UVD 6.3 | UVD 7[12] | ||||
| Video Coding Engine | N/A | VCE 1.0 | VCE 2.0 | VCE 3.0 or 3.1 | VCE 3.4 | VCE 4.0[12] | |||||||||
| TrueAudio | N/A | Via dedicated DSP | Via shaders | ||||||||||||
| FreeSync | N/A | ||||||||||||||
| Max. displays[lower-alpha 1] | 1–2 | 2 | 2–6 | ||||||||||||
| Max. resolution | Unknown | 2–6x 2560×1600 | 2–6x 4096×2160 @ 60 Hz | 2–6x 5120x2880 @ 60 Hz | TBA | ||||||||||
/drm/radeon[lower-alpha 2] |
N/A | ||||||||||||||
/drm/amdgpu[lower-alpha 2] |
N/A | experimental[23] | not in mainline yet | ||||||||||||
- ↑ More displays may be supported with native DisplayPort connections, or splitting the maximum resolution between multiple monitors with active converters.
- 1 2 DRM (Direct Rendering Manager) is a component of the Linux kernel. Support in this table refers to the most current version.
Operating system support
The VCE SIP core needs to be supported by the device driver. The device driver provides one or multiple interfaces, like e.g. OpenMAX IL. One of this interfaces is then used by end-user software, like e.g. GStreamer or HandBrake, to access the VCE hardware and make use of it.
AMD's proprietary device driver AMD Catalyst is available for multiple operating systems and support for VCE has been added to it. Additionally, a free device driver is available. This driver also supports the VCE hardware.
Linux

- Initial VCE support has been added on 4 February 2014 by Christian König of AMD to the free radeon driver.[24]
- Gallium3D state tracker for OpenMAX was added 24 October 2013 to Mesa 3D.[25]
- The free and open-source Radeon driver has been adapted to using OpenMAX with the GStreamer OpenMAX (gst-omx) support for exposing the VCE video encode engine.[26]
- AMD employee Leo Liu implemented h264 level support into the Mesa 3D state tracker.[27]
Windows
The software "MediaShow Espresso Video Transcoding" seems to utilize VCE and UVD to the fullest extent possible.[28]
XSplit Broadcaster supports VCE from version 1.3.[29]
Open Broadcaster Software (OBS Studio) supports VCE for recording and streaming. The original Open Broadcaster Software (OBS) requires a fork build in order to enable VCE.[30]
AMD Radeon Software Crimson supports VCE with built in game capture and use AMD AMF/VCE on APU or Radeon Graphics card to reduce FPS drop, when capture game or video content. [31]
See also
- Intel Quick Sync Video, Intel's equivalent SIP core
- Nvidia NVENC, Nvidia's equivalent SIP core
References
- 1 2 http://developer.amd.com/community/blog/2014/02/19/introducing-video-coding-engine-vce/%5B%5D
- 1 2 "Video & Movies: The Video Codec Engine, UVD3, & Steady Video 2.0". AnandTech. December 22, 2011. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ↑ "White Paper AMD UnifiedVideoDecoder (UVD)" (PDF). 2012-06-15. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ↑ "AnandTech Portal | AMD Radeon HD 7970 Review: 28nm And Graphics Core Next, Together As One". Anandtech.com. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- ↑ "AMD's Radeon HD 7970 graphics processor - The Tech Report - Page 5". The Tech Report. Retrieved 2014-03-27.
- ↑ "Radeon HD 8900 Specs". AMD. Retrieved 2016-07-18.
- ↑ http://lists.freedesktop.org/archives/dri-devel/2015-June/084083.html [pull] amdgpu drm-next-4.2
- ↑ Rick Merritt (2015-01-05). "AMD Describes Notebook Processor". EE Times. Retrieved 2015-01-10.
- ↑ http://wccftech.com/amd-embedded-roadmap-2014-2016-leaked-insight-gen-apus-gpus/ AMD Embedded Roadmap 2014-2016 Leaked – Gives Insight Into Next Gen 20nm APUs/SOCs and Discrete GPU Solutions
- ↑ http://www.kitguru.net/components/graphic-cards/anton-shilov/key-features-of-amds-third-iteration-of-gcn-architecture-revealed/ Key features of AMD’s third iteration of GCN architecture revealed
- ↑ http://www.xbitlabs.com/news/graphics/display/20140826114104_AMD_Quietly_Reveals_Third_Iteration_of_GCN_Architecture_with_Tonga_GPU.html AMD Quietly Reveals Third Iteration of GCN Architecture with Tonga GPU.
- 1 2 3 Killian, Zak (22 March 2017). "AMD publishes patches for Vega support on Linux". Tech Report. Retrieved 23 March 2017.
- ↑ "AMD Mobile “Carrizo” Family of APUs Designed to Deliver Significant Leap in Performance, Energy Efficiency in 2015" (Press release). 2014-11-20. Retrieved 2015-02-16.
- 1 2 "AMD VEGA10 and VEGA11 GPUs spotted in OpenCL driver". VideoCardz.com. Retrieved 6 June 2017.
- 1 2 Thomas De Maesschalck (2013-11-14). "AMD teases Mullins and Beema tablet/convertibles APU". Retrieved 2015-02-24.
- ↑ Tony Chen; Jason Greaves, "AMD's Graphics Core Next (GCN) Architecture" (PDF), AMD, retrieved 2016-08-13
- ↑ "How do I connect three or More Monitors to an AMD Radeon™ HD 5000, HD 6000, and HD 7000 Series Graphics Card?". AMD. Retrieved 2014-12-08.
- ↑ "A technical look at AMD’s Kaveri architecture". Semi Accurate. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ↑ Airlie, David (2009-11-26). "DisplayPort supported by KMS driver mainlined into Linux kernel 2.6.33". Retrieved 2016-01-16.
- ↑ "Radeon feature matrix". freedesktop.org. Retrieved 2016-01-10.
- ↑ Deucher, Alexander (2015-09-16). "XDC2015: AMDGPU" (PDF). Retrieved 2016-01-16.
- 1 2 Michel Dänzer (2016-11-17). "[ANNOUNCE] xf86-video-amdgpu 1.2.0". lists.x.org.
- ↑ Larabel, Michael (7 December 2016). "The Best Features Of The Linux 4.9 Kernel". Phoronix. Retrieved 7 December 2016.
- ↑ König, Christian (4 February 2014). "initial VCE support". mesa-dev (Mailing list). Retrieved 28 November 2015.
- ↑ König, Christian (24 October 2013). "OpenMAX state tracker". mesa-dev (Mailing list). Retrieved 28 November 2015.
- ↑ "AMD Open-Sources VCE Video Encode Engine Code". Phoronix. 2014-02-04. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ↑ "st/omx/enc: implement h264 level support". 2014-06-12. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ↑ "MediaShow Espresso Video Transcoding Benchmark". 2014-01-14. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ↑ "XSplit Broadcaster 1.3 maintenance update includes mainly performance enhancements and maintenance fixes including such noteworthy features such as support for AMD's VCE H.264 hardware encoder".
- ↑ "OBS branch with AMD VCE support". May 2, 2014. Retrieved 2017-05-20.
- ↑ "Radeon Software Crimson ReLive Edition 16.12.1 Release Notes". Retrieved 2017-05-20.