Sail components




Sail components include the features that define a sail's shape and function, plus its constituent parts from which it is manufactured. A sail may be classified in a variety of ways, including by its orientation to the vessel (e.g. fore-and-aft) and its shape, (e.g. (a)symmetrical, triangular, quadrilateral, etc.). Sails are typically constructed out of flexible material that is shaped by various means, while in use, to offer an appropriate airfoil, according to the strength and apparent direction of the wind. A variety of features and fittings allow the sail to be attached to lines and spars.
Whereas conventional sails form an airfoil with one layer of fabric, wingsails comprise a structure that has material on both sides to form an airfoil—much like a wing placed vertically on the vessel—and are beyond the scope of this article.
Classifications
Sails may be classified as either triangular, which describes sails that either come to one point of suspension at the top or where the sail comes to a point at the forward end, or quadrilateral, which includes sails that are attached to a spar at the top and have three other sides, or as square. They also may be classified as symmetrical (square sails and symmetric spinnakers) or asymmetrical (most other sails). Typically, asymmetrical sails perform better on points of sail closer to the wind and are designed for fore-and-aft rigs than symmetrical sails, which perform best on points of sail that are further from the wind direction.[1][2]
Triangular
Triangular sails have names for each of three edges and three corners. Rigs with such sails include Bermuda, cutter, lateen and vessels with mixed sail plans that include jibs and other staysails. Most triangular sails are classified as asymmetrical and fore and aft; symmetric spinnakers are symmetrical triangular sails that are designed for off-the-wind use.[3]
Quadrilateral
Gaff, gunter, lug, junk and some sprit sails have four sides and are set fore and aft so that one edge is leading into the wind. Naming conventions are consistent with triangular sails, except for the top edge and corners.[4]
Square
A square rig is a type of sail and rigging arrangement in which the primary driving sails are carried on horizontal spars which are perpendicular, or square, to the keel of the vessel and to the masts. These spars are called yards and their tips, beyond the last stay, are called the yardarms[5]. A ship mainly so rigged is called a square-rigger.[6]
Shape

The shape of a sail is defined by its edges and corners in the plane of the sail, laid out on a flat surface. The edges may be curved, either to extend the sail's shape as an airfoil or to define its shape in use. In use, the sail becomes a curved shape, adding the dimension of depth or draft.
Edges
The top of all sails is called the head, the leading edge is called the luff, the trailing edge is the leech, and the bottom edge is the foot.
- Head – The head is the upper edge of the sail, and is attached at the throat and peak to a gaff, yard, or sprit.[7] For a triangular sail the head refers to the topmost corner.
- Luff – The forward (leading) edge of a fore-and-aft sail is called the luff, which, in a mainsail, is parallel to the mast.[8] In a symmetrical sail that leech, which is the leading edge into the wind, may be called the luff.[7][9]
- Leech – The aft (back) edge of a fore-and-aft sail is called the leech (also spelled leach), which is opposite the luff, and on a triangular sail forms the hypotenuse of the triangle[8] The leech is either side edge of a symmetrical sail.[7][9]
- Foot – The foot of a sail is its bottom edge.[8] On a fore-and-aft mainsail, the foot is often attached, at the tack and clew, to a boom; on a square sail to a spar by clews on both ends; if no boom or spar is present, the sail is said to be "loose-footed".[9]
Roach
A fore-and-aft triangular mainsail achieves a better approximation of a wing form by extending the leech aft, beyond the line between the head and clew in an arc called the roach, rather than having a triangular shape. This added area would flutter in the wind and not contribute to the efficient airfoil shape of the sail without the presence of battens.[1] Offshore cruising mainsails sometimes have a hollow leech (the inverse of a roach) to obviate the need for battens and their ensuing likelihood of chafing the sail.[10]
Roach is a term also applied to square sail design—it is the arc of a circle above a straight line from clew to clew at the foot of a square sail, from which sail material is omitted. The roach allows the foot of the sail to clear stays coming up the mast, as the sails are rotated from side to side.[11]
Corners
The names of corners of sails vary, depending on shape and symmetry.
- Head – In a triangular sail, the corner where the luff and the leech connect is called the head.[12][8] On a square sail, the top corners are head cringles, where there are grommets, called cringles.[13]
- Peak – On a quadrilateral sail, the peak is the upper aft corner of the sail, at the top end of a gaff, a sprit or other spar.
