Edotreotide
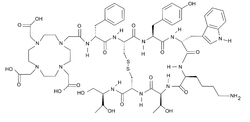 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-[4-[2-[[(2R)-1-[[(4R,7S,10S,13R,16S,19R)-10-(4-aminobutyl)-4-[[(2R,3R)-1,3-dihydroxybutan-2-yl]carbamoyl]-7-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-16-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-13-(1H-indol-3-ylmethyl)-6,9,12,15,18-pentaoxo-1,2-dithia-5,8,11,14,17-pentazacycloicos-19-yl]amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]-7,10-bis(carboxymethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetrazacyclododec-1-yl]acetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C65H92N14O18S2 | |
| Molar mass | 1,421.65 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
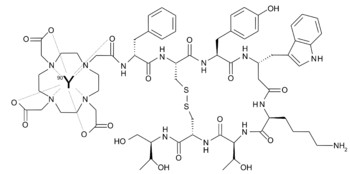
90Y labelled edotreotide
Edotreotide (USAN, codenamed SMT487, also known as (DOTA0-Phe1-Tyr3)octreotide, or DOTATOC) is a substance which, when bound to various radionuclides, is used in the treatment and diagnosis of certain types of cancer.[1]
It has been the subject of a trial by the National Cancer Institute to determine its effects in young cancer patients (up to 25 years of age) for its ability to locate malignant cancer cells without harming normal cells. Specific cancers being included in the trial include neuroblastoma, childhood brain tumours and gastrointestinal cancer.[2]
See also
- DOTA-TATE, a similar compound
References
- ↑ Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p1161.
- ↑ Radiolabeled Octreotide in Treating Children With Advanced or Refractory Solid Tumors
- Bushnell, D. L.; O'Dorisio, T. M.; O'Dorisio, M. S.; Menda, Y.; Hicks, R. J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Baulieu, J. -L.; Borson-Chazot, F.; Anthony, L.; Benson, A. B.; Oberg, K.; Grossman, A. B.; Connolly, M.; Bouterfa, H.; Li, Y.; Kacena, K. A.; Lafrance, N.; Pauwels, S. A. (2010). "90Y-Edotreotide for Metastatic Carcinoid Refractory to Octreotide". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 28 (10): 1652–1659. PMID 20194865. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.22.8585.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.