Dicobalt edetate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Kelocyanor | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.048.227 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H12Co2N2O8.6H2O | |
| Molar mass | 406.08 g/mol 514.18 g/mol (hexahydrate) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
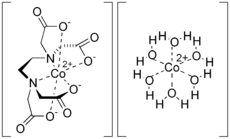
Dicobalt edetate is the coordination compound with the approximate formula Co2(EDTA)(H2O)6.
Solutions of this solid have been used in Europe as an antidote to cyanide poisoning.[1]
It is a derivative of the (non-natural) amino acid ethylenediaminetetraacetate.
Structure
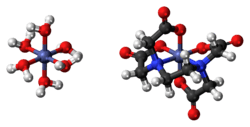
The compound is polymeric in the crystalline form. Half of the Co2+ ions are bound to the EDTA2− and the other Co2+ ions are bound to four water ligands as well as carboxylate ligands on the [Co(EDTA)]2− entity.[2] In aqueous solution, depolymerization occurs to give [Co(EDTA)]2− and [Co(H2O)6]2+ ions, each of which is kinetically labile and has a high affinity for cyanide.
Related compounds
Oxidation of [Co(II)(EDTA)]2− gives [Co(III)(EDTA)]−, which is so kinetically inert that it can be resolved optically.[3]
References
- ↑ Pickering WG (December 1985). "Cyanide toxicity and the hazards of dicobalt edetate". Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 291 (6509): 1644. PMC 1418389
 . PMID 2866807. doi:10.1136/bmj.291.6509.1644-a.
. PMID 2866807. doi:10.1136/bmj.291.6509.1644-a. - ↑ E. F. K. Mccandlish, T. K. Michael; Rose, N. J.; Neal, J. A.; Lingafelter, E. C.; Rose, N. J. (1978). "Comparison of the Structures and Aqueous Solutions of [(O-Phenylenediaminetetraacetato(2-)]Cobalt(II) and [Ethylenediaminetetraacetato(2-)]Cobalt(II)". Inorg. Chem. 17 (6): 1383–94. doi:10.1021/ic50184a001.
- ↑ Dwyer, F. P.; Garvan, F. L. (1960). "Resolution of the Ethylenediaminetetracetatocobaltate(III) Ion". Inorg. Synth. VI: 192–4. ISBN 978-0-470-13237-1. doi:10.1002/9780470132371.ch61.