Coeur d'Alene, Idaho
| Coeur d'Alene, Idaho | |
|---|---|
| City | |
|
Coeur d'Alene | |
| Nickname(s): Lake City; CDA | |
 Location of Coeur d'Alene in Kootenai County, Idaho. | |
 Coeur d'Alene, Idaho Location in the United States | |
| Coordinates: 47°41′34″N 116°46′48″W / 47.69278°N 116.78000°WCoordinates: 47°41′34″N 116°46′48″W / 47.69278°N 116.78000°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Idaho |
| County | Kootenai |
| Founded | 1878 |
| Incorporated | 1887 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Steven Widmyer |
| Area[1] | |
| • City | 16.20 sq mi (41.97 km2) |
| • Land | 15.74 sq mi (40.77 km2) |
| • Water | 0.46 sq mi (1.20 km2) |
| Elevation | 2,188 ft (667 m) |
| Population (2010)[2] | |
| • City | 44,137 |
| • Estimate (2016)[3] | 50,285 |
| • Density | 3,194.73/sq mi (1,233.46/km2) |
| • Urban | 486,225 (US: 82nd) |
| • Metro | 144,265 (US: 283rd) |
| • CSA | 679,989 (US: 69th) |
| Time zone | Pacific (UTC−8) |
| • Summer (DST) | Pacific (UTC−7) |
| ZIP code | 83814, 83815 |
| Area code(s) | 208 |
| FIPS code | 16-16750 |
| GNIS feature ID | 0379485 |
| Website |
www |
Coeur d'Alene (/ˌkɔər dəˈleɪn/ KOHR də-LAYN) is the largest city and county seat of Kootenai County, Idaho, United States.[4] It is the principal city of the Coeur d'Alene Metropolitan Statistical Area. As of the 2010 census, the population of Coeur d'Alene was 44,137.[5] The city is a satellite city of Spokane, which is located about 30 miles (48 km) to the west, in the state of Washington. The two cities are the key components of the Spokane-Coeur d'Alene Combined Statistical Area, of which Coeur d'Alene is the third largest city (after Spokane and its largest suburb, Spokane Valley).[6] Coeur d'Alene is the largest city in northern Idaho Panhandle. The city is situated on the north shore of Lake Coeur d'Alene, 25 miles (40 km) in length. Locally, Coeur d'Alene is known as the "Lake City", or simply called by its initials: "CDA".
The city of Coeur d'Alene has grown significantly in recent years, in part because of a substantial increase in tourism, encouraged by several resorts in the area. Broadcaster and media figure Barbara Walters called the city "a little slice of Heaven" and included it in her list of most fascinating places to visit. On November 28, 2007, Good Morning America broadcast the city's Christmas lighting ceremony because its display is among the largest in the United States. The Coeur d'Alene Resort takes up a prominent portion of the city's downtown. It is also near two major ski resorts: Silver Mountain Resort to the east in Kellogg, and Schweitzer Mountain Ski Resort to the north in Sandpoint.
The city is named after the Coeur d'Alene People, a federally recognized tribe of Native Americans who lived along the rivers and lakes of the region, in a territory of 5,500 square miles (14,000 km2) extending into Washington and Montana. They were first encountered by French fur traders in the late 18th and early 19th century, who referred to them as Cœur d'Alène, meaning "heart of an awl", reflecting their experience of the tribal traders as tough businessmen, "sharp-hearted" or "shrewd".[7]
History

The Coeur d'Alene people called themselves by the autonym Schitsu'umsh in Coeur d'Alene, one of the Salishan languages, meaning "The Discovered People" or "Those Who Are Found Here."
This area was extensively explored by David Thompson of the North West Company starting in 1807. The Oregon boundary dispute (or Oregon question) arose as a result of competing British and American claims to the Pacific Northwest of North America in the first half of the 19th century. The British had trading ties extending from Canada and had started settlements in present-day British Columbia and at Fort Astoria on the Pacific coast near the mouth of the Columbia River.
