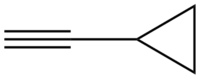
Cyclopropylacetylene
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Cyclopropylacetylene, ethynylcyclopropane | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.102.389 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H6 | |
| Molar mass | 66.10 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless to light yellow liquid |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 51–53 °C (124–127 °F; 324–326 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| H225, H315, H319, H412 | |
| P210, P273, P280, P305+351+338 | |
| Flash point | −17 °C (1 °F; 256 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Cyclopropylacetylene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C
5H
6.[1] Under normal conditions, the substance is a clear, flammable liquid. Cyclopropylacetylene is used as an important reagent to synthesize pharmaceuticals and other organic compounds.
Synthesis
Several methods have been published on the synthesis of cyclopropylacetylene. The earliest one start with the chlorination of cyclopropylmethylketone with phosphorus pentachloride.[2] Thereafter, the reaction product, 1-cyclopropyl-1,1-dichloroethane, is converted into cyclopropylacetylene via double dehydrochlorination. This occurs in presence of a strong base, such as potassium tert-butoxide, in dimethyl sulfoxide:
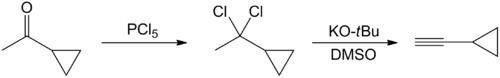
However, the yield of this method is not substantial (20-25%).[3] A one-pot synthesis of cyclopropylacetylene has been reported in which 5-chloro-1-pentyne reacts with n-butyl lithium or n-hexyl lithium. Cyclohexane is used as a solvent. The reaction is a metalization followed by a cyclization. The reaction product is then cooled, and an aqueous solution of ammonium chloride is added slowly. There is a two-phase mixture: a heavy water phase and a lighter organic phase containing cyclopropylacetylene.[3]
Applications
Cyclopropylacetylene is used as reagent in organic reactions. It is, for example, a building block of the HIV inhibitor efavirenz. It can also be used in the azide-alkyne Huisgen cycloaddition.
References
- ↑ "CYCLOPROPYL ACETYLENE". chemicalland21.com. Retrieved 31 May 2017.
- ↑ Hudson, C.E.; Bauld, N.L. (1972). "Quantitative analysis of cyclopropyl β hyperfine splittings". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 94 (4): 1158.
- 1 2 Corley, Edward G.; Thompson, Andrew S.; Huntington, Martha. "CYCLOPROPYLACETYLENE". orgsyn.org. p. 231. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.077.0231. Retrieved 31 May 2017.