Cyromazine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
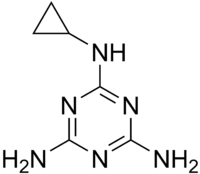
| IUPAC name
N-Cyclopropyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine | |
| Other names
Citation Larvadex Trigard Vetrazin | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.060.215 |
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10N6 | |
| Molar mass | 166.19 g/mol |
| Appearance | Crystalline |
| Melting point | 219 to 222 °C (426 to 432 °F; 492 to 495 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Cyromazine is a triazine insect growth regulator used as an insecticide and an acaricide. It is a cyclopropyl derivative of melamine. Cyromazine works by affecting the nervous system of the immature larval stages of certain insects.[2]
In veterinary medicine, cyromazine is used as an ectoparasiticide.
Regulation
The Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) provides a test method for analyzing cyromazine and melamine in animal tissues in its Chemistry Laboratory Guidebook which "contains test methods used by FSIS Laboratories to support the Agency's inspection program, ensuring that meat, poultry, and egg products are safe, wholesome and accurately labeled."[3][4] In 1999, in a proposed rule published in the Federal Register regarding cyromazine residue, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) proposed "remov[ing] melamine, a metabolite of cyromazine from the tolerance expression since it is no longer considered a residue of concern."[5]
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 12th Edition, 2845.
- ↑ Pesticide Fact Sheet from Pesticide Management Education Program, Cornell University
- ↑ "CYROMAZINE AND MELAMINE" (PDF). USDA FSIS. July 1991. Retrieved 2007-04-27.
- ↑ "Chemistry Laboratory Guidebook". USDA FSIS. Retrieved 2007-04-27.
- ↑ Environmental Protection Agency. Cyromazine; Pesticide Tolerance
External links
- Cyromazine at PAN Pesticides Database