The Oregon Treaty of 1846 ended the disputed joint occupation of the area in present-day Idaho when Britain ceded all rights to land south of the 49th parallel to the United States. When General William T. Sherman ordered a fort constructed on the lake in the 1870s, he gave it the name Fort Coeur d'Alene; hence the name of the city that grew around it. The name of the fort was later changed to Fort Sherman to honor the general.[8] North Idaho College, a community college, now occupies the former fort site. The lake was also named for the Coeur d'Alene.
Miners and settlers came to the region after silver deposits were found. It became the second-largest silver mining district in the country, generating both great wealth and extensive environmental contamination and damages. In the 1890s, two significant miners' uprisings took place in the Coeur d'Alene Mining District, where the workers struggled with high risk and low pay.[9] In 1892, the union's discovery of a labor spy in their midst, in the person of Charlie Siringo, sometime cowboy and Pinkerton agent, resulted in a strike that developed into a shooting war between miners and the company.
Years later Harry Orchard, who owned a share of the Hercules Mine in the nearby mountains before it began producing, confessed to a secret, brutal and little understood role in the Colorado Labor Wars. He later confessed to dynamiting a $250,000 mill belonging to the Bunker Hill Mining Company near Wardner during another miners' uprising in 1899. He returned later to Idaho to assassinate former Idaho Governor Frank Steunenberg in 1905.[10]
Geography
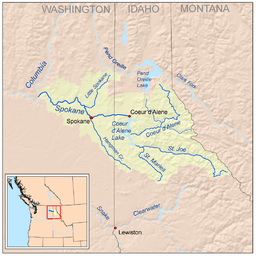
Coeur d'Alene is located at 47°41′34″N 116°46′48″W / 47.69278°N 116.78000°W (47.692845, −116.779910),[11] at an elevation of 2,180 ft (660 m) above sea level.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 16.08 square miles (41.65 km2), of which, 15.57 square miles (40.33 km2) is land and 0.51 square miles (1.32 km2) is water.[12]
The wooded lands east of the city have been designated for protection and management as the Coeur d'Alene National Forest. The city is surrounded by forest, which contains several lakes and campgrounds.
It is 30 miles (48 km) east of Spokane, Washington, and is part of a common metropolitan area. It is 311 miles (501 km) east of Seattle, Washington, on Puget Sound on the west side of the Cascade Mountains.
Climate
Coeur d'Alene has, depending on the definition, a dry-summer continental climate (Köppen Dsb), or a warm-summer Mediterranean climate (Csb), characterized by a cold, moist climate in winter, and very warm, dry conditions in summer. It straddles the border between USDA Plant Hardiness Zones 6B and 7A.[13] The monthly daily mean temperature ranges from is 29.8 °F (−1.2 °C) in December to 69.0 °F (20.6 °C) in July and August. Temperatures exceed 90 °F (32 °C) on 13 days per year, only occasionally reaching 100 °F (38 °C), while conversely, there may be several nights below 10 °F (−12 °C).[14] Snowfall averages 70 inches (178 cm) per year; precipitation is generally lowest in summer. The average first and last freeze of the season are October 12 and May 3, respectively.
