Dinitro-''ortho''-cresol
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Methyl-3,5-dinitrophenol | |
| Other names
3,5-Dinitro-ortho-cresol; 3,5-Dinitro-o-cresol; 4,6-Dinitro-2-hydroxytoluene; DNOC, 2-methyl-3,5-dinitrophenol, 4,6-Dinitro-o-cresol, 3,5-Dinitro-2-hydroxytoluene, 4,6-Dinitro-2-methyl phenol, DNC | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.821 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6N2O5 | |
| Molar mass | 198.13 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow solid[1] |
| Odor | odorless[1] |
| Density | 1.58 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 86.5 °C (187.7 °F; 359.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 312 °C (594 °F; 585 K) |
| 0.01% (20°C)[1] | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.00005 mmHg (20°C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | noncombustible [1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
7 mg/kg (oral, rat) 50 mg/kg (oral, cat) 21 mg/kg (oral, mouse) 24.6 mg/kg (oral, rabbit) 24.6 mg/kg (oral, guinea pig) 31 mg/kg (oral, rat)[2] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 0.2 mg/m3 [skin][1] |
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 0.2 mg/m3 [skin][1] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
5 mg/m3[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
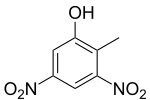
Dinitro-ortho-cresol (DNOC) is an organic compound with the structural formula CH3C6H2(NO2)2OH. It is a yellow solid that is only slightly soluble in water. DNOC and some related derivatives have been used as herbicides.
Preparation
This compound is prepared by dinitration of o-cresol. The resulting disulfonate is then treated with nitric acid to give DNOC. A variety of related derivatives are known including those where the methyl group is replaced by sec-butyl ("dinoseb"), tert-butyl ("dinoterb"), and 1-methylheptyl ("dinocap"). These are prepared by the direct nitration of the alkyphenols.[3]
Applications and safety
This toxicant interferes with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production.[4][5]
Symptoms of dinitro-ortho-cresol poisoning, due to ingestion or other forms of exposure, include confusion, headache, shortness of breath, and sweating.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0234". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ "Dinitro-o-cresol". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). 4 December 2014. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ↑ Gerald Booth "Nitro Compounds, Aromatic" in "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry" 2007; Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_411
- ↑ Parker, V. H.; Barnes, J. M.; Denz, F. A. (1951). "Some Observations on the Toxic Properties of 3:5-Dinitro-Ortho-Cresol". Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 8 (4): 226. doi:10.1136/oem.8.4.226.
- ↑ Harvey, DG; Bidstrup, PL; Bonnell, JA (1951). "Poisoning by dinitro-ortho-cresol; some observations on the effects of dinitro-ortho-cresol administered by mouth to human volunteers". British Medical Journal. 2 (4722): 13–6. PMC 2069381
 . PMID 14839311. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.4722.13.
. PMID 14839311. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.4722.13. - ↑ Chemical poisoning - Dinitrocresol