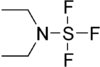
Diethylaminosulfur trifluoride
| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N,N-Diethylaminosuflur trifluoride | |||
| Other names
diethyl(trifluorosulfido)amine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| Abbreviations | DAST | ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.048.866 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H10F3NS | |||
| Molar mass | 161.19 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colourless oil | ||
| Density | 1.220 g/cm3 | ||
| Boiling point | 30 to 32 °C (86 to 90 °F; 303 to 305 K) at 3 mmHg | ||
| Reacts with water | |||
| Solubility | reacts with ethanol soluble in acetonitrile | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | corrosive, flammable, can be explosive | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Diethylaminosulfur trifluoride (DAST)[2] is the organosulfur compound with the formula Et2NSF3. This liquid is a fluorinating reagent used for the synthesis of organofluorine compounds. The compound is colourless; older samples assume an orange colour.
Use in organic synthesis
DAST converts alcohols to the corresponding alkyl fluorides as well as aldehydes and unhindered ketones to geminal difluorides. Carboxylic acids react no further than the acyl fluoride (sulfur tetrafluoride effects the transformation —CO2H → —CF3). DAST is used in preference to the more classical gaseous SF4, since as a liquid it is more easily handled. A slightly thermally more stable compound is morpho-DAST.[3] Acid-labile substrates are less likely to undergo rearrangement and elimination since DAST is less prone to contamination with acids. Reaction temperatures are milder as well - alcohols typically react at -78 °C and ketones around 0 °C.
Synthesis
DAST is prepared by the reaction of diethylaminotrimethylsilane and sulfur tetrafluoride:[4]
- Et2NSiMe3 + SF4 → Et2NSF3 + Me3SiF
The Organic Syntheses protocol calls for trichlorofluoromethane as a solvent, a compound that has been banned under the Montreal Protocol and is no longer available as a commodity chemical. Diethyl ether may be used instead with no decrease in yield.[5] Because of the dangers involved in the preparation of DAST (glass etching, possibility of exothermic events), it is often purchased from a commercial source. At one time Carbolabs[6] was one of the few suppliers of the chemical but a number of companies now sell DAST.
Safety and alternative reagents
Upon heating, DAST converts to SF4 and (NEt2)2SF2, a high-boiling and explosive compound. To minimize accidents, samples are maintained below 50 °C. Bis-(2-methoxyethyl)aminosulfur trifluoride (Deoxo-Fluor) and morpholinosulfur trifluoride (morpho-DAST or MOST) are related reagents which are more thermally stable.
Recent alternatives[7][8] have been manufactured by OmegaChem based on DAST but crystalline and with better handling properties. The XtalFluor range[9] offers XtalFluor-E (diethylamine) and XtalFluor-M (morpholine) difluorosulfonium salts (tetrafluoroborates).
See also
References
- ↑ A. H. Fauq, "N,N-Diethylaminosulfur Trifluoride" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (Ed: L. Paquette) 2004, J. Wiley & Sons, New York.
- ↑ Middleton, William J. (1975-03-01). "New fluorinating reagents. Dialkylaminosulfur fluorides". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 40 (5): 574–578. ISSN 0022-3263. doi:10.1021/jo00893a007.
- ↑ Markovskii, LN; Pashinnik, VE; KIRSANOVA, NA (1975). "SULFUR BIS (DIALKYLAMINO) DIFLUORIDES". ZHURNAL ORGANICHESKOI KHIMII. 11: 74–77 – via Web of Science.
- ↑ W. J. Middleton, E. M. Bingham "Diethylaminosulfur Trifluoride" Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 6, p.440; Vol. 57, p.50. Online version
- ↑ L. N. Markovskij; V. E. Pashinnik; A. V. Kirsanov (1973). "Application of Dialkylaminosulfur Trifluorides in the Synthesis of Fluoroorganic Compounds". Synthesis. 1973: 787–789. doi:10.1055/s-1973-22302.
- ↑ REACTION OF SULFOXIDES WITH DIETHYLAMINOSULFUR TRIFLUORIDE: FLUOROMETHYL PHENYL SULFONE, A REAGENT FOR THE SYNTHESIS OF FLUOROALKENES, Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 9, p.446 (1998); Vol. 72, p.209 (1995)
- ↑ l’Heureux, A.; Beaulieu, F.; Bennett, C.; Bill, D. R.; Clayton, S.; Laflamme, F. O.; Mirmehrabi, M.; Tadayon, S.; Tovell, D.; Couturier, M. (2010). "Aminodifluorosulfinium Salts: Selective Fluorination Reagents with Enhanced Thermal Stability and Ease of Handling†,‡". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 75 (10): 3401–3411. doi:10.1021/jo100504x.
- ↑ Beaulieu, F.; Beauregard, L. P.; Courchesne, G.; Couturier, M.; Laflamme, F. O.; l’Heureux, A. (2009). "Aminodifluorosulfinium Tetrafluoroborate Salts as Stable and Crystalline Deoxofluorinating Reagents". Organic Letters. 11 (21): 5050–5053. PMC 2770860
 . PMID 19799406. doi:10.1021/ol902039q.
. PMID 19799406. doi:10.1021/ol902039q. - ↑ http://www.omegachem.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=53