| Climate data for Coeur d'Alene, Idaho (1981−2010 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 60 (16) |
62 (17) |
73 (23) |
94 (34) |
98 (37) |
104 (40) |
108 (42) |
109 (43) |
102 (39) |
88 (31) |
71 (22) |
60 (16) |
109 (43) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 35.5 (1.9) |
40.2 (4.6) |
49.0 (9.4) |
56.4 (13.6) |
65.2 (18.4) |
72.3 (22.4) |
81.5 (27.5) |
82.5 (28.1) |
72.6 (22.6) |
58.0 (14.4) |
44.0 (6.7) |
34.3 (1.3) |
57.6 (14.2) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 30.5 (−0.8) |
33.5 (0.8) |
40.2 (4.6) |
46.6 (8.1) |
54.4 (12.4) |
61.6 (16.4) |
68.9 (20.5) |
69 (21) |
60.1 (15.6) |
48.2 (9) |
37.9 (3.3) |
29.8 (−1.2) |
48.39 (9.14) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 25.4 (−3.7) |
26.7 (−2.9) |
31.4 (−0.3) |
36.7 (2.6) |
43.6 (6.4) |
50.9 (10.5) |
56.3 (13.5) |
55.5 (13.1) |
47.6 (8.7) |
38.4 (3.6) |
31.7 (−0.2) |
25.2 (−3.8) |
39.1 (3.9) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −30 (−34) |
−29 (−34) |
−13 (−25) |
5 (−15) |
21 (−6) |
28 (−2) |
36 (2) |
32 (0) |
17 (−8) |
2 (−17) |
−13 (−25) |
−26 (−32) |
−30 (−34) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.18 (80.8) |
2.13 (54.1) |
2.34 (59.4) |
1.88 (47.8) |
2.16 (54.9) |
1.98 (50.3) |
.94 (23.9) |
.87 (22.1) |
1.01 (25.7) |
1.95 (49.5) |
3.72 (94.5) |
3.52 (89.4) |
25.68 (652.4) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 10.4 (26.4) |
4.2 (10.7) |
1.9 (4.8) |
.3 (0.8) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
3.9 (9.9) |
11.7 (29.7) |
32.4 (82.3) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 13.4 | 10.6 | 11.6 | 10.3 | 11.9 | 9.4 | 4.6 | 4.5 | 6.3 | 10.8 | 15.2 | 12.8 | 121.3 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 4.8 | 2.7 | 1.1 | .2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | .1 | 2.0 | 5.4 | 16.2 |
| Source: NOAA (extremes 1895−present) [14] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1890 | 491 | — | |
| 1900 | 508 | 3.5% | |
| 1910 | 7,291 | 1,335.2% | |
| 1920 | 6,447 | −11.6% | |
| 1930 | 8,297 | 28.7% | |
| 1940 | 10,049 | 21.1% | |
| 1950 | 12,198 | 21.4% | |
| 1960 | 14,291 | 17.2% | |
| 1970 | 16,228 | 13.6% | |
| 1980 | 19,913 | 22.7% | |
| 1990 | 24,563 | 23.4% | |
| 2000 | 34,514 | 40.5% | |
| 2010 | 44,137 | 27.9% | |
| Est. 2016 | 50,285 | [3] | 13.9% |
2010 census
As of the census[2] of 2010, there were 44,137 people, 18,395 households, and 10,813 families residing in the city. The population density was 2,834.7 inhabitants per square mile (1,094.5/km2). There were 20,219 housing units at an average density of 1,298.6 per square mile (501.4/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 93.8% White, 0.4% African American, 1.2% Native American, 0.8% Asian, 0.1% Pacific Islander, 0.9% from other races, and 2.8% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 4.3% of the population.
There were 18,395 households of which 29.9% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 42.2% were married couples living together, 11.6% had a female householder with no husband present, 5.0% had a male householder with no wife present, and 41.2% were non-families. 31.4% of all households were made up of individuals and 12.1% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.33 and the average family size was 2.92.
The median age in the city was 35.4 years. 22.9% of residents were under the age of 18; 11.6% were between the ages of 18 and 24; 26.7% were from 25 to 44; 24% were from 45 to 64; and 14.6% were 65 years of age or older. The gender makeup of the city was 48.6% male and 51.4% female.
2000 census
As of the census of 2000, there were 34,514 people, 13,985 households, and 8,852 families residing in the city. The population density was 2,629/sq mi (1,014.9/km2). There were 14,929 housing units at an average density of 1,137/sq mi (439.0/km2). Coeur d'Alene's racial makeup was:
- 95.80% White
- 0.22% Black
- 0.77% American Indian
- 0.61% Asian
- 0.09% Pacific Islander
- 0.63% from other races
- 1.88% from two or more races
Hispanic or of any race were 2.70% of the population.
