Dichloroaniline
Dichloroanilines are chemical compounds which consist of an aniline ring substituted with two chlorine atoms and have the molecular formula C6H5Cl2N. There are six isomers of dichloroaniline. As aniline derivatives, they are named with the amino group in position 1. They are all colorless, although commercial samples can appear colored due to the presence of impurities. Several derivatives are used in the production of dyes and herbicides.[1]
The six isomers are:
| Compound name | CAS# | Chemical structure | Melting point | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2,3-Dichloroaniline | 608-27-5 | 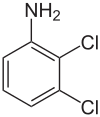 | 20–25 °C (68–77 °F)[2] | |
| 2,4-Dichloroaniline | 554-00-7 |  | 59–62 °C (138–144 °F)[3] | |
| 2,5-Dichloroaniline | 95-82-9 | 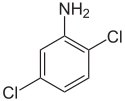 | 47–50 °C (117–122 °F)[4] | Precursor to dyes and pigments, such as Pigment Yellow 10[1] |
| 2,6-Dichloroaniline | 608-31-1 |  | 36–38 °C (97–100 °F)[5] | |
| 3,4-Dichloroaniline | 95-76-1 |  | 69–71 °C (156–160 °F)[6] | |
| 3,5-Dichloroaniline | 626-43-7 |  | 46–52 °C (115–126 °F)[7] |
References
- 1 2 Thomas Kahl, Kai-Wilfrid Schröder, F. R. Lawrence, W. J. Marshall, Hartmut Höke, Rudolf Jäckh "Aniline" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2007; John Wiley & Sons: New York. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_303
- ↑ "2,3-Dichloroanline". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ↑ "2,4-Dichloroanline". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ↑ "2,5-Dichloroanline". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ↑ "2,6-Dichloroanline". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ↑ "3,4-Dichloroanline". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ↑ "3,5-Dichloroanline". Sigma-Aldrich.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.