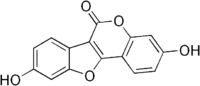
Coumestan
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[1]Benzoxolo[3,2-c]chromen-6-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 236.22 g/mol |
| Melting point | 187 to 188 °C (369 to 370 °F; 460 to 461 K)[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Coumestan is a heterocyclic organic compound. Coumestan forms the central core of a variety of natural compounds known collectively as coumestans. Coumestans are oxidation products of pterocarpan[2] that are similar to coumarin. Coumestans, including coumestrol, a phytoestrogen, are found in a variety of plants. Food sources high in coumestans include split peas, pinto beans, lima beans, and especially alfalfa and clover sprouts.[3]
Coumestrol has about the same binding affinity for the ER-β estrogen receptor as 17β-estradiol, but much less affinity than 17α-estradiol, although the estrogenic potency of coumestrol at both receptors is much less than that of 17β-estradiol.[4]
Because of the estrogenic activity of some coumestans, a variety of syntheses have been developed that allow the preparation of coumestans so that their pharmacological effects can be explored.[5][6]
Coumestans
References
- ↑ Singh, Rishi Pal; Singh, Daljeet (1985). "An elegant synthesis of 6H-benzofuro[3,2-c][1]benzopyran-6-ones". Heterocycles. 23 (4): 903. doi:10.3987/R-1985-04-0903.
- ↑ V. A. Tuskaev (April 2013). "Synthesis and biological activity of coumestan derivatives (Review)". Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal. 47 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1007/s11094-013-0886-5.
- ↑ Barbour S. Warren; Carol Devine (July 2001). "Phytoestrogens and Breast Cancer". Program on Breast Cancer and Environmental Risk Factors. Cornell University. Retrieved 2011-03-19.
- ↑ Kuiper GG, Lemmen JG, Carlsson B, Corton JC, Safe SH, van der Saag PT, van der Burg B, Gustafsson JA; Lemmen; Carlsson; Corton; Safe; Van Der Saag; Van Der Burg; Gustafsson (1998). "Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor beta". Endocrinology. 139 (10): 4252–4263. PMID 9751507. doi:10.1210/endo.139.10.6216.
- ↑ Yao, Tuanli; Yue, Dawei; Larock, Richard C (2005). "An Efficient Synthesis of Coumestrol and Coumestans by Iodocyclization and Pd-Catalyzed Intramolecular Lactonization". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 70 (24): 9985–9989. PMID 16292831. doi:10.1021/jo0517038.
- ↑ Takeda, Norihiko; Miyata, Okiko; Naito, Takeaki (2007). "Efficient synthesis of benzofurans utilizing [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement triggered by N-trifluoroacetylation of oxime ethers: short synthesis of natural 2-arylbenzofurans". European Journal of Organic Chemistry. 2007 (9): 1491–1509. doi:10.1002/ejoc.200601001.