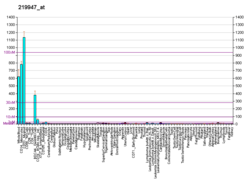
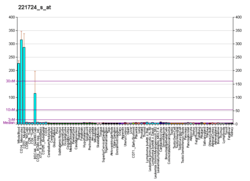
CLEC4A
C-type lectin domain family 4 member A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLEC4A gene.[3][4]
This gene encodes a member of the C-type lectin/C-type lectin-like domain (CTL/CTLD) superfamily. Members of this family share a common protein fold and have diverse functions, such as cell adhesion, cell-cell signalling, glycoprotein turnover, and roles in inflammation and immune response. The encoded type 2 transmembrane protein may play a role in inflammatory and immune response. Multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. This gene is closely linked to other CTL/CTLD superfamily members on chromosome 12p13 in the natural killer gene complex region.[4]
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Bates EE, Fournier N, Garcia E, Valladeau J, Durand I, Pin JJ, Zurawski SM, Patel S, Abrams JS, Lebecque S, Garrone P, Saeland S (Sep 1999). "APCs express DCIR, a novel C-type lectin surface receptor containing an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif". J Immunol. 163 (4): 1973–83. PMID 10438934.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: CLEC4A C-type lectin domain family 4, member A".
External links
Further reading
- Drickamer K (1999). "C-type lectin-like domains.". Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 9 (5): 585–90. PMID 10508765. doi:10.1016/S0959-440X(99)00009-3.
- Huang X, Yuan Z, Chen G, et al. (2001). "Cloning and characterization of a novel ITIM containing lectin-like immunoreceptor LLIR and its two transmembrane region deletion variants.". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 281 (1): 131–40. PMID 11178971. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.4322.
- Richard M, Veilleux P, Rouleau M, et al. (2002). "The expression pattern of the ITIM-bearing lectin CLECSF6 in neutrophils suggests a key role in the control of inflammation.". J. Leukoc. Biol. 71 (5): 871–80. PMID 11994513.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899.
. PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899.
- Ebner S, Sharon N, Ben-Tal N (2003). "Evolutionary analysis reveals collective properties and specificity in the C-type lectin and lectin-like domain superfamily.". Proteins. 53 (1): 44–55. PMID 12945048. doi:10.1002/prot.10440.
- Richard M, Thibault N, Veilleux P, et al. (2003). "The ITIM-bearing CLECSF6 (DCIR) is down-modulated in neutrophils by neutrophil activating agents.". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 310 (3): 767–73. PMID 14550269. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.09.077.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. PMC 528928
 . PMID 15489334. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504.
. PMID 15489334. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504.
- Richard M, Thibault N, Veilleux P, et al. (2006). "Granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor reduces the affinity of SHP-2 for the ITIM of CLECSF6 in neutrophils: a new mechanism of action for SHP-2.". Mol. Immunol. 43 (10): 1716–21. PMID 16360206. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2005.10.006.
- Lorentzen JC, Flornes L, Eklöw C, et al. (2007). "Association of arthritis with a gene complex encoding C-type lectin-like receptors.". Arthritis Rheum. 56 (8): 2620–32. PMID 17665455. doi:10.1002/art.22813.
 . PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899.
. PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. . PMID 15489334. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504.
. PMID 15489334. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504.