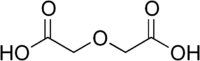
Diglycolic acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(carboxymethyloxy)acetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.476 |
| EC Number | 203-823-5 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O5 | |
| Molar mass | 134.09 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Diglycolic acid is an aliphatic dicarboxylic acid, its acidity is between the one of acetic acid and oxalic acid.[1] It is formed in the oxidation of diethylene glycol in the body and can lead to severe complications with fatal outcome.[2]
Preparation
Already in the 1860s the production of diglycolic acid by oxidation of diethylene glycol with concentrated nitric acid was described by A. Wurtz.[3]
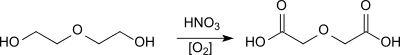
In parallel, W. Heintz reported the synthesis of diglycolic acid from chloroacetic acid by heating with sodium hydroxide solution.[4]
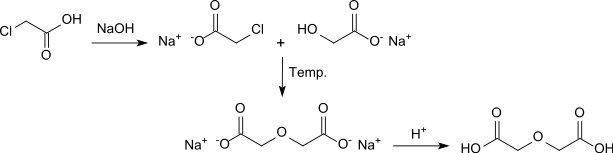
In a version with barium hydroxide solution as an alkaline medium, diglycolic acid is obtained in 68% yield after acidification.[5]
The yields of the described reactions are unsatisfactory for use on a technical scale.
The single-stage nitric acid process gives even in the presence of an oxidation catalyst (vanadium(V)oxide) yields of only 58-60%.[6] In a multi-stage process of nitric acid oxidation at 70 °C and multiple crystallization steps, evaporation of the residues and return of the diethylene glycol-containing mother liquor, product yields of up to 99% (based on diethylene glycol) can be achieved.[7]
The oxidation of diethylene glycol with air, oxygen or ozone avoids the use of expensive nitric acid and prevents the inevitable formation of nitrous gases.[8] In the presence of a platinum catalyst, yields of 90% can be obtained by air oxidation.[9]
On a bismuth platinum contact catalyst, yields of 95% are to be achieved under optimized reaction conditions.[10]
The oxidation of 1,4-dioxan-2-one (p-dioxanone, a lactone which is used as a comonomer in biodegradable polyesters with nitric acid or dinitrogen tetroxide) is also described with yields of up to 75%.[11]

Properties
Diglycolic acid is readily water soluble and crystallizes from water in monoclinic prisms as a white, odorless solid. At an air humidity of more than 72% and 25 °C the monohydrate is formed. The commercial product is the anhydrous form as a free-flowing flakes.[12]
Application
Diesters of diglycolic acid with (branched) higher alcohols can be used as softeners for polyvinyl chloride (PVC) with comparable properties as di-n-octyl phthalate (DOP).[13]
Basic solutions of diglycolic acid are described for the removal of limescale deposits in gas and oil bores, as well as in systems such as heat exchangers or steam boilers.[14]
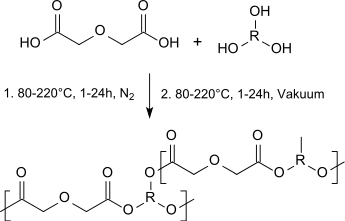
Diglycolic acid can be used as a diester component in homo- and copolymeric polyesters (so-called polyalkylene diglycolates) which are biocompatible and biodegradable and can be used alone or in blends with aliphatic polyesters as tissue adhesives, cartilage substitutes or as implant materials:[15]
References
- ↑ L. Bhattacharyya, J. Rohrer, ed. (2012), Appendix 1: DISSOCIATION CONSTANTS (pKa) OF ORGANIC ACIDS (AT 20 °C), in Applications of Ion Chromatography for Pharmaceutical and Biological Products, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., doi:10.1002/9781118147009.app1
- ↑ A.A. Roscher, E. Jussek, T. Noguchi, S. Franklin (1975), [PDF "Fatal Accidental Diglycolic Acid Intoxication"], Bull. Soc. Pharm. Environ. Pathol. III (4), PDF
- ↑ A. Wurtz (1861), "Umwandlung des Aethylens zu complicirten organischen Säuren" (in German), Liebigs Ann. Chem. 117 (1): pp. 136–140, doi:10.1002/jlac.18611170114
- ↑ W. Heintz (1862), "Ueber die Diglycolsäure (Paraäpfelsäure)" (in German), Ann. Phys. 191 (2): pp. 280–295, doi:10.1002/andp.18621910206
- ↑ K.E. Füger (1959) (in German), [PDF Synthese und katalytische Reduktion von Glykolsäure und Glykolsäureestern, Promotionsarbeit ETH Zürich], Juris-Verlag, PDF
- ↑ C. Erk (1991), "Condensation of diglycolic acid dichloride with polyglycols, 5. An improved synthesis of cyclic polyether-esters by cyclization", Liebigs Ann. Chem. 10: pp. 1083–1084, doi:10.1002/jlac.1991199101186
- ↑ US 4066691, "Process for the production of pure diglycolic acid by oxidation if diethylene glycol with nitric acid"
- ↑ US 3879452, "Method for making diglycolic acid, dipropionic acid and the salts thereof"
- ↑ US 4256916, "Oxidation of polyethylene glycols to dicarboxylic acids"
- ↑ Y-Y. Zhang, Z.-Y. Liang, Y.-D. Zhang (2012-05), [PDF "Preparation of Diglycolic Acid via Oxidation of Diethylene Glycol with Molecular Oxygen"], Fine Chemicals, PDF
- ↑ US 3952054, "Process for preparing diglycolic acid"
- ↑ W.M. Bruner, L.T. Sherwood, Jr. (1949), "Diglycolic acid – a new commercial dibasic acid", Ind. Eng. Chem. 41 (8): pp. 1653–1656, doi:10.1021/ie50476a032
- ↑ US 3173888, "Diesters of diglycolic acid and vinyl chloride polymers plastized therewith"
- ↑ US 3639279, "Scale removal composition and method using salt of diglycolic acid and base at pH above 5"
- ↑ US 5696178, "Absorbable polyalkylene diglycolates"