Constanze Mozart
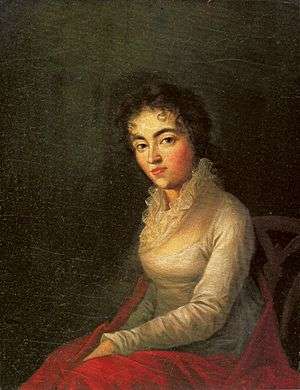
Maria Constanze Cäcilia Josepha Johanna Aloysia Mozart (née Weber) (5 January 1762 – 6 March 1842) was the wife of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart.
Early years
Constanze Weber was born in Zell im Wiesental, a town near Lörrach in Baden-Württemberg, in the south-west of Germany, then Further Austria. Her mother was Cäcilia Weber, née Stamm. Her father, Fridolin Weber, worked as a "double bass player, prompter, and music copyist."[1] Fridolin's half-brother was the father of composer Carl Maria von Weber. Constanze had two older sisters, Josepha and Aloysia, and one younger one, Sophie. All four were trained as singers and Josepha and Aloysia both went on to distinguished musical careers, later on performing in the premieres of a number of Mozart's works.
During most of Constanze's upbringing, the family lived in her mother's hometown of Mannheim, an important cultural, intellectual, and musical center of the time. The 21-year-old Mozart visited Mannheim in 1777 on a job-hunting tour with his mother and developed a close relationship with the Weber family. He fell in love, not with the 15-year-old Constanze, but with Aloysia.[2] While Mozart was in Paris, Aloysia obtained a position as a singer in Munich, and the family accompanied her there. She rejected Mozart when he passed through Munich on his way back to Salzburg.[2]
The family moved to Vienna in 1779, again following Aloysia as she pursued her career. One month after their arrival, Fridolin died.[2] By the time Mozart moved to Vienna in 1781, Aloysia had married Joseph Lange, who agreed to help Cäcilia Weber with an annual stipend, and she also took in boarders to make ends meet. The house where the Webers lived (on the second floor) was at Am Peter 11, and bore a name (as houses often did at the time): Zum Auge Gottes ("God's Eye").[3]
Marriage to Mozart
On first arriving in Vienna on 16 March 1781,[4] Mozart stayed at the house of the Teutonic Order with the staff of his patron, Archbishop Colloredo. In May, he "was obliged to leave," and chose to board in the Weber household, originally intending "to stay there only a week."[5]
After a while, it became apparent to Cäcilia Weber that Mozart was courting Constanze, now 19, and in the interest of propriety, she requested that he leave.[6] Mozart moved out on 5 September to a third-floor room in the Graben.
The courtship continued, not entirely smoothly. Surviving correspondence indicates that Mozart and Constanze briefly broke up in April 1782, over an episode involving jealousy (Constanze had permitted another young man to measure her calves in a parlor game).[7] Mozart also faced a very difficult task getting permission for the marriage from his father, Leopold.[8]
The marriage finally took place in an atmosphere of crisis. Daniel Heartz suggests that eventually Constanze moved in with Mozart, which would have placed her in disgrace by the mores of the time.[9] Mozart wrote to Leopold on 31 July 1782, "All the good and well-intentioned advice you have sent fails to address the case of a man who has already gone so far with a maiden. Further postponement is out of the question."[10] Heartz relates, "Constanze's sister Sophie had tearfully declared that her mother would send the police after Constanze if she did not return home [presumably from Mozart's apartment]."[9] On 4 August, Mozart wrote to Baroness von Waldstätten, asking: "Can the police here enter anyone's house in this way? Perhaps it is only a ruse of Madame Weber to get her daughter back. If not, I know no better remedy than to marry Constanze tomorrow morning or if possible today."[10]
The marriage did indeed take place that day, 4 August 1782. In the marriage contract, Constanze "assigns to her bridegroom five hundred gulden which [...] the latter has promised to augment with one thousand gulden", with the total "to pass to the survivor". Further, all joint acquisitions during the marriage were to remain the common property of both.[11] A day after the marriage took place, the consent of Wolfgang's father arrived in the mail.
The couple had six children, of whom only two survived infancy.