There were 13,985 households out of which 31.7% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 47.7% were married couples living together, 11.5% had a female householder with no husband present, and 36.7% were non-families. 28.2% of all households were made up of individuals and 11.3% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.39 and the average family size was 2.93.
In the city, the population was spread out with:
- 24.9% under the age of 18,
- 11.7% from 18 to 24
- 27.9% from 25 to 44
- 20.7% from 45 to 64
- 14.8% 65 years of age or older
The median age was 35 years. For every 100 females there were 93.7 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 89.3 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $33,001, and the median income for a family was $39,491. Males had a median income of $31,915 versus $21,092 for females. The per capita income for the city was $17,454. About 9.3% of families and 12.8% of the population were below the poverty line, including 13.5% of those under age 18 and 8.1% of those age 65 or over.
Economy
The city is the healthcare, educational, media, manufacturing, retail and recreation center for northern Idaho. Several mining firms are headquartered in the city, among them Hecla Mining (NYSE: HL). The Coeur d'Alene Resort is also a major employer.
Commercial
Coeur d'Alene's retail has expanded greatly in recent years with the opening of new stores and entertainment venues. Coeur d'Alene's Riverstone development houses a 14-theater Regal Cinemas, condominiums, a Hampton Inn, a park, restaurants, and local retailers. The North Idaho Centennial Trail bike path cuts through the Riverstone complex alongside an abandoned railroad right of way. The Citylink transit system adjoins the northwest entrance of the Riverstone complex.
Giant statues of bird feathers line Northwest Boulevard, celebrating the rich heritage associated with the Coeur d'Alene Tribe. Art galleries and cafes are along Sherman Avenue, Coeur d'Alene's main street. During summer, artists and musicians frequent Sherman Square.
In 2009, Coeur d'Alene ranked No. 12 on Newsmax magazine's list of the "Top 25 Most Uniquely American Cities and Towns," a piece written by current CBS News travel editor Peter Greenberg. In determining his ranking, Greenberg commended the city for "embracing its natural beauty and creating a small business-friendly environment that has helped develop its thriving tourism industry."[16]
Education
The Coeur d'Alene School District #271 serves 10,300 students with its two high schools, three middle schools, an alternative middle/high school, a dropout retrieval school, and 10 elementary schools. The district has a staff of 550 teachers, 47 administrators and 552 support personnel to provide education for the Coeur d'Alene, Hayden and Dalton communities.
In addition to Honors and Advanced Placement courses, Coeur d'Alene and Lake City High Schools began offering the rigorous International Baccalaureate Diploma Program. Two of the elementary schools are implementing the IB Primary Years Program. Because of a lack of funding, the Coeur d'Alene High School dropped the IBE Diploma Program in fall 2009.[17]
District #271 students who qualify are also eligible for dual enrollment with North Idaho College and advanced technical and specialized courses at Riverbend Professional Technical Academy in Post Falls.
A partnership with the City of Coeur d'Alene Police Department provides five School Resource Officers. Through an alliance with Kootenai Health, the District is served by seven school nurses.
Coeur d'Alene also has a Charter school. Its teaching curriculum is based on setting higher college-preparatory standards than many other schools. The school enforces a strict dress code policy for students to maintain a professional academic atmosphere. Coeur d'Alene Charter Academy is a regular middle–high school; it is publicly funded with open admission to any students residing in the state. However, students' families must arrange for their own transportation to the school. The Coeur d'Alene Charter Academy is expanding into neighboring lots to add classrooms.
