Colonial French
| Colonial French | |
|---|---|
| Region | Louisiana |
| Extinct | merged with Cajun |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | None |
|
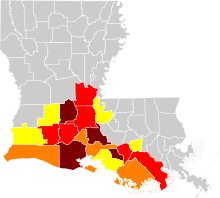
French spread in Louisiana. Parishes marked in yellow are those where 4–10% of the population speak French or Louisiana French at home, orange 10–15%, red 15–20%, brown 20–30%. | |
Colonial French (commonly known as Colonial Louisiana French) is a variety of Louisiana French. It is associated with the Cajun French dialect and Louisiana Creole French, a related creole language. Formerly spoken widely in what is now the U.S. state of Louisiana, it has since merged into Cajun French.[1][2]
Colonial French is conventionally described as the form of French spoken in Lower French Louisiana prior to the late arrival of Acadians after the Great Upheaval of the mid-18th century, which resulted in the birth of the Cajun dialect. The prestige dialect still used by Creoles and Cajuns is often identified as deriving from Colonial French, but some linguists differentiate between the two, referring to the latter as Plantation Society French.[2][3]
Historically spoken by Louisiana Creole population in lower French Louisiana, Colonial French is generally considered to have been adopted by whites, blacks and Cajuns. It is known among the educated that it has been relabeled "Cajun French" among Cajuns and CODOFIL.[2][4] Most linguists consider it to have largely been relabeled Cajun French by Cajuns and whites, which is distinguishable from Louisiana Creole French.[1]
Following the Great Upheaval in the mid-18th century, when many Acadians relocated to French Louisiana, Colonial French was beginning to be assimilated by the Acadians or "Cajuns". Some scholars suggested that it survived as the prestige dialect spoken by Creoles, both white and of color, into the 21st century. There are populations of Creoles and Cajuns among other ethnic groups in the parishes of St. Martin, Avoyelles, Iberia, Pointe-Coupée, St. Charles, St. Landry, St. Mary, St. Tammany, Plaquemines, and other parishes south of Orleans, that still speak this prestige dialect.
However, linguists have pointed out this prestige dialect is distinct from the pre-Upheaval Colonial French, and is largely derived from the standard French of the mid-19th century, Spanish, African languages, and Native Americans languages. As such, in 1998 linguist Michael Picone of the University of Alabama introduced the term "Plantation Society French" for the prestige dialect.[2][3] There is a history of diglossia between Plantation Society French and Louisiana Creole French.[3] Plantation Society French, at any rate, is quite close to the Standard French of the time of its origin, with some possible differences in pronunciation and vocabulary use.[2]
Unremarkably, it is still spoken by the Louisiana Indians, such as the Houmas, Avoyelles, Choctaw and other tribal remnants, all present in pre-Acadian Louisiana and still present in contemporary Louisiana.[5]
History
.svg.png)
The French settled in Louisiana (then la Louisiane or New France), establishing the Creole culture and language there. French immigration was at its peak during the 17th and 18th centuries and then small waves in the 19th century until the start of the American Civil War, bringing large numbers of francophones speaking something more similar to today's Metropolitan French into Louisiana. Over time, through contact between groups, such as the white Creoles, Creoles de couleur, native tribes, Africans, the Spanish etc. there was a high rate of intermarriage, the dialects would mix, to produce the French we today call Louisiana French.
Over time Louisiana French became the firmly established language of many south Louisiana parishes, mainly the Creole Parishes (among “Cajuns” it is known as Acadiana).
Louisiana French, although originally spoken by the French & Métis Creoles of Southern Louisiana, is also spoken by Acadian-Creoles/“Cajuns” but, also by other ethnic groups that lived in the Créole settlement of Lower Louisiana. Creoles, Amerindian ethnic groups such as the Houma, Chitimacha, Pointe-au-Chien,[6] Bayougoula, Tunica-Biloxi, Atakapa, Opelousa, Okelousa, and Avoyel, already spoke this variety of French prior to the late arrival of the Acadian people in Louisiana, as noted by Captain Jean-Bernard Bossu who traveled with and witnessed Bienville himself speaking this "common language" in his work Travels Through That Part of American Formerly Called Louisiana 1768; pp. 254–255. This unusual blend of Colonial French was also noticed by Pierre-Clement de Laussat during a lunch visit with the Creole French Canterelle family. Upon arrival of their Houma Indian relatives these French Creoles began conversing in "French and Choctaw" according to the surprised Governor. Additional witness to this remarkable Louisiana French, comes from J.F.H. Claiborne, in his Mississippi the Province, the Territory and the State w/ Biographical' Notices of Eminent Citizens: Vol. 1, publication date 1880, a cousin of Louisiana's first American Governor, who also noted the "unusual patois of provincial French and Choctaw" spoken by coureur de bois, Louis LeFleur.