- Throat – On a quadrilateral sail, the throat is the upper forward corner of the sail, at the bottom end of a gaff or other spar.[14] Gaff-rigged sails, and certain similar rigs, employ two halyards to raise the sails: the throat halyard raises the forward, throat end of the gaff, while the peak halyard raises the aft, peak end.[15]
- Clew – The corner where the leech and foot connect is called the clew on a fore-and-aft sail. On a jib, the sheet is connected to the clew; on a mainsail, the sheet is connected to the boom (if present) near the clew.[8] Clews are the lower two corners of a square sail. Square sails have sheets attached to their clews like triangular sails, but the sheets are used to pull the sail down to the yard below rather than to adjust the angle it makes with the wind.[16] The corner where the leech and the foot connect is called the clew.[8] In the case of a symmetrical spinnaker, each of the lower corners of the sail is a clew. However, under sail on a given tack, the corner to which the spinnaker sheet is attached is called the clew, and the corner attached to the spinnaker pole is referred to as the tack. [16]
- Tack – The corner on a fore-and-aft sail where the luff and foot connect is called the tack[8] and, on a mainsail, is located where the boom and mast connect.[8][17] On a square sail underway, the tack is the windward clew and also the line holding down that corner.[18]
Draft
Those triangular sails that are attached to both a mast along the luff and a boom along the foot have depth, known as draft or draught, which results from the luff and foot being curved, rather than straight as they are attached to those spars. Draft creates a more efficient airfoil shape for the sail. Draft can also be induced in triangular staysails by adjustment of the sheets and the angle from which they reach the sails.[19]
Construction
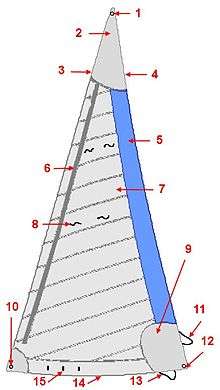

Sails are constructed of fabrics that may be woven or manufactured as films. The sail are often assembled of multiple panels that are arrayed in a manner that transfers the load from the wind to the sail's attachment points—a combination of corners and edges—that transmits the load into the mast and powers the boat. Construction of such sails requires stitching, bonding, reinforcements and other features to achieve this. Other sails are constructed directly from fibers, filaments and films.
Materials
The characteristics of a sail are due to design, construction and the attributes of the fibers, which are woven together to make the sail cloth. There are several key factors in evaluating a fiber for suitability in weaving a sail-cloth:[1][3]
- Initial modulus – The ability to resist stretching. Higher resistance is better for upwind sails.
- Breaking strength (tenacity) – Measured as a force per cross sectional area of fiber. Higher is better for sails.
- Creep – Describes the long term stretch of a fiber or fabric. A material with creep may have a superior modulus, but lose its shape over time.
- Resistance to ultraviolet light – Strength loss from exposure to the Sun’s UV rays measured by a standardized exposure test.
- Flex strength – Strength lost due to bending, folding, or flogging, which is frequently measured with an industry standard 50 fold test.
- Cost-effectiveness – Both the initial cost and its durability of the material define its cost-effectiveness over time.
