Counties of Croatia
| Counties of Croatia Hrvatske županije (Croatian) | |
|---|---|
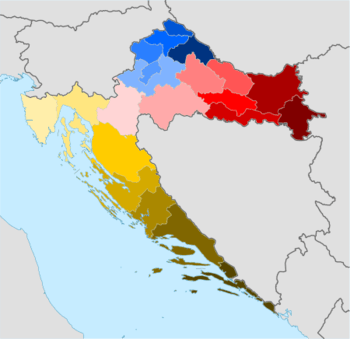
Counties of Croatia: Bjelovar-Bilogora Brod-Posavina Dubrovnik-Neretva Istria Karlovac Koprivnica-Križevci Krapina-Zagorje Lika-Senj Međimurje Osijek-Baranja Požega-Slavonia Primorje-Gorski Kotar Šibenik-Knin Sisak-Moslavina Split-Dalmatia Varaždin Virovitica-Podravina Vukovar-Srijem Zadar City of Zagreb Zagreb County
| |
| Category | Unitary state |
| Location | Republic of Croatia |
| Number | 20 Counties |
| Populations | 50,927 (Lika-Senj) – 790,017 (Zagreb) |
| Areas | 640 km2 (247 sq mi) (Zagreb) – 5,350 km2 (2,067 sq mi) (Lika-Senj) |
| Government | County government, National government |
| Subdivisions | Municipality and City |
The counties of Croatia (Croatian: županije) are the primary administrative subdivisions of the Republic of Croatia.[1] Since they were re-established in 1992, Croatia has been divided into 20 counties and the capital city of Zagreb, which has the authority and legal status of both a county and a city (separate from the surrounding Zagreb County).[2][3] As of 2015, the counties are subdivided into 128 cities and 428 (mostly rural) municipalities.[4][5]
Government
County assembly (Croatian: županijska skupština) is a representative and deliberative body in each county. Assembly members are elected for a four-year term by popular vote (proportional system with closed lists and d'Hondt method) in local elections.[6]
The executive branch of each county's government is headed by a county prefect (county president) (Croatian: župan), except that a mayor heads the city of Zagreb's executive branch. Croatia's county prefects (with two deputy prefects), mayor of Zagreb (with two deputy mayors)[7] are elected for a four-year term by a majority of votes cast within applicable local government units, with a runoff election if no candidate achieves a majority in the first round of voting (majoritarian vote, two-round system)[6]. County prefects (with deputy prefects and mayor of Zagreb with his/her deputies) can be recalled by a referendum. County administrative bodies are administrative departments and services which are established for the performance of works in the self-governing domain of the county, as well as for the performance of works of state administration transferred to the county. Administrative departments and services are managed by heads (principals) nominated by the county prefect on the basis of a public competition.[8]
In each county exists a State Administration Office (Croatian: Ured državne uprave) which performs the tasks of the central government. Head of State Administration Office is appointed by the Croatian Government (in the City of Zagreb the mayor is responsible for the state administration).
Funding and tasks
The counties are funded by the central government, as well as from county-owned businesses, county taxes and county fees. County taxes include a five percent inheritance and gift tax, a motor vehicle tax, a vessel tax and an arcade game machine tax.[9][10]
The counties are tasked with performing general public administration services, primary and secondary education, government funded healthcare, social welfare, administration pertaining to agriculture, forestry, hunting, fisheries, mining, industry and construction, and other services to the economy at the county level, as well as road transport infrastructure management and issuing of building and location permits and other document in relation to construction in the county area excluding the area of the big city and the county seat city; the central government and local (city and municipal) governments may also perform each of those tasks at their respective levels according to the law.[8]
The Croatian County Association was set up in 2003 as a framework for inter-county cooperation.[11]
Nomenclature
The Croatian (singular) term županija was originally applied to territory controlled by a župan (official title).[12] Since the 12th century, the counties have also been referred to by the Latin term comitatus.[12]
History
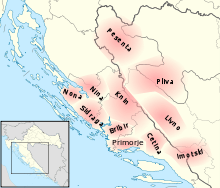
Croatia was first subdivided into counties in the Middle Ages.[13] Counties were first introduced in Croatia during the House of Trpimirović's rule. The exact number and borders of these early counties are difficult to determine accurately; they were considered to encompass areas subordinated to a single centre of local authority, but the possessions of significant nobles had a legal status separate from local authority.