"Créole" as a noun is different from créole as an adjective. Despite the "Creole myth" of both Charles Gayarre' of New Orleans and that of later 'Creoles de couleur' and some contemporary associations of 'creole' as a racial qualifier, the term is not "polysemous" historically-speaking. As shown in the works of German scholar Georg Friederici's Amerikanisches Wörterbuch and in Louisiana's courthouse records and documents of the French and Spanish colonial periods, the term was consistently used generically to represent native, or "locally-born” in contrast to "foreign-born". Regardless of whether a person was born of African or Native ancestry or white origins, he or she was "Créole" in colonial Louisiana. Créole (lower case)as an adjective simply meant “native”. Through the interactions between such groups of French, African, and Native American, Spanish, German, and Italians "Louisiana French" became a lingua franca used among all, now known as Louisiana French or because as they were all speakers of this creolized French, they referred to their language "Créole French" as did the uneducated African slaves and poor Creoles even as the descendants of the Acadians in Louisiana refer to this same "Creole" French (Louisiana French), as "Cajun French."
In today’s society Créoles are able glean this lingua franca in the Dictionary of Louisiana French As Spoken In Cajun, Creole & Indian Communities (2010) edited by Albert Valdman and other authorities on the pre-Acadian language, as well as, in the Dictionary of Louisiana Creole, although it is heavily phoneticized in the international phonetic script which tends to give the misleading impression that Louisiana Creole is an entirely unrelated language.
Louisiana French is not only spoken by the French Creoles but also by Metis Creoles such as the Chitimacha, Houma, Biloxi, Tunica, Choctaw, and also by Whites or Cajuns, French, Vietnamese, Cambodian, Laotian, Syrian, Lebanese, Irish and others. Individuals and groups of individuals, through innovation, adaptation and contact, continually enrich the French language spoken in Louisiana, seasoning it with linguistic features sometimes only found in Louisiana
Parishes where Louisiana French is spoken
Louisiana Creole State welcome sign
Primarily it is spoken in Pointe Coupee, Lafayette, and Natchitoches, but is also spoken in:
- Acadia
- Ascension
- Allen
- Assumption
- Avoyelles
- Calcasieu
- Cameron
- Evangeline
- Iberia
- Iberville
- Jefferson (Grand Isle)
- Jefferson Davis
- Lafourche
- St. Charles
- St. James
- St. Landry
- St. Martin
- St. Mary
- Terrebonne
- Vermilion
Borrowed words

Louisiana's Colonial French-Choctaw Patois,a creole French-Indian patois, remains the language known as "Louisiana French" complete with its unusual Mobilian-Choctaw jargon.[6] Due to the consistent relations between the Native American tribes and the indigenous Louisiana Creole people, their lingua franca became what many today call Colonial French-Choctaw Patois or Colonial French Koine. It is regarded as a "marriage of the Colonial French of the French maritime world and the unique 'Lower Louisiana' Mobilian-Choctaw Jargon".[7] Louisiana French-Choctaw Patois, native speakers being primarily Louisiana's Afro-French and Metis Creoles, has a host of words of Native American origin.
Words of Native American origin
| Words of Native American Origin[8] | ||
|---|---|---|
| Term | Gloss | Origin |
| | Bayou | Choctaw bayuk |
| | Raccoon | Choctaw or Mobilian shaui |
| | Bowfin | Choctaw shupik, "mudfish" |
| | Palmetto | Carib allatani |
| | Pecan | Algonquian via Mobilian |
| | Sunfish | Choctaw patàssa "flat" |
| | Persimmon | Illinois piakimin, via Mobilian |
| | (Black)bird | Possibly Atakapa t'sak |
In contrast to the Acadians, the Louisiana French Canadian and European soldiers of Bienville's Alabama would intermarry largely among the Choctaw Amerindian families (of the Muskogean family of Indians), and among other Amerindian families friendly to the French in both "Lower and Upper Louisiana” – then, including what are now the American States of Louisiana, Mississippi, parts of Texas, Alabama, Illinois, Missouri, Michigan and the Great Lakes regions where French-Canadian and their metis descendants continue to live and speak their dialects of French.[6]
Subdialects
Louisiana's Colonial French-Choctaw Patois often varies by community and ethnic group.