Traditionally, sails were made from flax or cotton canvas.[3] Materials used in sails, as of the 21st Century, include nylon for spinnakers—where light weight and elastic resistance to shock load are valued—and a range of fibers, used for triangular sails, that includes Dacron, aramid fibers—including Kevlar, and other liquid crystal polymer fibers—including Vectran.[3][1]
Woven materials, like Dacron, may specified as either high or low tenacity, as indicated, in part by their denier count (a unit of measure for the linear mass density of fibers). High-tenacity Dacron comes in multiples of 220, 350 and 570 deniers, whereas low-tenacity Dacron comes in multiples of 150, 250, and 400 deniers. Sailcloth is typically heat-shrunk to tighten the weave and then receives a chemical bonding finish of melamine. Such cloth is typically specified by deniers for warp and fill (weft), e.g. 220/570.[20]
Panels and laminations
.jpg)
Conventional sails comprise panels, which are most often stitched together, at other times adhered. There are two basic configurations, cross-cut and radial. Cross-cut sails have the panels sewn parallel to one another, often parallel to the foot of the sail, and are the least expensive of the two sail constructions. Triangular cross-cut sail panels are designed to meet the mast and stay at an angle from either the warp or the weft (on the bias) to allow stretching along the luff, but minimize strutting on the luff and foot, where the fibers are aligned with the edges of the sail.[21]
Radial sails have panels that "radiate" from corners in order to efficiently transmit stress and are typically higher-performance than cross-cut sails. A bi-radial sail has panels radiating from two of three corners; a tri-radial sail has panels radiating from all three corners. Mainsails are more likely to be bi-radial, since there is very little stress at the tack, whereas head sails (spinnakers and jibs) are more likely to be tri-radial, because they are tensioned at their corners.[3]
Higher-performance sails may be laminated, constructed directly from multiple plies of filaments, fibers, taffetas, and films—instead of woven textiles—and adhered together. Molded sails are laminated sails formed over a curved mold and adhered together into a shape that does not lie flat.[3]
 Cross-cut panels
Cross-cut panels Bi-radial panels
Bi-radial panels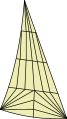 Tri-radial panels
Tri-radial panels
Stitching and bonding
Conventional sail panels are sewn together. Sails are tensile structures, so the role of a seam is to transmit a tensile load from panel to panel. For a sewn, textile sail this is done through thread and is limited by the strength of the thread and the strength of the hole in the textile through which it passes. Sail seams are often overlapped between panels and sewn with zig-zag stitches that create many connections per unit of seam length.[3] Measures for seam structural attributes—shown with a typical value for a sewn seam—include:[22]
- Breaking force (newtons) – 630 newtons (140 lbf)
- Elongation (percent) – 22%
- Strength (newtons/millimetre) – 14 newtons per millimetre (3.1 lbf/mm)
- Modulus of elasticity (newtons/millimetre) – 1.2 newtons per millimetre (0.27 lbf/mm)
Whereas textiles are typically sewn together, other sail materials may be ultrasonically welded—a technique whereby high-frequency ultrasonic acoustic vibrations are locally applied to workpieces being held together under pressure to create a solid-state weld. It is commonly used for plastics, and especially for joining dissimilar materials.[22]
Edge construction

Sails have a variety of treatments at their edges, either to attach the sail to a stay, spar or mast or to prevent a free edge from fluttering or fraying.
- Bolt ropes are sewn onto the edges of the sail to reinforce them, or to fix the sail into a groove in the boom, in the mast, or in the luff foil of a roller-furling jib.[11]
- Leech lines are found on mainsails and large jibs to tighten the leech and prevent fluttering. They run through a sleeve on the leech from the head to the clew, where there is usually a clam cleat to tighten it. Occasionally, foot lines perform an analogous function on a loose-footed sail.[10]
- UV protection panels are usually affixed to the leech and foot of roller furling jibs to prevent ultraviolet rays from reaching the sailcloth while the sail is not in use. These are typically a dark color to absorb the harmful rays.[23]
Reinforcements at attachment points

The corners of triangular sails are typically areas of high stress and consequently often have reinforced layers and tape radiating from, whether cross-cut or radial in construction. Their corners are always attached to a shackle, attached to a line or spar—the halyard at the head, a shackle at the tack, and the outhaul at the clew. The connecting shackle runs through a grommet at each of these points. There are additional points where reinforcing and grommets may occur: at the cunningham, a downhaul used to flatten a mainsail (jibs may have a similar feature), and along the foot of a Genoa jib to allow a line to lift it out of the waves. The head of a triangular sail may have a rigid headboard riveted to it in order to transfer load from the sail to the halyard.[21]
Square sails and gaff-rigged sails also have grommets at corners. Only the clews on a square sail take a comparatively large amount of stress, because the head is supported along the spar. Three sides of gaff-rigged sails are attached to a mast or spar.[16]
Battens

A sail batten is a flexible insert in a fore-and-aft sail that provides added stiffness and definition to the sail's airfoil cross-section.[1] The most common use of sail battens is in the roach of a mainsail. The batten extends the leech past the line that runs from the head and the clew of the sail to create a wider sail towards the top. Cruising sailboats may have four to six battens. Racing sailboats may have full-length battens, as well, that allow for better sail shape.[1] Battens are also found in jibs of beach-cat catamarans.[24] Most battens are fiberglass pultrusions with a thin, rectangular cross section.[1]
Junk rigs feature full-length battens that facilitate short-handed sail handling, including reefing. The battens are attached loosely to the mast with lines called batten parrels that allow fore-and-aft motion as the sail is controlled by individual sheets leading to multiple battens.[25]
Fittings
Sails usually have fittings attached to them that transmit force through a small area. These include grommets, which reinforce fabric at an attachment points and connections to lines; hoops and slides, which attach sails to spars; and reefing features, which may reefing lines attached to the sail or grommets that have reefing lines running through them. Additional features include tell-tales, windows—used on dinghy sails[26]—and lettering and other graphics that include sail numbers and manufacturers logos, etc.
