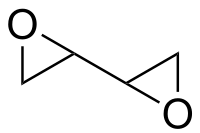
Diepoxybutane
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,2’-Bioxirane | |
| Other names
1,1'-Bi[ethylene oxide]; 1,2:3,4-Diepoxybutane; 1,3-Butadiene diepoxide; Bioxirane; Butadiene dioxide; Butane diepoxide; Dioxybutadiene | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | DEB |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.527 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 86.09 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.113 g/cm3 (18 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | 4 °C (39 °F; 277 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 138 °C (280 °F; 411 K)[1] |
| Miscible[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 46 °C (115 °F; 319 K)[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Diepoxybutane (also known as butane diepoxide, butadiene diepoxide, or 1,2:3,4-diepoxybutane) is a chemical compound with two epoxide functional groups. It is used as a chemical intermediate, as a curing agent for polymers, as a cross-linking agent for textiles, and as a preservative.[2]
Diepoxybutane is a carcinogen.[2]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- 1 2 Diepoxybutane Report on Carcinogens, Twelfth Edition (2011)
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.