Prairie French
Prairie French is spoken among Creole, Cajun, and (other) white residents in southwest Louisiana.
Bayou French
Bayou French is primarily spoken among white French Creoles, other white people, and American Indians in southeast Louisiana. It has many old lost Acadian phrases and sayings that sound crude to most other Louisiana French speakers.
Natchitoches French
Although known as Natchitoches French, this variety is spoken not only by those Metis Creoles of Natchitoches Parish. This dialect has a heavy Choctaw influence when compared to other dialects. One aspect of note is the use of "Halito," a Choctaw word for "Hello," when greeting one's elders.
The numbers of this dialect have dwindled greatly; not many native speakers of this dialect survive.
Pointe Coupée Parish French
Many speakers of this dialect are bilingual in both Louisiana Creole and Louisiana French-Choctaw Patois. Hence, there is a heavy presence of code-switching and lexical borrowing among Louisiana Creole, Louisiana French-Choctaw Patois, and English [9]
Code-switching and lexicon borrowing
Code-switching occurs frequently in southwestern Louisiana, especially in Pointe Coupee French. In southwestern Louisiana it is common to hear individuals use Colonial French-Choctaw Patois and Louisiana Creole French. This is typical for many language contact situations.[10]
Code-switching was once viewed as a sign of poor language skills, but it is now understood to be an indication of proficiency in the two languages which a speaker employs. Fluent French speakers frequently alternate from French to American English or Creole, while less proficient speakers usually will not.[11]
Examples of code-switching in Louisiana French spoken by a 64-year-old woman in Pierre Part
1. Il y avait une fois il drivait, il travaillait huit jours on et six jours off. Et il drivait, tu sais, six jours off. Ça le prendrait vingt-quatre heures straight through. Et là il restait quatre jours ici et il retournait. So quand la seconde fois ç’a venu, well, il dit, “Moi, si tu viens pas,” il dit, “je vas pas.” Ça fait que là j’ai été. Boy! Sa pauvre mère. “Vas pas!”
One time he was driving, he was working eight days on and six days off. And he was driving, y’know, six days off. It would take him twenty-four hours straight through. And he would stay here four days and then go back. So when the second time came, well, he said, “If you don’t come,” he said, “I’m not going.” So I went. Boy! His poor mother. “Don’t go!” she said. “Don’t go!”[10]
2. Le samedi après-midi on allait puis…wringer le cou de la volaille. Et le dimanche, well, dimanche ça c’était notre meilleure journée qu’on avait plus de bon manger. Ma mère freezait de la volaille et on avait de la poutine aux craquettes.
Saturday afternoon we would go…wring the chicken’s neck. And on Sunday, well, Sunday, that was our best day for eating well. My mother would freeze some chicken and we would have some poutine aux craquettes.[11]
Notable speakers
- Sybil Kein
- John LaFleur II
- Christophe Landry
- Rosie Ledet
- Boozoo Chavis
- Clifton Chenier
- John Delafose
- C.J Chenier
- Ambrose Sam
- Barry Jean Ancelet
- Calvin Borel [12]
- Michael Doucet
- Canray Fontenot
- Richard Guidry
- Stephen Ortego
- Zachary Richard
- Mabel Sonnier Savoie
See also
- Cajun English
- Cajun French
- Endangered language
- French in the United States
- List of Louisiana parishes by French-speaking population
- Louisiana Creole French
- Louisiana French
References
Footnotes
- 1 2 "What is Cajun French?". Department of French Studies, Louisiana State University. Retrieved September 3, 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Cane River Valley French – Languages and Labels Archived 2007-12-23 at the Wayback Machine. – Tulane University
- 1 2 3 Picone, Michael. "The Rise and Fall of Plantation Society French" (abstract) Archived 2007-09-27 at the Wayback Machine., presented at the Creole Studies Conference: Creole Legacies, New Orleans, October 23–25, 2003.
- ↑ Squint, Kirstin. "A Linguistic and Cultural Comparison of Haitian Creole and Louisiana Creole" Postcolonial Text, Vol 1, No 2 (2005).
- ↑ II, John LaFleur (2014-07-02). Louisiana's Creole French People: Our Language, Food & Culture: 500 Years Of Culture (Kindle Locations 429-430). . Kindle Edition.