Hardware
Where sails are attached to a mast, spar, or stay there is some kind of connection—often it's the bolt rope running through a groove in the mast, boom, or head foil—otherwise, there is a piece of hardware involved, e.g.:
- Gaff sails usually have hoops that slide up and down the mast.[4]
- Bermuda mainsails may have slides attached to the luff that match tracks on the mast and boom. These may be attached to the luff through grommets with webbing or a nylon shackle or with webbing sewn directly on the sail.[20]
- Jibs that are not roller-furling usually have hanks, clips that attach to the stay. This applies to other staysails, as well.[3]
Other hardware includes cam cleats, used to tension luff and foot lines.[10]
Reefing points

Different categories of sails are reefed (reduced in size) in different manners and therefore have different fixtures that achieve shortening of sail. Traditional canvas square and gaff-rigged sails have one ore more rows of reefing lines that pass through the sail, which reach around the sail that has been gathered in to reduce its size and secure the remaining unreefed sail to the spar (square rig) or boom (gaff rig).[27] Gaff-rigged sails require an extra set of lines to secure the part of the leech that becomes the new clew. These are called reef pendents that drop through a comb on the boom, where they are secured, as needed.[4]
Mainsails on Bermuda rigs typically have paired grommets that secure the luff and leech to the boom, as the sail is lowered to reduce its area. These become the new tack and clew. A reefing line typically runs through the reef point on the luff to quickly secure the new clew. The grommet that becomes the new tack is typically hooked onto the boom. There may be grommets along the line between the new tack and clew that allow ties to pass through around the boom.[27]
Tell-tales
Tell-tales are pieces of yarn, thread or tape that are affixed to sails to help visualize airflow over their surfaces. Typically, they are mounted near the luff of sails, but they are also found on the leach on some sails. To windward, a sagging tell-tale indicates still air, either from stalling (indicated on the leeward side, when the sail is sheeted in too far, compared to the apparent wind) or pinching (indicated on the windward side, when the sail isn't sheeted in far enough, compared to the apparent wind).[1]
Legends
- ↑ Genoa jib
- Head
- Reinforcement
- Luff
- Leech
- Anti-UV covering
- Head foil attachment
- Panel(s)
- Telltales
- Reinforcement
- Tack
- Leech control
- Clew
- Foot control
- Foot
- Furling marks
- ↑ Gaff mainsail
- Luff
- Foot
- Leech
- Head
- Throat
- Tack
- Clew
- Peak
- Throat cringle
- Reefing cringle
- Tack cringle
- Clew cringle
- Reefing cringle
- Peak cringle
- Reinforcing tape
- Bolt rope
- Batten pocket
- Panels
- Reef line
- Reefing point
- Reefing line
See also
References
Citations
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Textor, Ken (1995). The New Book of Sail Trim. Sheridan House, Inc. p. 228. ISBN 0924486813.
- ↑ Mclaughlan, Ian (2014). The Sloop of War: 1650-1763. Seaforth Publishing. p. 288. ISBN 9781848321878.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Hancock, Brian; Knox-Johnson, Robin (2003). Maximum Sail Power: The Complete Guide to Sails, Sail Technology, and Performance. Nomad Press. p. 288. ISBN 9781619304277.
- 1 2 3 Cunliffe, Tom (2004). Hand, Reef and Steer. Sheridan House, Inc. p. 178. ISBN 9781574092035.
- ↑ Oxford English Dictionary
- ↑ Keegan, John (1989). The Price of Admiralty. New York: Viking. p. 280. ISBN 0-670-81416-4.