The following eleven are usually listed as the oldest counties of Croatia, dating back to the 10th century:[14]
- Livno (encompassing the Livanjsko polje)
- Cetina (centered on the Cetina river, with its seat in Stolac)
- Imotski (south of Livno County and Biokovo)
- Pliva (around the Pliva and Vrbas rivers)
- Pset or Pesenta (between the Una and Sana rivers)
- Primorje or Klis (along the Adriatic's coast between Šibenik and Omiš, with its seat in the Klis Fortress)
- Bribir (to the west of Primorje County)
- Nona (around Nin and Zadar)
- Knin (with its seat in the Knin Fortress)
- Sidraga (in the area between Bribir County and Zadar)
- Nina or Luka (between Knin, Nona, Sidraga and Bribir counties)
In the same period, the counties in Pannonian Croatia (north of Gvozd Mountain) are poorly documented. It is generally thought that the Pannonian counties were directly subject to the Croatian monarchy, unlike the southern counties controlled by nobles.[12]
The county number, extent and authority have varied significantly, reflecting: changes in the monarchial and noble relative influences; Ottoman conquest and Croatian recapture of various territories; and societal and political changes through several centuries.[12][15] In the 13th and 14th century, the Croatian nobility grew stronger and the counties defined by the king were reduced to a legislative framework, while military and financial power was concentrated in the feudal lords. Other forms of administration that overlapped with county administration in this period included the Roman Catholic Church and the free royal cities, and separately the cities of Dalmatia. After Croatia became a crown land of the Habsburg Monarchy in 1527, the importance of counties faded even further, but was gradually restored after 1760.[12]
The divisions have changed over time, reflecting: territorial losses to Ottoman conquest and subsequent Croatian recapture of some territory; changes in the political status of Dalmatia, Dubrovnik and Istria; and political circumstances, including the personal union and settlement between Croatia and Hungary.[12][15]
In the 19th century, the Revolutions of 1848 in the Habsburg areas brought upon numerous political changes and introduced a civic government of the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia as part of Austria-Hungary, which in turn proceeded to absorb the Croatian and Slavonian Military Frontiers in 1881. During the second half of the 19th century Croatian counties went through various reorganizations (1848-1850, 1850-1854, 1854-1861, 1861-1870, 1870-1874, 1874-1886, 1886-1914) that also reflected the position of the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia within the Austrian Empire (after 1867 the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy); the last major reorganisation of the counties was in 1886, when eight counties were established within the kingdom. This layout largely remained in effect until the Croatian counties were abolished in 1922,[12][15] while some minor adjustments of county boundaries happened in 1913.[16] The counties were set up as self-governmental units in contrast to earlier county incarnations since the Middle Ages. Each had an assembly (Croatian županijska skupština) with the wealthiest taxpayers comprising half the assembly members and elected members comprising the remaining half. Supreme prefect (Croatian veliki župan) was appointed by the king and county officials by the ban. Managing board of each county had 6 members elected by the county assembly, while the remaining members were county officials ex officio (supreme prefect, viceprefect, county health supervisor etc). Counties were divided into districts (Croatian kotari as government units similar to Austrian Bezirke), while municipalities (Croatian općine) and cities (Croatian gradovi) were units of local self-government.[12]
