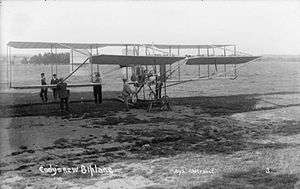
Cody Circuit of Britain biplane
| Cody Circuit of Britain biplane | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | competition aircraft |
| National origin | United Kingdom |
| Designer | S.F. Cody |
| First flight | 1911 |
| Number built | 1 |
| Developed from | Cody Michelin Cup biplane |
The Cody Circuit of Britain biplane, also known as the Cody III, was the third powered aircraft built by Samuel Franklin Cody. It was flown by him in various competitions during 1911, including the Daily Mail Circuit of Britain competition in which Cody was the only British contestant to complete the course. On 29 October Cody set a new British endurance record in the aircraft, flying for five hours and fifteen minutes.
Design
Developed from his Michelin Cup winning machine of 1910 and using the same 60 horsepower (45 kW) Green engine the Cody Circuit of Britain biplane was a pusher biplane with a single frontal elevator supported by booms at the centre and either end and two rear-mounted rudders, each supported by a boom at top and bottom and fitted with a small horizontal fixed stabiliser. The tail was the most obvious difference between this aircraft and its predecessor. Like the Michelin Cup aircraft, it had a tricycle undercarriage with an added long rear skid and distinctive wheels mounted on each lower wingtip.[1]
Operational history
The Circuit of Britain biplane made its maiden flight on 13 July 1911.[2]
- The aircraft, flown by Cody, was entered for the Daily Mail Circuit of Britain race: Cody came fourth, his aircraft being the only British aircraft to complete the 1,010 mile course.
- Cody won second place in the Manville Prize contest with a flight of 2 hours 16 minutes.
- On 11 September Cody won the British Empire Michelin Cup No.2 flying the Circuit of Britain biplane, with a 125 miles (201 km) cross-country flight lasting 3 h 6 min 30 s, being the only competitor to finish the course.[2]
- On 29 October Cody won the British Empire Michelin Cup No.1, covering 261.5 miles (420.8 km) over a closed circuit at Laffan's Plain in 5 h 15 min, a new British duration record.[2]
On 3 July 1912 the aircraft was severely damaged on landing when Major H.D. Harvey-Kelly clipped a tree with one wingtip and crashed. Cody, who was instructing Harvey-Kelly, was severely injured in the crash. The airframe was subsequently cannibalised to build the Cody V with which Cody won the 1912 Military Aeroplane Competition held at Larkhill on Salisbury Plain.
Specifications
Data from Lewis, P British Aircraft 1809-1914. London: Putnam, 1962 p.195
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Capacity: 1
- Length: 30 ft (9.1 m)
- Wingspan: 40 ft (12 m)
- Wing area: 450 sq ft (42 m2)
- Empty weight: 1,750 lb (794 kg)
- Gross weight: 2,250 lb (1,021 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Green C.4 4-cylinder inline water-cooled, 60 hp (45 kW)
- Propellers: 2-bladed Chauvière[3]
Performance
- Maximum speed: 58 mph (93 km/h; 50 kn)
- Range: 350 mi (304 nmi; 563 km)
- Service ceiling: 5,000 ft (1,500 m)
- Wing loading: 5.55 lb/sq ft (27.1 kg/m2)
See also
- Related development
Notes
References
- Jarrett, Philip. "Cody and His Aeroplanes:Samuel Franklin Cody:His Life and Times". Air Enthusiast, No. 82, July/August 1999. pp. 6–17. Stamford, UK:Key Publishing. ISSN 0143-5450.
- Lewis, P British Aircraft 1809-1914. London: Putnam 1962