Coded aperture
.jpg)
Coded Apertures or Coded-Aperture Masks are grids, gratings, or other patterns of materials opaque to various wavelengths of light. The wavelengths are usually high-energy radiation such as X-rays and gamma rays. By blocking light in a known pattern, a coded "shadow" is cast upon a plane. The properties of the original light sources can then be mathematically reconstructed from this shadow. Coded apertures are used in X- and gamma ray imaging systems, because these high-energy rays cannot be focused with lenses or mirrors.
Rationale
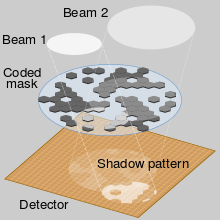
Imaging is usually made at optical wavelengths by lenses and mirrors. However, for X-rays and γ-rays, lenses and mirrors do not exist, or else are impractical. Image modulation by apertures is therefore often used instead. The pinhole camera is the most basic form of such a modulation imager, but its disadvantage is low throughput, as its small aperture allows through little radiation. Only a tiny fraction of the light passes through the pinhole, which causes a low signal-to-noise ratio. To solve this problem, the mask can contain many holes, in one of several particular patterns, for example. Multiple masks, at varying distances from a detector, add flexibility to this tool. Specifically the modulation collimator, invented by Minoru Oda, was used to identify the first cosmic X-ray source and thereby to launch the new field of X-ray astronomy in 1965. Many other applications in other fields, such as tomography, have since appeared.
In a coded aperture more complicated than a pinhole camera, images from multiple apertures will overlap at the detector array. It is thus necessary to use a computational algorithm (which depends on the precise configuration of the aperture arrays) to reconstruct the original image. In this way a sharp image can be achieved without a lens. The image is formed from the whole array of sensors and is therefore tolerant to faults in individual sensors; on the other hand it accepts more background radiation than a focusing-optics imager (e.g., a refracting or reflecting telescope), and therefore is normally not favored at wavelengths where these techniques can be applied.
The coded aperture imaging technique is one of the earliest forms of computational photography and has a strong affinity to astronomical interferometry
Well known types of masks
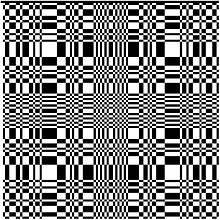
Different mask patterns exhibit different image resolutions, sensitivities and background-noise rejection, and computational simplicities and ambiguities, aside from their relative ease of construction.
- FZP = Fresnel Zone Plate
- ORA = Optimized RAndom pattern
- URA = Uniformly Redundant Array
- HURA = Hexagonal Uniformly Redundant Array[1]
- MURA = Modified Uniformly Redundant Array
- Levin
- Veeraraghavan
Coded-Aperture Space Telescopes
- Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer (RXTE) - ASM
- BeppoSAX - Wide Field Camera (1996-2002)
- INTEGRAL - IBIS and SPI
- Swift - BAT (2004- )
- Ultra-Fast Flash Observatory Pathfinder mission (planned launch in mid-2013) and UFFO-100 (its next generation) [2]
- Astrosat - CZTI (Launched in 2015)
- SVOM - ECLAIRs (Launched in 2021)
- In addition, the SAS-3 and RHESSI missions detect radiation based on a combination of masks and rotational modulation
See also
- Pinhole camera
- Deconvolution
- Rotational Modulation Collimator
- Computational photography
- Tomographic reconstruction and X-ray computed tomography
References
External links
- Coded Aperture Imaging in High-Energy Astronomy
- In the news: Sky-high system to aid soldiers. Aug 2008