The traditional division of Croatia into counties was abolished in 1922, when the oblasts of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes were introduced; these were later replaced by the banovinas of Yugoslavia.[17] Socialist Republic of Croatia, as a constituent part of post-World War II Yugoslavia had approximately 100 municipalities as main governmental units and local government entities. The counties were reintroduced in 1992, but with significant territorial alterations from the pre-1922 subdivisions; for instance, before 1922 Transleithanian Croatia was divided into eight counties, but the new legislation established fourteen counties in the same territory. Međimurje County was established in the eponymous region acquired through the 1920 Treaty of Trianon.[18][19] The county borders have sometimes changed since their 1992 restoration (for reasons such as historical ties and requests by cities); the latest revision took place in 2006.[4]
Today's counties correspond to tier three of the European Union (EU) Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS) division of Croatia. The NUTS Local Administrative Unit (LAU) divisions are two-tiered; the LAU 1 divisions for Croatia also match the counties (in effect making these the same as the NUTS 3 units).[20]
Lists of counties
Current
Former

| County | Seat | Area (1886–1912)[16] | Population (1910)[23] | Arms | Geographic coordinates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bjelovar-Križevci | Bjelovar | 5,048 km2 (1,949 sq mi) | 331,385 |  | 45°55′14″N 16°45′54″E / 45.92056°N 16.76500°E |
| Lika-Krbava | Gospić | 6,217 km2 (2,400 sq mi) | 203,973 | 44°42′28″N 15°21′12″E / 44.70778°N 15.35333°E | |
| Modruš-Rijeka | Ogulin | 4,874 km2 (1,882 sq mi) | 231,354 |  | 45°19′30″N 14°58′28″E / 45.32500°N 14.97444°E |
| Požega | Požega | 4,938 km2 (1,907 sq mi) | 263,690 |  | 45°22′45″N 17°31′4″E / 45.37917°N 17.51778°E |
| Syrmia | Vukovar | 6,848 km2 (2,644 sq mi) | 410,007 | 45°4′53″N 19°15′33″E / 45.08139°N 19.25917°E | |
| Varaždin | Varaždin | 2,521 km2 (973 sq mi) | 305,558 |  | 46°15′7″N 16°11′38″E / 46.25194°N 16.19389°E |
| Virovitica | Osijek | 4,852 km2 (1,873 sq mi) | 269,199 |  | 45°38′27″N 17°51′30″E / 45.64083°N 17.85833°E |
| Zagreb | Zagreb | 7,215 km2 (2,786 sq mi) | 587,378 | .svg.png) | 45°38′27″N 16°11′57″E / 45.64083°N 16.19917°E |
See also
- Administrative divisions of Croatia
- Flags of the counties of Croatia
- List of current prefects of Croatia
- History of Croatia
- Former counties of Croatia (in Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia)
- Counties of the Independent State of Croatia
- ISO 3166-2:HR
Notes
References
- ↑ The Constitution of the Republic of Croatia (consolidated text) - Croatian Parliament.Retrieved 5 October 2016.
- ↑ "Gospodarski profil Grada Zagreba i Zagrebačke županije" [Economic profile of the City of Zagreb and the Zagreb County] (in Croatian). Croatian Chamber of Economy. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ↑ "Zakon o područjima županija, gradova i općina u Republici Hrvatskoj" [Territories of Counties, Cities and Municipalities of the Republic of Croatia Act]. Narodne novine (in Croatian). 30 January 1997. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- 1 2 3 "Zakon o područjima županija, gradova i općina u Republici Hrvatskoj" [Territories of Counties, Cities and Municipalities of the Republic of Croatia Act]. Narodne novine (in Croatian). 28 July 2006. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ↑ "Popovača dobila status grada". Poslovni dnevnik (in Croatian). 12 April 2013. Retrieved 27 January 2014.
- 1 2 "Zakon o lokalnim izborima" [Local Elections Act]. Narodne novine (in Croatian) (144/2012). 21 December 2012. Retrieved 5 October 2016.
- ↑ Also city mayors and municipality presidents with deputies.
- 1 2 "Zakon o lokalnoj i područnoj (regionalnoj) samoupravi (pročišćeni tekst)" [Local and Regional Self-Government Act (consolidated text)]. Narodne novine (in Croatian) (19/2013). 18 February 2013. Retrieved 5 October 2016.
- ↑ "The Croatian tax system". Croatian Tax Administration. Retrieved 15 April 2012.