High Schools
- Coeur d'Alene High School
- Lake City High School
Middle Schools
- Canfield Middle School
- Woodland Middle School
- Lakes Middle School
Elementary Schools
- Atlas Elementary School
- Borah Elementary School
- Bryan Elementary School
- Dalton Elementary School
- Fernan Elementary School
- Hayden Meadows Elementary School
- Skyway Elementary School
- Sorensen Elementary School
- Winton Elementary School
- Ramsey Elementary School
Specialty Schools
- Fernan STEM Academy
- Kootenai Technical Education Campus – KTEC
- Lake City Junior Academy
- Lakes Magnet Middle School
- Ramsey Magnet School of Science
- Sorensen Magnet School of the Arts and Humanities
- Venture High School
- Charter Academy
Infrastructure

Transportation
Roads and highways
Coeur d'Alene is accessed from Interstate 90 at Exits 11 through 15. The greater Coeur d'Alene area is almost entirely dependent upon private automobiles for transportation. Combined with the city's rapid growth since 1990, relative congestion now occurs on a significant portion of the area highways, notably U.S. 95 between Northwest Blvd. north to Hayden, and on several under-developed arterial streets such as Atlas, Ramsey, and Government Way. Before the construction of I-90, the city was served by U.S. Route 10, which ran through downtown. This route is Northwest Boulevard and Sherman Avenue. The former US 10, between I-90 exits 11 and 15, is now designated as Interstate 90 Business.
Public transportation

Free public bus service is available to area residents, provided by Citylink. Citylink buses operate in the urbanized area of Kootenai County, leaving the Riverstone Transfer Station every sixty minutes, seven days a week, including holidays. Buses are wheelchair accessible and can transport up to two bicycles.
The bus system comprises four separate routes:
- Urban Route B – Serves Post Falls, Hayden and West Coeur d'Alene.
- Urban Route C – Serves Downtown Coeur d'Alene, Fernan and Hayden.
- Rural Route – Serves the towns of Worley, Plummer, Tensed and DeSmet.
- Link Route – Connects the two transfer stations at Riverstone and Worley.
As of April 2012, major changes were made to the current routes, including the elimination of the "Urban Route A", which went out to Stateline, 125 new stops added to the system, the "Urban Route B" and the "Urban Route C" became two-way service instead of loop service, and the routes leaving from Riverstone more frequently, from every eighty-five minutes down to sixty. Changes were made primarily due to budget cuts.[19]
Airports
The closest major airport serving Coeur d'Alene and North Idaho is the Spokane International Airport, which is served by five airlines and is 40 miles (64 km) to the west in Spokane, Washington. Coeur d'Alene Airport – Pappy Boyington Field (KCOE) is a general aviation airport in Hayden, north of the city near U.S. 95.
The local Coeur d'Alene Airport is a public-use, general aviation airport. In 1941, the Coeur d’Alene Chamber of Commerce promoted the purchase of 720 acres (290 ha) of land on the Rathdrum Prairie for the Coeur d’Alene Airport. The facility was built in 1942 by the Army Engineers at a cost of over $400,000. It was designated as an alternate to Weeks Field (now, Kootenai County Fairgrounds) when a war training program was in operation for World War II.
Utilities
The city of Coeur d'Alene provides for municipal water, sewer and stormwater management, street lighting, garbage collection, and recycling.
Healthcare
Kootenai Health is the primary medical center serving the Coeur d'Alene and north Idaho area. With over 2,600 employees, it is the largest employer in Kootenai County.[20]
Events and attractions

- Coeur d'Alene is the home of Ironman Coeur d'Alene, which started in 2003. This Ironman Triathlon is held each year on the fourth Sunday in June. It starts at the Coeur d'Alene resort, where triathletes start the competition with a 2.4-mile (3.9 km) swim in Lake Coeur d'Alene, followed by a 112-mile (180 km) bike, finishing with a 26.2-mile (42.2 km) run.[21]
- Coeur d'Alene is the site of the Christian Youth Theater (CYT) North Idaho headquarters.
- Annually in June, CDA hosts "Car d' Alene," where all the hot cars, both new and old, are brought out on display for admiration and bragging rights.[22]
- The first weekend in August North Idaho Community College hosts Art on the Green. An arts and crafts outdoor festival sponsored by Citizens' Council for the Arts.
