Diporiphora winneckei
| Diporiphora winneckei | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Canegrass dragon | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Iguania |
| Family: | Agamidae |
| Genus: | Diporiphora |
| Species: | D. winneckei |
| Binomial name | |
| Diporiphora winneckei Lucas & Frost, 1896 | |
Diporiphora winneckei (the canegrass dragon, blue-lined dragon or Winnecke's two-pored dragon) is a small, terrestrial, diurnal (active during the day)[1] lizard endemic to Australia.[2] It is found in throughout arid zones of Australia and is also a common house pet.[1]
Etymology
The specific name, winneckei, is in honor of Australian explorer Charles George A. Winnecke (1856–1902).[3]
Description
Diporiphora winneckei is a slim lizard with a long tail and limbs, approximately 15–24 cm (5.9–9.4 in) in length.[4] It is a grey or pale brown to reddish-brown colour, with a thick grey ventral band that runs from the nape to the tail.[4] It also has creamy-yellow (female) or silver grey (male) stripes that run down each side of its back, converging at the pelvis. Dark angular blotches lie between the stripe and the ventral band of female, while males have fewer or no blotches visible.[5] The dragon also has a creamy mid lateral stripe that runs from eye to ear on each side. The dragons have homogenous scales as well as weak gular and postauricular folds. They lack the spines and crest that many other dragons display.[6]
Taxonomy
Canegrass dragons were first officially described in 1896 by Lucas and Frost.[1] Their common name originates from the fact that they are often found in canegrass. Their scientific name, Diporiphora winneckei, suggests they have two visible pores, however the pores are not visible on this species.[6] The closest species to the canegrass dragon is Amelia’s dragon (Diporiphora ameliae) which was split from the canegrass dragon as a new species in 2012. Amelia’s dragon has four longitudinal ventral stripes when compared to the canegrass dragons two ventral stripes, as well as having postauricular fold and spines, which the canegrass dragon lacks.[1]
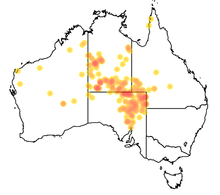
Distribution and habitat
The canegrass dragon is an endemic species found in the arid zones of Australia, with a rainfall of less than 500mm.[4] It’s predominantly found in the region surrounding the junction of the Northern Territory, Queensland, New South Wales and South Australian borders. However it also occupies habitat across Western Australia as far as the northern West Australian coastline. The dragon is usually found on desert sand ridges or other sandy soils in amongst ground litter, cane grass, spinifex or hummock grasses.[5] The dragon is rarely sighted, despite not being rare, due to its excellent camouflage and secretive behaviour.[1]
Reproduction
Canegrass dragons reach sexual maturity at around one year old. During the breeding season, the male will attract a female by repeated head bobs, which displays his willingness to mate. If the female is not ready she will run away, however if she is, she will lower her head several times to show she is interested. The breeding season for the dragons is from October to April and in that time the female can lay between four and six clutches. After fertilization, the eggs will develop in approximately two to three weeks. The dragons are oviparous, and will lay between one and three eggs per clutch in a small nest in moist sandy soil.[1]
Diet
Canegrass dragons feed during the days and are insectivorous. However they have been found on some occasions to consume leafy greens and flowers.[1]
Threats
Although the canegrass dragon is not currently listed as a conservation concern, it is still subject to those threats that threaten all Australian reptiles. These threats include introduced diseases, death on roads, habitat modification, degradation and loss and feral predators such as foxes, dogs, cats and even cane toads.[7]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Van Der Reijden , J. (2014, August 18). The captive maintenance and breeding of Diporiphora winneckei (Canegrass dragon) at the Alice Springs Desert Park. Retrieved from Australasian society of zoo keeping inc: http://www.aszk.org.au/docs/cane_grass_dragon.pdf
- ↑ Diporiphora winneckei at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database. Accessed 5 October 2014.
- ↑ Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. ISBN 978-1-4214-0135-5. (Diporiphora winneckei, p. 288).
- 1 2 3 Swan, G. (1995). Canegrass Two-line Dragon. In G. Swan, A photographic Guide to Snakes & other reptiles of Australia (p. 107). Frenchs Forest: NewHolland Publishers.
- 1 2 Wilson, S., & Swan, G. (2013). Canegrass Dragon; Blue-lined Dragon. In S. Wilson, & G. Swan, A complete guide to reptiles of Australia Fourth Edition (p. 406). Chatswood: New Holland Publishers.
- 1 2 Cogger, H. G. (1994). Diporiphora winneckei. In H. G. Cogger, Reptiles and Amphibians of Australia (p. 336). Chatswood: Imago Productions.
- ↑ Macdonald, S. (2014, August 18). Canegrass dragon. Retrieved from Australian Reptile Online Database: http://www.arod.com.au/arod/reptilia/Squamata/Agamidae/Diporiphora/winneckei