Darfur Dome
The Darfur Volcanic Province from ISS.
Darfur Dome or Darfur Volcanic Province is an area about 100x400 km in area in Western Sudan, the result of a volcanic plume[1][2] which created its best-known and central feature, Deriba Crater. It also produced the surrounding Marra Mountains (Jebel Marra)[3][4] and Tagabo Hills, formed around 16 and 10 Ma., and the Meidob Hills which arose around 6.8 Ma.[5] The plume is linked to stress resolution along the Central African Fault Zone.
 Deriba Caldera
Deriba Caldera Jebel Marra Deriba Lakes
Jebel Marra Deriba Lakes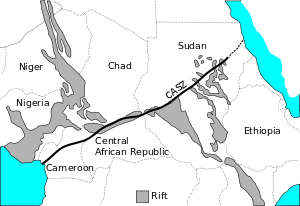 Central Africa showing CASZ.
Central Africa showing CASZ.
Notes
- ↑ "The Darfur Dome, western Sudan: the product of a subcontinental mantle plume", G. Franz, International Journal of Earth Sciences, Volume 83, Number 3 / October, 1994
- ↑ "Plume related alkaline magmatism in central Africa—the Meidob Hills (W Sudan)", Gerhard Franza, Gesine Steiner, Frank Volker, Dieter Pudlo and Konrad Hammerschmidt, Chemical Geology, Volume 157, Issues 1-2, 3 May 1999, Pages 27-47
- ↑ Google Maps
- ↑ "Jebel Marra, a dormant volcano in Darfur Province, Western Sudan", J. R. Vail, Bulletin of Volcanology, Volume 36, Number 1 / March, 1972
- ↑ G. Franz
Coordinates: 13°5′0″N 24°20′0″E / 13.08333°N 24.33333°E
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.