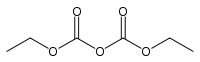
Diethyl pyrocarbonate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Diethyl dicarbonate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.039 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Diethylpyrocarbonate |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O5 | |
| Molar mass | 162.14 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.101 g/mL at 25 °C 1.121 g/mL at 20 °C |
| Boiling point | 93 to 94 °C (199 to 201 °F; 366 to 367 K) at 24 hPa |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful |
| R-phrases (outdated) | R22 R36/37/38 |
| Flash point | 69 °C (156 °F; 342 K) closed cup |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
Oral - rat - 850 mg/kg |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate Dimethyl dicarbonate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC), also called diethyl dicarbonate (IUPAC name), is used in the laboratory to inactivate RNase enzymes in water and on laboratory utensils. It does so by the covalent modification of histidine (most strongly), lysine, cysteine, and tyrosine residues.[1][2]
DEPC-treated (and therefore RNase-free) water is used in handling of RNA in the laboratory to reduce the risk of RNA being degraded by RNases.
Water is usually treated with 0.1% v/v DEPC for at least 2 hours at 37 °C and then autoclaved (at least 15 min) to inactivate traces of DEPC. Inactivation of DEPC in this manner yields CO2 and ethanol. Higher concentrations of DEPC are capable of deactivating larger amounts of RNase, but remaining traces or byproducts may inhibit further biochemical reactions such as in vitro translation. Furthermore, chemical modification of RNA such as carboxymethylation is possible when traces of DEPC or its byproducts are present, resulting in impaired recovery of intact RNA even after buffer exchange (after precipitation).

DEPC is unstable in water and susceptible to hydrolysis to carbon dioxide and ethanol, especially in the presence of a nucleophile. For this reason, DEPC cannot be used with Tris or HEPES buffers. In contrast, it can be used with phosphate-buffered saline or MOPS.[3] A handy rule is that enzymes or chemicals which have active -O:, -N: or -S: cannot be treated with DEPC to become RNase-free, as DEPC reacts with these species. Furthermore, DEPC degradation products can inhibit in vitro transcription.
DEPC derivatization of histidines is also used to study the importance of histidyl residues in enzymes. Modification of histidine by DEPC results in carbethoxylated derivates at the N-omega-2 nitrogen of the imidazole ring. DEPC modification of histidines can be reversed by treatment with 0.5 M hydroxylamine at neutral pH.
DEPC can also be used for probing the structure of double-stranded DNA.<needs reference />
References
- ↑ Chirgwin, John M; et al. (1979). "Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sourcesenriched in ribonuclease". Biochemistry. 18 (24): 5294–5299. PMID 518835. doi:10.1021/bi00591a005.
- ↑ Wolf, Barry; Lesnaw, Judith A.; Reichmann, Manfred E. (1970). "A Mechanism of the Irreversible Inactivation of Bovine Pancreatic Ribonuclease by Diethylpyrocarbonate. A General Reaction of Diethylpyrocarbonate with Proteins". European Journal of Biochemistry. 13 (3): 519–25. PMID 5444158. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00955.x.
- ↑ "FAQ about DEPC". Sigma-Aldrich. Retrieved 12 August 2012.