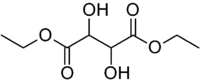
Diethyl tartrate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Diethyl 2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate | |
| Other names
Diethyl 2,3-dihydroxysuccinate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.622 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H14O6 | |
| Molar mass | 206.19 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colourless |
| Density | 1.204 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 280 °C (536 °F; 553 K) |
| low | |
| -113.4·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Diethyl tartrate is an organic compound, the ethyl ester of tartaric acid. It exists in both as a chiral isomer, showing both left- and right-handed forms, as well as a meso stereoisomer, which is not chiral. The chiral isomer is far more common.
In the Sharpless epoxidation, diethyl tartrate and titanium isopropoxide form a chiral catalyst in situ.[1]
References
- ↑ J. Gordon Hill, K. Barry Sharpless, Christopher M. Exon, and Ronald Regenye (1985). "Enantioselective Epoxidation of Allylic Alcohols: (2S,3S)-3-Propyloxiranemethanol". Org. Synth. 63: 66.; Coll. Vol., 7, p. 461
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.