- Raimund Leopold (17 June – 19 August 1783)[12]
- Karl Thomas Mozart (21 September 1784 – 31 October 1858)
- Johann Thomas Leopold (18 October – 15 November 1786)[13]
- Theresia Constanzia Adelheid Friedericke Maria Anna (27 December 1787 – 29 June 1788)[14][15]
- Anna Maria (b/d 16 November 1789)[16]
- Franz Xaver Wolfgang Mozart (26 July 1791 – 29 July 1844)
After Mozart's death

Mozart died in 1791, leaving debts and placing Constanze in a difficult position. At this point Constanze's business skills came into fruition: she obtained a pension from the emperor, organized profitable memorial concerts, and embarked on a campaign to publish the works of her husband.[17] These efforts gradually made Constanze financially secure and ultimately, wealthy.[18] She sent Karl and Franz to Prague to be educated by Franz Xaver Niemetschek, with whom she collaborated on the first full-length biography of Mozart.
Toward the end of 1797, she met Georg Nikolaus von Nissen, a Danish diplomat and writer who, initially, was her tenant.[19] The two began living together in September 1798,[20] and were married in Pressburg (today Bratislava) in 1809. From 1810 to 1820, they lived in Copenhagen, and subsequently travelled throughout Europe, especially Germany and Italy. They settled in Salzburg in 1824. Both worked on a biography of Mozart; Constanze eventually published it in 1828, two years after her second husband's death.
During Constanze's last years in Salzburg, she had the company of her two surviving sisters, Aloysia and Sophie, also widows, who moved to Salzburg and lived out their lives there.[21]
Influences on Mozart's music

Constanze was a trained musician and played a role in her husband's career. Two instances can be given.
The extraordinary writing for soprano solo in the Great Mass in C minor (for example, in the "Christe eleison" section of the Kyrie movement, or the aria "Et incarnatus est") was intended for Constanze, who sang in the 1783 premiere of this work in Salzburg. Maynard Solomon in his Mozart biography speculatively describes the work as a love offering.
During the period of the couple's courtship, Mozart began making visits to Baron Gottfried van Swieten, who let him examine his extensive collection of manuscripts of work by Bach and Handel. Mozart was excited by this material, and he prepared a number of compositions in Baroque style. An important impetus was Constanze, who apparently fell in love at this time with Baroque counterpoint. This is known from a letter Mozart wrote to his sister Nannerl on 20 April 1782. The letter was accompanied by a manuscript copy of the composer's Fantasy and Fugue, K. 394.
I composed the fugue first and wrote it down while I was thinking out the prelude. I only hope that you will be able to read it, for it is written so very small; and I hope further that you will like it. Another time I shall send you something better for the clavier. My dear Constanze is really the cause of this fugue's coming into the world. Baron van Swieten, to whom I go every Sunday, gave me all the works of Händel and Sebastian Bach to take home with me (after I had played them to him). When Constanze heard the fugues, she absolutely fell in love with them. Now she will listen to nothing but fugues, and particularly (in this kind of composition) the works of Händel and Bach. Well, as she has often heard me play fugues out of my head, she asked me if I had ever written any down, and when I said I had not, she scolded me roundly for not recording some of my compositions in this most artistically beautiful of all musical forms and never ceased to entreat me until I wrote down a fugue for her.[22]
The experience of writing in Baroque style had an important influence on the later work of Mozart, in the C Minor Mass as well as in later secular works, such as the last movement of the 41st Symphony or the opera The Magic Flute.
Treatment by biographers

According to the Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians, Constanze has been treated harshly and unfairly by a number of her biographers: "Early 20th-century scholarship severely criticized her as unintelligent, unmusical and even unfaithful, and as a neglectful and unworthy wife to Mozart. Such assessments (still current) were based on no good evidence, were tainted with anti-feminism and were probably wrong on all counts."[1] Complaints about unfairness to Constanze also appear in several recent Mozart biographies: Braunbehrens (1990), Solomon (1995), and Halliwell (1998).[24]
Alleged photograph
Since first being brought to scholarly attention in 1958, numerous media sources and publications have asserted over the years that a single surviving print reportedly showing the only known image of Mozart's widow is that of Constanze (Mozart) Nissen herself at age 78. The photograph, or daguerreotype, was supposedly taken in Altotting, Bavaria in October 1840 outside the home of composer Max Keller. However, several Mozart scholars have refuted the claim as a hoax for various reasons. First, the photograph could not have been taken outdoors since claims that the lenses to produce such images were not invented by Joseph Petzval until after Constanze had died in 1842.[25] Second, it is documented that Constanze was crippled from debilitating arthritis in her final years of life. As Agnes Selby, author of Constanze, Mozart's Beloved, offered her opinion regarding the photograph on the Classical Music Guide Forums website on July 8, 2006: "There is absolutely no way she could have traveled to visit Maximillian Keller during the period when the photograph was taken. Contrary to the statements made in the newspaper, Constanze had no contact with Keller since 1826."[25][26]
Legacy
The Royal Conservatory of Brussels conserves several autograph documents from Constance Mozart, including letters to her son Franz Xaver Wolfgang Mozart, as well as a small illustrated Album de Souvenirs, dated 1789 but covering the 1801–1823 period in which she collects memories, impressions and poems (ref. Jean-Lucien Hollenfeltz fund, B-Bc-FH-163).
