Co-simulation
In co-simulation the different subsystems which form a coupled problem are modeled and simulated in a distributed manner. Hence, the modeling is done on the subsystem level without having the coupled problem in mind. Furthermore, the coupled simulation is carried out by running the subsystems in a black-box manner. During the simulation the subsystems will exchange data.
Problem Partitioning - From Monolithic to Co-Simulation
The partitioning procedure identifies the process of spatial separation of the coupled problem into multiple partitioned subsystems.
Communication Patterns
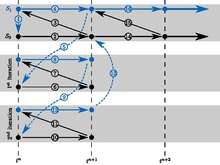
Gauss-Seidel (serial)
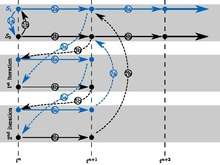
Jacobi (parallel)
Problem Decomposition
The term decomposition is used for the process of defining the input/output relations for each individual subsystem.
Coupling Algorithms
Iterative
Software realization
Functional Mock-up Interface
For signals co-simulation can be performed with a standardized interface called Functional Mock-up Interface.
Agent-based model
Agent-based model is a modeling approach of complex systems. Each simulator is seen as an agent and "behaves" according to its associated simulator. The agents interact, exchange data, between each other in a network. The simulation environment Mecysco is an implementation of this approach
References
- Sicklinger, S.; Belsky, V.; Engelmann, B.; Elmqvist, H.; Olsson, H.; Wüchner, R.; Bletzinger, K.-U. (11 May 2014). "Interface Jacobian-based Co-Simulation". International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering. 98 (6): 418–444. doi:10.1002/nme.4637.