- The local college art program had a public art campaign called "Moose on the Loose," when local artists and college art students painted and decorated a dozen or so life-size moose statues with various colors and accessories. After being displayed, the pieces were auctioned off to local businesses as a fundraiser. The moose were installed on sites from downtown near Sherman Ave. to Government Way on the CdA/Hayden boundary. The moose have become both a town landmark and a popular scavenger hunt item.[23]
- Coeur d'Alene has become a destination for golf enthusiasts. The Coeur d'Alene Resort Golf Course is considered one of the best in the United States. Its 14th hole features the world's only movable floating green.[24]
- The North Idaho Centennial Trail passes through Coeur d'Alene.
- Coeur d'Alene and the surrounding area provide many outdoor recreational opportunities, such as: mountain biking, hiking, camping, fishing, hunting, etc.
- The Snake Pit Derby Dames are based here; they are an all-female flat track roller derby league. The competitive season is March–November and Bouts (matches) draw large crowds.[25]
- Every year in November, the Friday after Thanksgiving marks the start of Coeur d'Alene's Christmas Lighting Ceremony including a parade, fireworks and special holiday candles given out by the local downtown businesses.
- The Coeur d'Fondo, a bike race that ranges from 15 miles to 108 miles (24–174 km), is held annually in summer.
- The Coeur d'Alene crossing is a swimming challenge, in which swimmers try to cross the lake.
In popular culture
- The 12th track of Alter Bridge's third album AB III is named after the city and is inspired by lead singer Myles Kennedy's spending time here as a child.
- Harold Covington features Coeur d'Alene repeatedly in his Northwest Trilogy historical novels as the place where the Northwest revolt began.
- In the book Walk Two Moons, Coeur d'Alene is a stop on the main character Salamanca Tree Hiddle's trip.
- The narrator in Iris DeMent's 1993 song Easy's Gettin' Harder Every Day wishes she could "run away to Coeur d'Alene."
- In Tom Clancy's fourth book in the Net Force series, Breaking Point , a character hides in the Aryan Nations compound (now destroyed) in Hayden Lake (referred to as Coeur d'Alene).
- Sam Bourne's novel The Righteous Men, refers to this city as home of the Aryan Nations. However, the Aryan Nations' home was in nearby Hayden Lake. It is since defunct, demolished after a lawsuit and the bankruptcy of the Aryan Nations.
- Luke Redfield's song, "Coeur d'Alene," from his 2010 album, Ephemeral Eon, depicts a simple love story in the city.
- Listed in Patricia Schultz's book 1,000 Places to See Before You Die.[26]
- The independent film Smoke Signals, based on stories by Sherman Alexie, feature characters of the Coeur d'Alene Tribe who live on its reservation and have a quest auto trip.
- The film Teenage Dirtbag is set here. It was written and directed by Regina Crosby, who grew up in Coeur d'Alene. She was inspired by events from her time in high school.
- The film Kid Cannabis was set here.
- The indie folk band The Head and the Heart released a song entitled Coeur d'Alene that is included on their 2011 debut album The Head and the Heart.
- Kylie Scott's Stage Dive and Dive Bar novels feature Coeur d'Alene as the hometown of several of the characters and as the location for the Dive Bar.
Notable people
- Leepu Nizamuddin Awlia, automotive designer, originally from Bangladesh, lives and works here.
- Rocky Bridges (1927-2015), former MLB baseball player, lived in Coeur d'Alene.[27]
- Gregory "Pappy" Boyington, World War II-flying ace and Colonel, was born in Coeur d'Alene on December 4, 1912. He was a member of the AVG (Flying Tigers) and later the commander of the famous Black Sheep Squadron.[28] The local airport is now named in his honor.
- Dorthea Dahl, Norwegian-born American writer, wrote and published her collections of short stories and her novel while residing near Coeur d'Alene.
- Adrienne Dore, model and actress.
- Patty Duke, Academy Award-winning actress, lived in Coeur d'Alene from the mid-1990s until her death in 2016.
- Dennis Franz, actor, resides in Coeur d'Alene.
- Robert Lamphere, FBI agent who helped track down a number of Soviet atomic spies.[29]
- Sage Kotsenburg, snowboarder who won the first gold medal at the 2014 Winter Olympics for men's snowboard slopestyle in Sochi, Russia, was born in Coeur d'Alene.[30]
- Chuck Missler, former CEO of Western Digital.