See also
- Biographies of Mozart—for Constanze's possible role in launching a variety of biographical myths about her first husband
References
Notes
- 1 2 Grove, article "Mozart," section 4
- 1 2 3 Solomon 1995
- ↑ Solomon 1995, 253
- ↑ Deutsch 1965, 193
- ↑ Deutsch 1965, 196
- ↑ Solomon 1995, 255
- ↑ Solomon 1995, 259
- ↑ Solomon 1995, 258
- 1 2 Heartz (2009, 47)
- 1 2 Quoted from Heartz (2009, 47)
- ↑ Deutsch 1965, p. 204
- ↑ Mozart Day by Day – 1783, Mozarteum
- ↑ Mozart Day by Day – 1786, Mozarteum
- ↑ Mozart Day by Day – 1787, Mozarteum
- ↑ Mozart Day by Day – 1788, Mozarteum
- ↑ Mozart Day by Day – 1789, Mozarteum
- ↑ Griffin, Lynne; Kelly McCann (1992). The Book of Women. Holbrook, MA: Bob Adams, Inc. p. 5. ISBN 1-55850-106-1.
- ↑ Wolff (2012:8), citing Bauer, writes, "Constanze, who survived the composer by more than a half-century and upon her death in 1842 still left her two sons a major fortune of some 30,000 florins in cash, bonds, and savings accounts – all based on earnings from Mozart's music,"
- ↑ Grove Dictionary
- ↑ Deutsch 1965, 485–486
- ↑ Solomon 1995, 502
- ↑ Text of letter taken from http://www.schillerinstitut.dk/bach.html. Not all scholars take Mozart at his word; he had a motivation to exaggerate Constanze's refinement and taste, since Leopold was opposed strongly to his son marrying her (Heartz 2009, 63; Halliwell 1998).
- ↑ Mueller von Asow, E. H. "Zu einer unbekannten Photographie Constanze Mozarts.", Österreichische Musikzeitschrift 13 (1958): 93–95.
- ↑ The earlier critics accused of unfairness variously include Alfred Einstein, Wolfgang Hildesheimer, and Arthur Schurig.
- 1 2 Chris Pasles (July 16, 2006). "Photo of Mozart's wife a hoax". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved September 8, 2016.
- ↑ Rosie Pentreathr (27 January 2016). "10 Mozart myths". Retrieved September 8, 2016.
Sources
- Bauer, Günther (2009) Mozart: Geld, Ruhm, und Ehre. Bad Honnef.
- Braunbehrens, Volkmar (1986) Mozart in Vienna: 1781–1791, Timothy Bell Trans, HarperPerennial. ISBN 0-06-097405-2
- Davenport, Marcia (1932) Mozart, The Chautauqua Press.
- Carr, Francis (1983) Mozart & Constanze. London: Murray. (1983) ISBN 0-7195-4091-7
- Deutsch, Otto Erich (1965) Mozart: A Documentary Biography. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Gärtner, Heinz (1991) Constanze Mozart: after the Requiem. Portland: Amadeus Press (1991) ISBN 0-931340-39-X
- Glover, Jane (2005) Mozart's Women.
- Halliwell, Ruth (1998) The Mozart Family: Four Lives in a Social Context. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Heartz, Daniel (2009) Mozart, Haydn and early Beethoven, 1781–1802. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 0-393-06634-7.
- Selby, Agnes (November 1999). Constanze, Mozart's Beloved. Wahroonga: Turton & Armstrong Pty. Ltd. ISBN 0-908031-71-8.
- Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians. On-line edition, copyright 2007 by Oxford University Press.
- Solomon, Maynard (1995) Mozart: A Life, Harper Collins.
- Wolff, Christoph (2012) Mozart at the Gateway to His Fortune. New York: Norton.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Constanze Mozart. |