- 1 2 II, John LaFleur (2014-07-02). Louisiana's Creole French People: Our Language, Food & Culture: 500 Years Of Culture (Kindle Locations 359-363). . Kindle Edition.
- ↑ II, John LaFleur (2014-07-02). Louisiana's Creole French People: Our Language, Food & Culture: 500 Years Of Culture (Kindle Location 276). . Kindle Edition.
- ↑ Read, William A. 1931. Louisiana-French. Revised edition. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press.
- ↑ Klinger, Thomas A. (2003). If I Could Turn My Tongue Like That: The Creole Language of Point Coupee Parish, Louisiana
- 1 2 Blyth, Carl (1997). French and Creole in Louisiana. New York, N.Y.: Plenum Press. p. 40. ISBN 0-306-45464-5.
- 1 2 Blyth, Carl (1997). French and Creole in Louisiana. New York, N.Y.: Plenum Press. p. 41. ISBN 0-306-45464-5.
- ↑ http://www.drf.com/news/calvin-borel-face-horse-racing
Bibliography
- Brasseaux, Carl A (2005). French, Cajun, Creole, Houma: A Primer on Francophone Louisiana. Bâton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press.
- LaFleur, John II, (2014). Louisiana's Creole French People: Our Language, Food & Culture: 500 Years Of Culture. (Kindle Locations 429-430. Kindle Edition.
- LaFleur, John II, (2012). Louisiana's French Creole Culinary & Linguistic Traditions: Facts vs. Fiction Before and Since Cajunization.
- Klinger, Thomas A. (2003). If I Could Turn My Tongue Like That: The Creole Language of Pointe Coupee Parish, Louisiana ISBN 0807127795.
- Read, William A. (2008). Louisiana Place Names of Indian Origin: A Collection of Words, edited and with an Introduction by George M. Riser University of Alabama Press.
- Ekberg, Carl J. (2007). Stealing Indian Women: Native Slavery In The Illinois Country, University of Illinois Press.
- Bossu, Jean-Bernard, Travels To That Part of America Formerly Called Louisiana, 1768; p.197; 254-255.
- Laussat, Pierre-Clement de, (1803) Memoirs of My Life... p. 55, Book Two, December 1803- July 1804. Translated by Sister Agnes-Josephine Pastwa, O.S.F., 1978.
- Claiborne, J.F.H., Mississippi: the Province, the Territory and the State, with Biographical Notices of Eminent Citizens, Vol.1 publication date 1880. Caption: Louis LeFleur, father of Greenwood LeFleur
General references
- Dictionary of Louisiana French as Spoken in Cajun, Creole, and American Indian Communities, senior editor Albert Valdman. ISBN 978-1-60473-403-4 Jackson: University Press of Mississippi, 2010.
- Language Shift in the Coastal Marshes of Louisiana by Kevin J. Rottet ISBN 0-8204-4980-6. Peter Lang Publishing, Inc.
- Tonnerre mes chiens! A glossary of Louisiana French figures of speech by Amanda LaFleur ISBN 0-9670838-9-3. Renouveau Publishing.
- French, Cajun, Creole, Houma: A Primer of Francophone Louisiana by Carl A. Brasseaux ISBN 978-0807130360. Louisiana State University Press (March 1, 2005).
- Isle of Canes by Elizabeth Shown Mills. ISBN 978-1593313067 Ancestry.com (September 1, 2006).
- Creole: The History and Legacy of Louisiana's Free People of Color by Sybil Kein (Kindle Edition). ISBN 0807126012
- Landry, Rodrigue, Réal Allard, and Jacques Henry. "French in South Louisiana: towards language loss." Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development (1996) 17#6 pp: 442-468.
- Malveaux, Vivian (2009). Living Creole and Speaking It Fluently. AuthorHouse.
- Kein, Sybil (2009). Creole: the history and legacy of Louisiana's free people of color. Louisiana State University Press.
- Jolivette, Andrew (2007). Louisiana Creoles: Cultural Recovery and Mixed-Race Native American Identity. Lexington Books.
- Gehman, Mary (2009). The Free People of Color of New Orleans: An Introduction. Margaret Media, Inc.
- Clark, Emily (2013). The Strange History of the American Quadroon: Free Women of Color in the Revolutionary Atlantic World. The University of North Carolina Press.
- Dominguez, Virginia (1986). White by Definition: Social Classification in Creole Louisiana. Rutgers University Press.
- Hirsch, Arnold R. (1992). Creole New Orleans: Race and Americanization. Louisiana State University Press.