- Brock Osweiler, NFL quarterback.
- Trevor Prangley, pro mixed-martial artist with a background in wrestling and a former fighter in the UFC; he was born in South Africa and now resides in Coeur d'Alene.
- Rollin Putzier, NFL player.
- Bruce Reed, previous CEO of the Democratic Leadership Council (DLC) and previous Chief of Staff to U.S. Vice President Joe Biden.
- Luke Ridnour, NBA point guard.[31]
- Charles Sellier, television producer and director; his credits included The Life and Times of Grizzly Adams.[32][33]
- Robert Titsch, co-founder of the television network C-SPAN.
- Evelyn Venable, actress, died in Coeur d'Alene.
- Wayne Gretzky, NHL player.
Sister cities
Coeur d'Alene has one sister city:
References
- ↑ "2016 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved Jul 26, 2017.
- 1 2 "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2012-12-18.
- 1 2 "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved June 9, 2017.
- ↑ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on 2011-05-31. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2011-05-20. Retrieved 2016-04-20.
- ↑ "Annual Estimates of the Population of Combined Statistical Areas: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2013". 2013 Population Estimates. United States Census Bureau, Population Division. June 16, 2014. Archived from the original on June 27, 2014. Retrieved June 16, 2014.
- ↑ Frey, Rodney. "Coeur d'Alene (Schitsu'umsh)". Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- ↑ An Illustrated History of North Idaho, Western Historical Publishing Company, Spokane, Washington (1903).
- ↑ Roughneck—The Life and Times of Big Bill Haywood, Peter Carlson, 1983, pages 53–54.
- ↑ Roughneck—The Life and Times of Big Bill Haywood, Peter Carlson, 1983, pages 91–92.
- ↑ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- ↑ "US Gazetteer files 2010". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2012-06-26. Retrieved 2012-12-18.
- ↑
- 1 2 "NowData – NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2012-02-15.
- ↑ "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Archived from the original on May 12, 2015. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- ↑ Greenberg, Peter. "Newsmax Magazine Rates the Top 25 Most Uniquely American Cities And Towns". Retrieved 15 January 2014.
- ↑ , CDA Press
- 1 2 3 4 http://www.cdaschools.org/domain/298
- ↑ KMPO Staff. "Kootenai County - CITYLINK SERVICE REDUCTION - Summary Sheet - FAQ's". KMPO Transportation Blog. Blogspot. Retrieved 27 February 2013.
- ↑ "Mission, Vision and Facts - Kootenai Health". www.kh.org. Retrieved 2017-03-17.
- ↑ http://www.ironmancda.com/
- ↑
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-03-07. Retrieved 2009-01-07.
- ↑
- ↑ Archived 2010-06-14 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-03-06. Retrieved 2009-01-07.
- ↑ http://www.startiger.com/l?searchid=9419870&id=43265
- ↑ "G.H. Boyington", Arlington National Cemetery
- ↑ Rhodes, Richard. Dark Sun. Simon & Schuster, New York, 1995. pg. 336
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2014-03-02. Retrieved 2014-03-02.
- ↑
- ↑ Hevesi, Dennis (2011-02-04). "Charles Sellier Jr., Creator of ‘Grizzly Adams,’ Dies at 67". New York Times. Retrieved 2011-02-11.
- ↑ Dumas, Michael (2011-02-08). "Charles Sellier Jr., creator of 'Grizzly Adams,' dies at 67". Press-Register. Retrieved 2011-02-11.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Coeur d'Alene, Idaho. |
-
 Coeur d'Alene travel guide from Wikivoyage
Coeur d'Alene travel guide from Wikivoyage - Coeur d'Alene Convention & Visitor Bureau official website
- Coeur d'Alene Idaho Downtown Association Official Web Site
- Official website of the city of Coeur d'Alene
- Old School Coeur d'Alene
- "Coeur d’Alene, Idaho". C-SPAN Cities Tour. December 2013.
