DOK2
| DOK2 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||
| Aliases | DOK2, p56DOK, p56dok-2, docking protein 2 | ||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 1332623 HomoloGene: 2957 GeneCards: DOK2 | ||||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||||
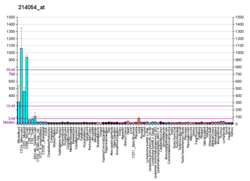 | |||||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 8: 21.91 – 21.91 Mb | Chr 14: 70.77 – 70.78 Mb | |||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [1] | [2] | |||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Docking protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DOK2 gene.[3][4][5]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is constitutively tyrosine phosphorylated in hematopoietic progenitors isolated from chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) patients in the chronic phase. It may be a critical substrate for p210(bcr/abl), a chimeric protein whose presence is associated with CML. This encoded protein binds p120 (RasGAP) from CML cells.[5]
Interactions
DOK2 has been shown to interact with INPP5D[6] and TEK tyrosine kinase.[7][8]
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Di Cristofano A, Carpino N, Dunant N, Friedland G, Kobayashi R, Strife A, Wisniewski D, Clarkson B, Pandolfi PP, Resh MD (March 1998). "Molecular cloning and characterization of p56dok-2 defines a new family of RasGAP-binding proteins". J Biol Chem. 273 (9): 4827–30. PMID 9478921. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.9.4827.
- ↑ Garcia A, Prabhakar S, Hughan S, Anderson TW, Brock CJ, Pearce AC, Dwek RA, Watson SP, Hebestreit HF, Zitzmann N (March 2004). "Differential proteome analysis of TRAP-activated platelets: involvement of DOK-2 and phosphorylation of RGS proteins". Blood. 103 (6): 2088–95. PMID 14645010. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-07-2392.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: DOK2 docking protein 2, 56kDa".
- ↑ Dunant NM, Wisniewski D, Strife A, Clarkson B, Resh MD (2000). "The phosphatidylinositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase SHIP1 associates with the dok1 phosphoprotein in bcr-Abl transformed cells". Cell. Signal. 12 (5): 317–26. PMID 10822173. doi:10.1016/S0898-6568(00)00073-5.
- ↑ Jones N, Dumont DJ (1998). "The Tek/Tie2 receptor signals through a novel Dok-related docking protein, Dok-R". Oncogene. 17 (9): 1097–108. PMID 9764820. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202115.
- ↑ Master Z, Jones N, Tran J, Jones J, Kerbel RS, Dumont DJ (2001). "Dok-R plays a pivotal role in angiopoietin-1-dependent cell migration through recruitment and activation of Pak". EMBO J. 20 (21): 5919–28. PMC 125712
 . PMID 11689432. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.21.5919.
. PMID 11689432. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.21.5919.
Further reading
- Jiang H, Harris MB, Rothman P (2000). "IL-4/IL-13 signaling beyond JAK/STAT.". J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 105 (6 Pt 1): 1063–70. PMID 10856136. doi:10.1067/mai.2000.107604.
- Jones N, Dumont DJ (1998). "The Tek/Tie2 receptor signals through a novel Dok-related docking protein, Dok-R.". Oncogene. 17 (9): 1097–108. PMID 9764820. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202115.
- Jones N, Dumont DJ (2000). "Recruitment of Dok-R to the EGF receptor through its PTB domain is required for attenuation of Erk MAP kinase activation.". Curr. Biol. 9 (18): 1057–60. PMID 10508618. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(99)80458-8.
- Némorin JG, Duplay P (2000). "Evidence that Llck-mediated phosphorylation of p56dok and p62dok may play a role in CD2 signaling.". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (19): 14590–7. PMID 10799545. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.19.14590.
- Dunant NM, Wisniewski D, Strife A, et al. (2000). "The phosphatidylinositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase SHIP1 associates with the dok1 phosphoprotein in bcr-Abl transformed cells.". Cell. Signal. 12 (5): 317–26. PMID 10822173. doi:10.1016/S0898-6568(00)00073-5.
- Némorin JG, Laporte P, Bérubé G, Duplay P (2001). "p62dok negatively regulates CD2 signaling in Jurkat cells.". J. Immunol. 166 (7): 4408–15. PMID 11254695. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.166.7.4408.
- Grimm J, Sachs M, Britsch S, et al. (2001). "Novel p62dok family members, dok-4 and dok-5, are substrates of the c-Ret receptor tyrosine kinase and mediate neuronal differentiation.". J. Cell Biol. 154 (2): 345–54. PMC 2150770
 . PMID 11470823. doi:10.1083/jcb.200102032.
. PMID 11470823. doi:10.1083/jcb.200102032. - Master Z, Jones N, Tran J, et al. (2001). "Dok-R plays a pivotal role in angiopoietin-1-dependent cell migration through recruitment and activation of Pak.". EMBO J. 20 (21): 5919–28. PMC 125712
 . PMID 11689432. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.21.5919.
. PMID 11689432. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.21.5919. - Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899.
. PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. - Salomon AR, Ficarro SB, Brill LM, et al. (2003). "Profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation pathways in human cells using mass spectrometry.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (2): 443–8. PMC 141014
 . PMID 12522270. doi:10.1073/pnas.2436191100.
. PMID 12522270. doi:10.1073/pnas.2436191100. - Jones N, Chen SH, Sturk C, et al. (2003). "A unique autophosphorylation site on Tie2/Tek mediates Dok-R phosphotyrosine binding domain binding and function.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 (8): 2658–68. PMC 152553
 . PMID 12665569. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.8.2658-2668.2003.
. PMID 12665569. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.8.2658-2668.2003. - Master Z, Tran J, Bishnoi A, et al. (2003). "Dok-R binds c-Abl and regulates Abl kinase activity and mediates cytoskeletal reorganization.". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (32): 30170–9. PMID 12777393. doi:10.1074/jbc.M301339200.
- Gérard A, Favre C, Garçon F, et al. (2004). "Functional interaction of RasGAP-binding proteins Dok-1 and Dok-2 with the Tec protein tyrosine kinase.". Oncogene. 23 (8): 1594–8. PMID 14647425. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207283.
- Brill LM, Salomon AR, Ficarro SB, et al. (2004). "Robust phosphoproteomic profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation sites from human T cells using immobilized metal affinity chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry.". Anal. Chem. 76 (10): 2763–72. PMID 15144186. doi:10.1021/ac035352d.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. PMC 528928
 . PMID 15489334. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504.
. PMID 15489334. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. - Rush J, Moritz A, Lee KA, et al. (2005). "Immunoaffinity profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation in cancer cells.". Nat. Biotechnol. 23 (1): 94–101. PMID 15592455. doi:10.1038/nbt1046.
- Van Slyke P, Coll ML, Master Z, et al. (2005). "Dok-R mediates attenuation of epidermal growth factor-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase and Akt activation through processive recruitment of c-Src and Csk.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 25 (9): 3831–41. PMC 1084282
 . PMID 15831486. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.9.3831-3841.2005.
. PMID 15831486. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.9.3831-3841.2005.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.