- ↑ Anto Bajo; Mihaela Bronić (December 2004). "Fiskalna decentralizacija u Hrvatskoj: problemi fiskalnog izravnanja" [Fiscal Decentralisation in Croatia: Problems of Fiscal Equalisation]. Financijska teorija i praksa (in Croatian). Institute of Public Finance. 28 (4): 445–467. Retrieved 21 June 2012.
- ↑ "Croatian County Association". Retrieved 10 April 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Josip Vrbošić (September 1992). "Povijesni pregled razvitka županijske uprave i samouprave u Hrvatskoj" [A historical review of the development of county administration and self-government in Croatia]. Društvena istraživanja (in Croatian). Ivo Pilar Institute of Social Sciences. 1 (1): 55–68. ISSN 1330-0288. Retrieved 9 April 2012.
- ↑ Oleg Mandić (1952). "O nekim pitanjima društvenog uređenja Hrvatske u srednjem vijeku" [On some issues regarding Croatia's social system in the Middle Ages] (PDF). Historijski zbornik (in Croatian). Školska knjiga. 5 (1–2): 131–138. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ↑ "Iz povijesti Splitsko-dalmatinske županije IV." [Outline of history of the Split-Dalmatia County (4)] (in Croatian). Split-Dalmatia County. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- 1 2 3 Ivo Goldstein (1996). Hrvatske županije kroz stoljeća [Croatian counties through the centuries] (in Croatian). Školska knjiga. p. 86. ISBN 9789530613676. Retrieved 10 April 2012.
- 1 2 Branko Dubravica (January 2002). "Političko-teritorijalna podjela i opseg civilne Hrvatske u godinama sjedinjenja s vojnom Hrvatskom 1871–1886" [Political and territorial division and scope of civilian Croatia in the period of unification with the Croatian military frontier 1871–1886]. Politička misao (in Croatian). University of Zagreb, Faculty of Political Sciences. 38 (3): 159–172. ISSN 0032-3241. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
- ↑ Richard C. Frucht (2005). Eastern Europe: An Introduction to the People, Lands, and Culture. ABC-CLIO. p. 429. ISBN 9781576078006. Retrieved 18 October 2011.
- ↑ Mark Biondich (2000). Stjepan Radić, the Croat Peasant Party, and the politics of mass mobilization, 1904–1928. University of Toronto Press. p. 11. ISBN 9780802082947. Retrieved 18 October 2011.
- ↑ "Zakon o područjima županija, gradova i općina u Republici Hrvatskoj" [Territories of Counties, Cities and Municipalities of the Republic of Croatia Act]. Narodne novine (in Croatian). 30 December 1992. Archived from the original on 28 August 2013. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ↑ "Nacionalno izviješće Hrvatska" [Croatian National Report] (PDF) (in Croatian). Council of Europe. January 2010. Retrieved 25 February 2012.
- 1 2 "Counties, surface area, population, towns, municipalities and settlements, 2011 census". Croatian Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
- ↑ "Gross domestic product for Republic of Croatia, statistical regions at level 2 and counties, 2011". Croatian Bureau of Statistics. 14 February 2014. Retrieved 14 July 2015.
- ↑ Mira Kolar-Dimitrijević (October 1991). "Utjecaj Prvog svjetskog rata na kretanje stanovništva i stočarstva na području Hrvatske i Slavonije" [Impact of World War I on population and animal husbandry trends in the area of Croatia and Slavonia]. Radovi Zavoda za hrvatsku povijest (in Croatian). University of Zagreb, Croatian History Institute. 24 (1): 41–56. ISSN 0353-295X. Retrieved 10 April 2012.
Sources
- Croatian Parliament (2013-02-18). "Zakon o lokalnoj i područnoj (regionalnoj) samoupravi (pročišćeni tekst)". Narodne novine (in Croatian) (19/2013). Retrieved 2016-04-10.
- Croatian Parliament (2012-12-21). "Zakon o lokalnim izborima". Narodne novine (in Croatian) (144/2012). Retrieved 2016-04-10.
- "The Constitution of the Republic of Croatia (consolidated text)". Croatian Parliament. Retrieved 2016-10-04.