- 1 2 3 King, Hattendorf & Estes 2000, p. 283.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 SAIL Editors. "Know How: Sailing 101". Sail Magazine. Retrieved 4 October 2016.
- 1 2 3 King, Hattendorf & Estes 2000, p. 271.
- 1 2 3 Nicolson, Ian (1998). A Sail for All Seasons: Cruising and Racing Sail Tips. Sheridan House, Inc. p. 124. ISBN 9781574090475.
- 1 2 Kipping, Robert (1847). The Elements of Sailmaking: Being a Complete Treatise on Cutting-out Sails, According to the Most Appproved Methods in the Merchant Service... F.W. Norie & Wilson. pp. 58–72.
- ↑ Jobson 2008, p. 208.
- ↑ Knight, Austin N. (1921). Modern Seamanship (8 ed.). New York: D. van Nostrand Company. p. 831.
- ↑ Underhill, Harold (1938). "Glossary". Sailng Ship Rigs and Rigging (Second, 1958 ed.). Glasgow: Brown, Son and Ferguson. p. 114.
- ↑ King, Hattendorf & Estes 2000, p. 429.
- 1 2 3 King, Hattendorf & Estes 2000, p. 146.
- ↑ "Sailing Quick Reference Guide" (PDF). Wayzata Yacht Club. Wayzata Yacht Club. Retrieved 4 October 2016.
- ↑ King, Hattendorf & Estes 2000, p. 416.
- ↑ Jinks, Simon. "Adjusting Sail Draft". Royal Yachting Association. Royal Yachting Association. Retrieved 4 October 2016.
- 1 2 Rice, Carol (January 1995), "A first-time buyers checklist", Cruising World, 21, pp. 34–35, ISSN 0098-3519, retrieved 2017-01-13
- 1 2 Colgate, Stephen (1996). Fundamentals of Sailing, Cruising, and Racing. W. W. Norton & Company. p. 384. ISBN 9780393038118.
- 1 2 Jones, I.; Stylios, G.K. (2013), Joining Textiles: Principles and Applications, Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles, Elsevier, p. 624, ISBN 9780857093967, retrieved 2017-01-12
- ↑ Pinney, Tor (2002). Ready for Sea!: How to Outfit the Modern Cruising Sailboat and Prepare Your Vessel and Yourself for Extended Passage-making and Living Aboard. Sheridan House, Inc. p. 256. ISBN 9781574091441.
- ↑ Berman, Phil (1999). Catamaran Sailing: From Start to Finish. W. W. Norton & Company. p. 219. ISBN 9780393318807.
- ↑ Mudie, Rosemary; Mudie, Colin (1975), The history of the sailing ship, Arco Publishing Co., p. 152
- ↑ Sleight, Steve (2011). The Complete Sailing Manual (3 ed.). Penguin. p. 448. ISBN 9780756697600.
- 1 2 Hahne, Peter (2005). Sail Trim: Theory and Practice. Sheridan House, Inc. p. 120. ISBN 9781574091984.
Sources
- Jobson, Gary (2008). Sailing Fundamentals (Revised ed.). New York: Simon and Schuster. p. 224. ISBN 1439136785.
- King, Dean; Hattendorf, John B.; Estes, J W. (2000). A sea of words: a lexicon and companion for Patrick O'Brian's seafaring tales (3 ed.). New York: Henry Holt. p. 518. ISBN 978-0-8050-6615-9.
Further reading
- MacKenzie, Mike (2005–2012). "Home page". Sea Talk Nautical Dictionary: The Dictionary of English Nautical Language. Retrieved January 15, 2014.
- Rousmaniere, John (June 1998). The Illustrated Dictionary of Boating Terms: 2000 Essential Terms for Sailors and Powerboaters (Paperback). W. W. Norton & Company. p. 174. ISBN 0393339181. ISBN 978-0393339185
- Smyth, W. H.; Belcher, E. (1867). The sailor's word-book: An alphabetical digest of nautical terms, including some more especially military and scientific ... as well as archaisms of early voyagers, etc. London: Blackie and Son.
- A naval encyclopædia: comprising a dictionary of nautical words and phrases; biographical notices, and records of naval officers; special articles of naval art and science. Philadelphia: L.R. Hamesrsly & Co. 1881. Retrieved January 23, 2014. at Internet Archive

